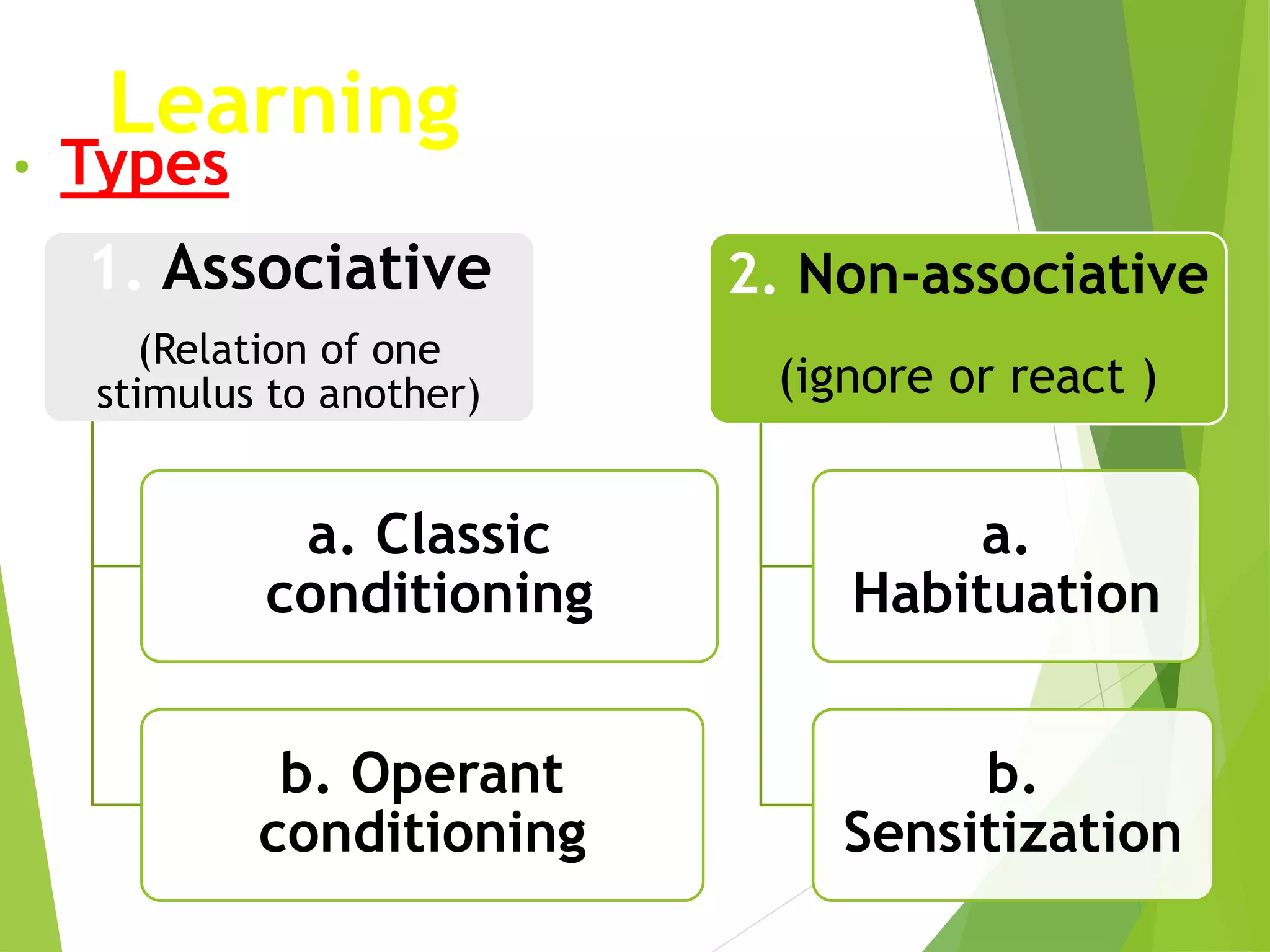
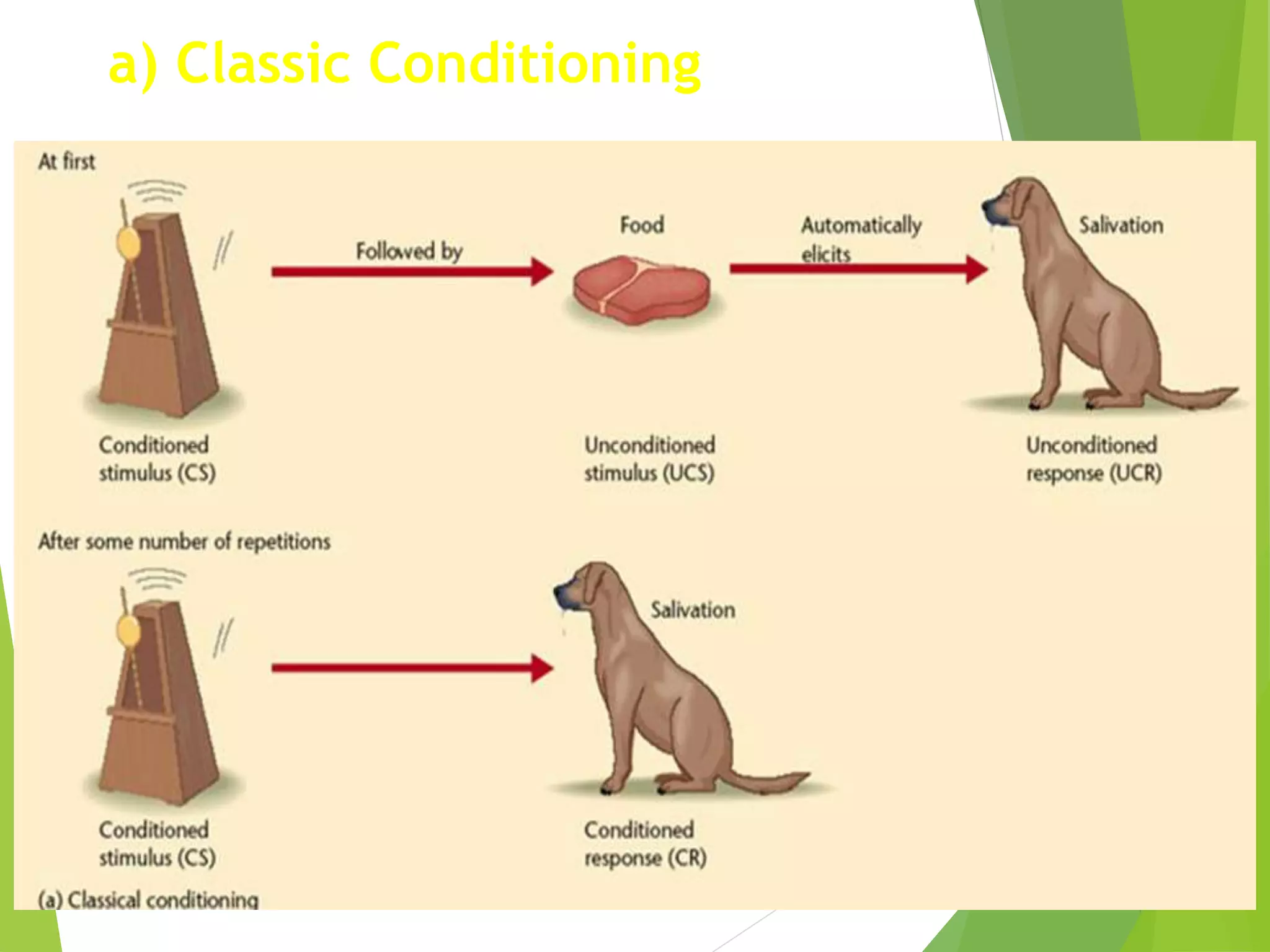
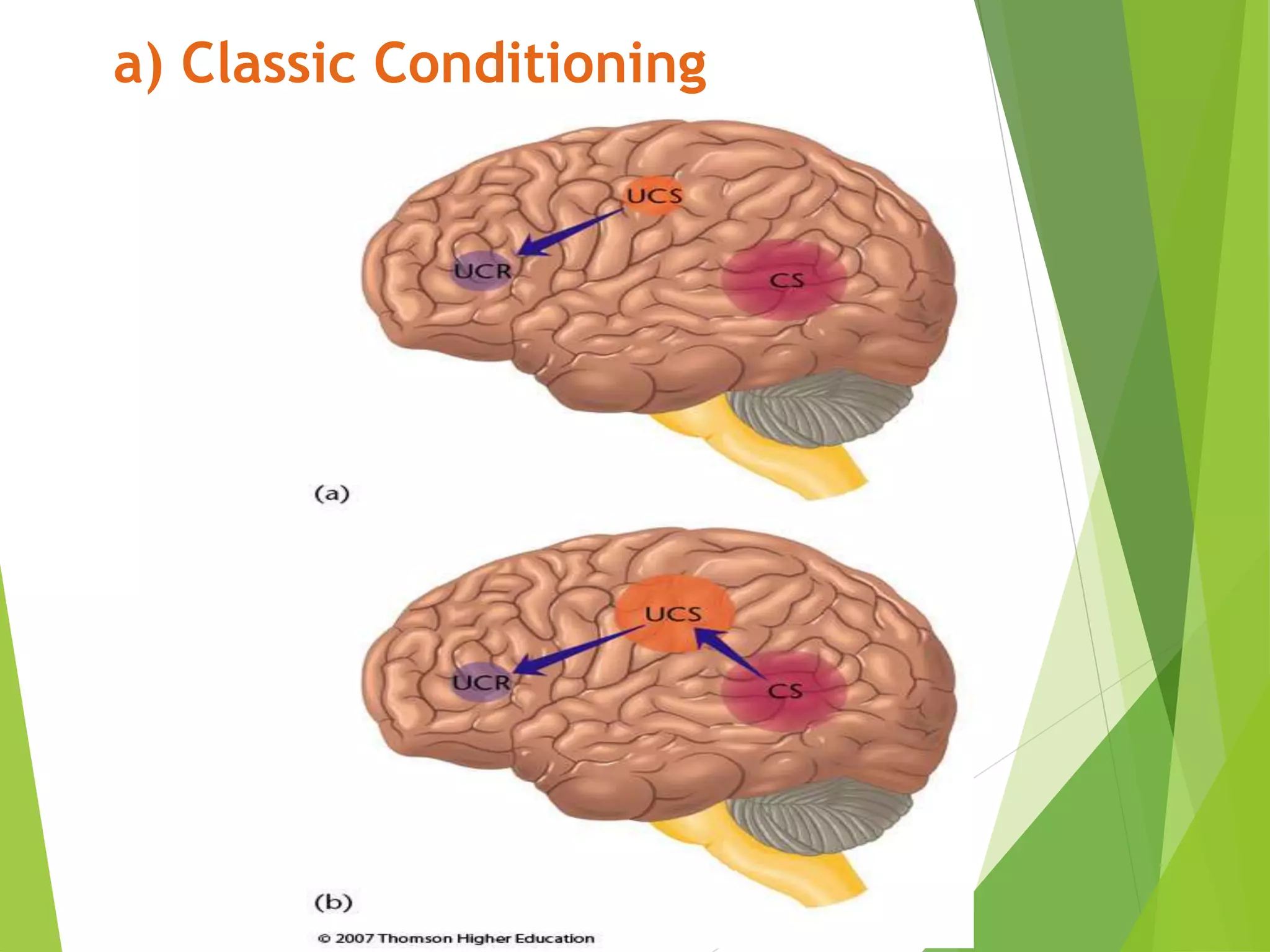
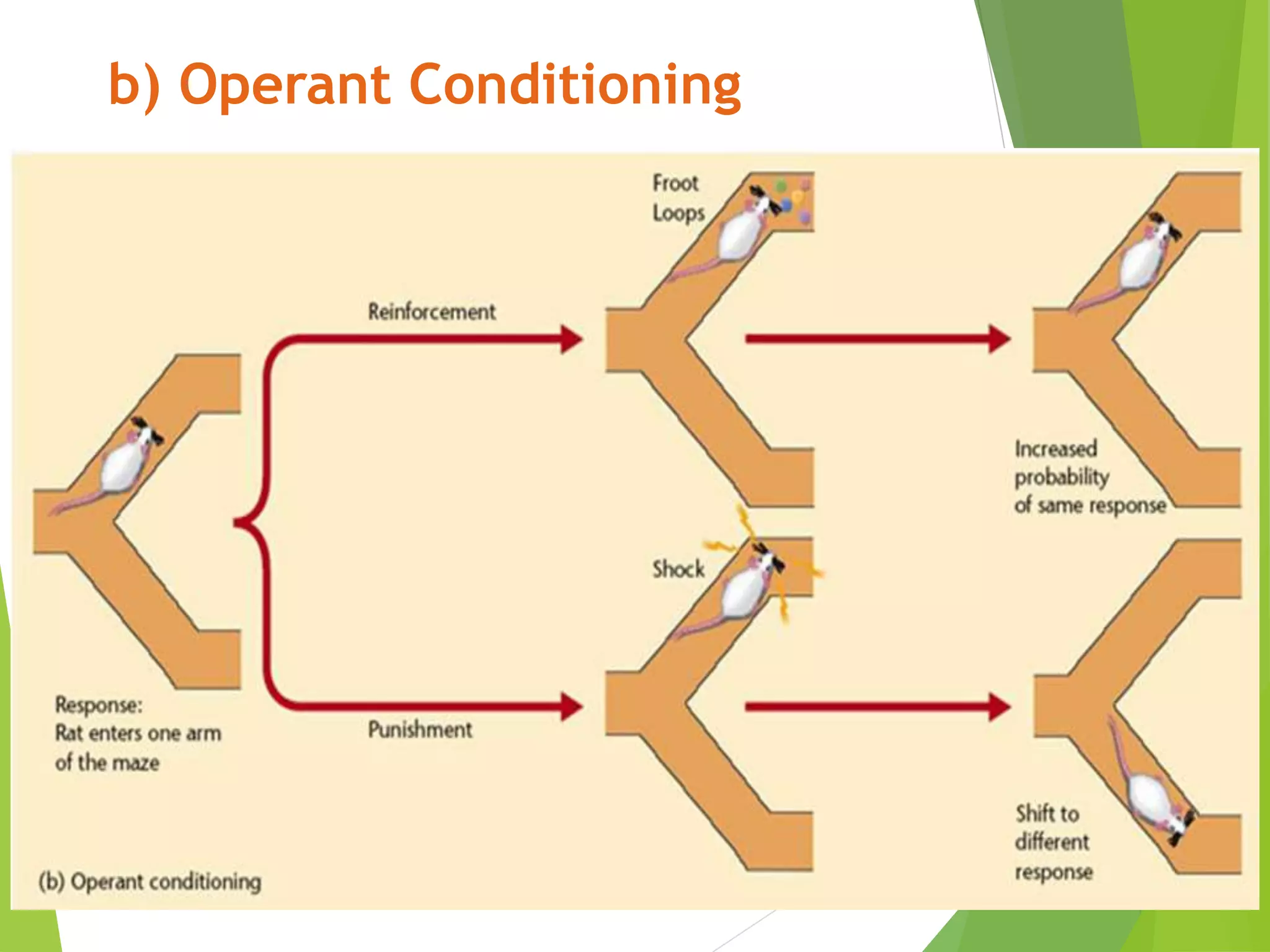
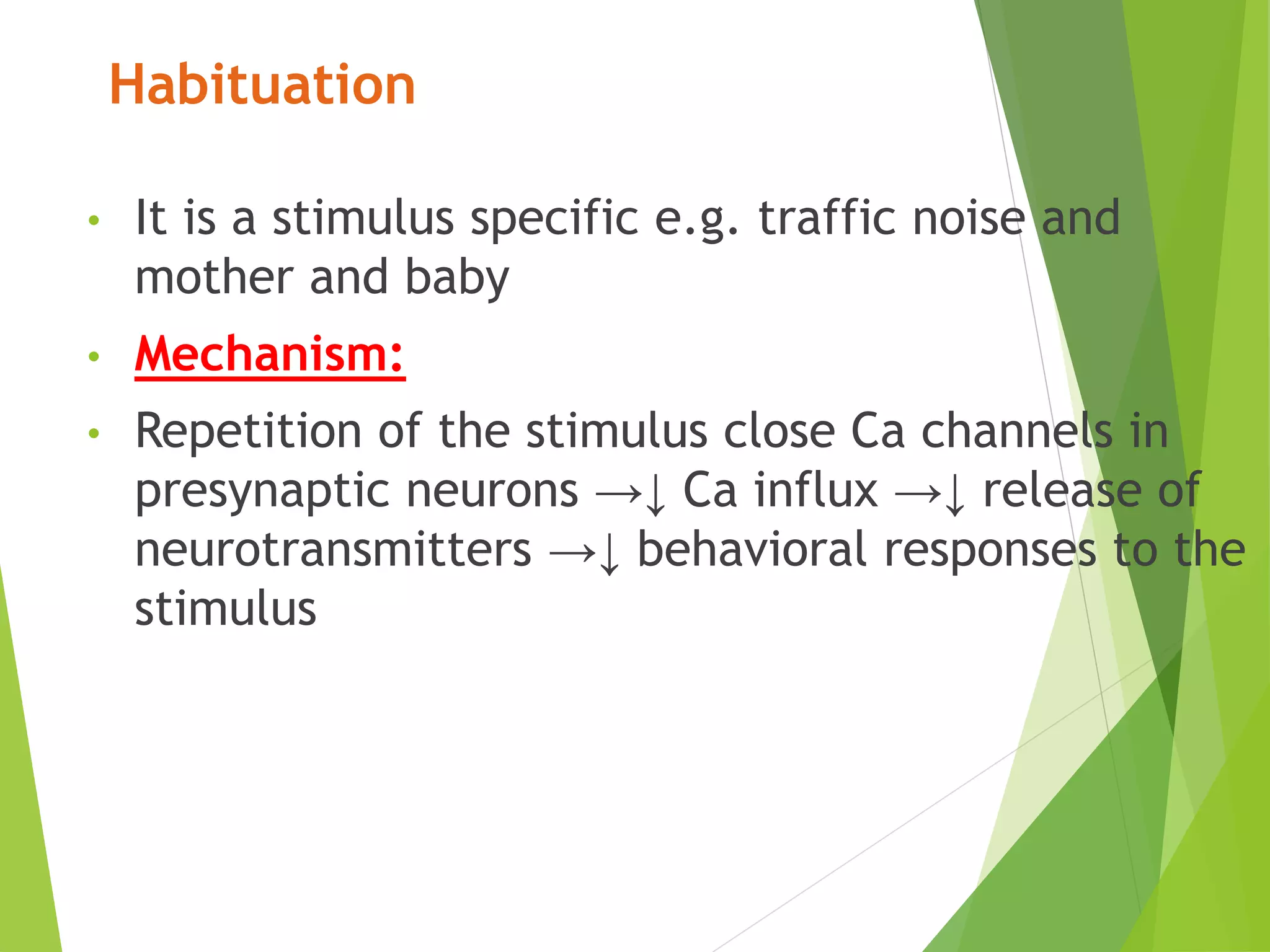
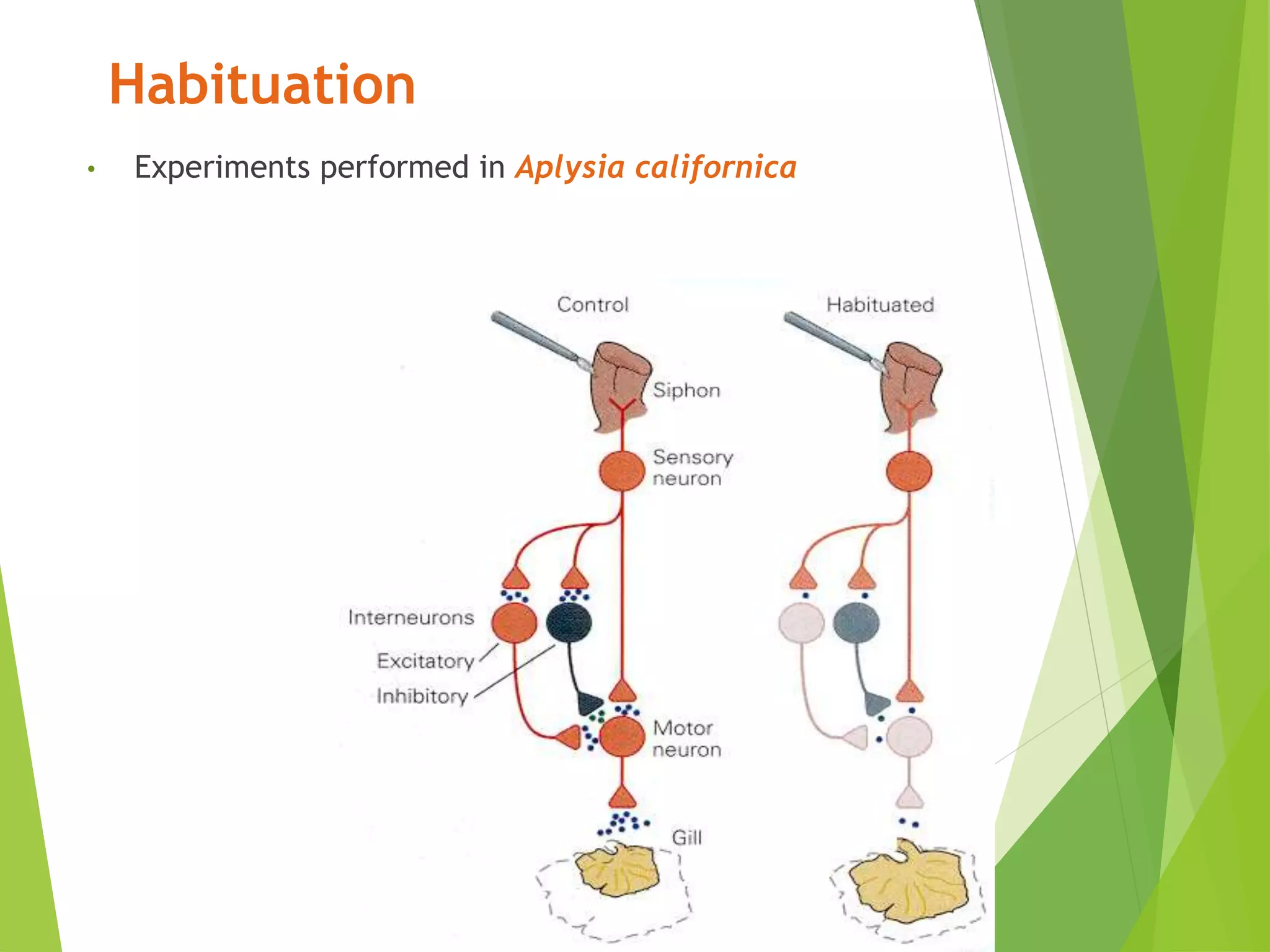
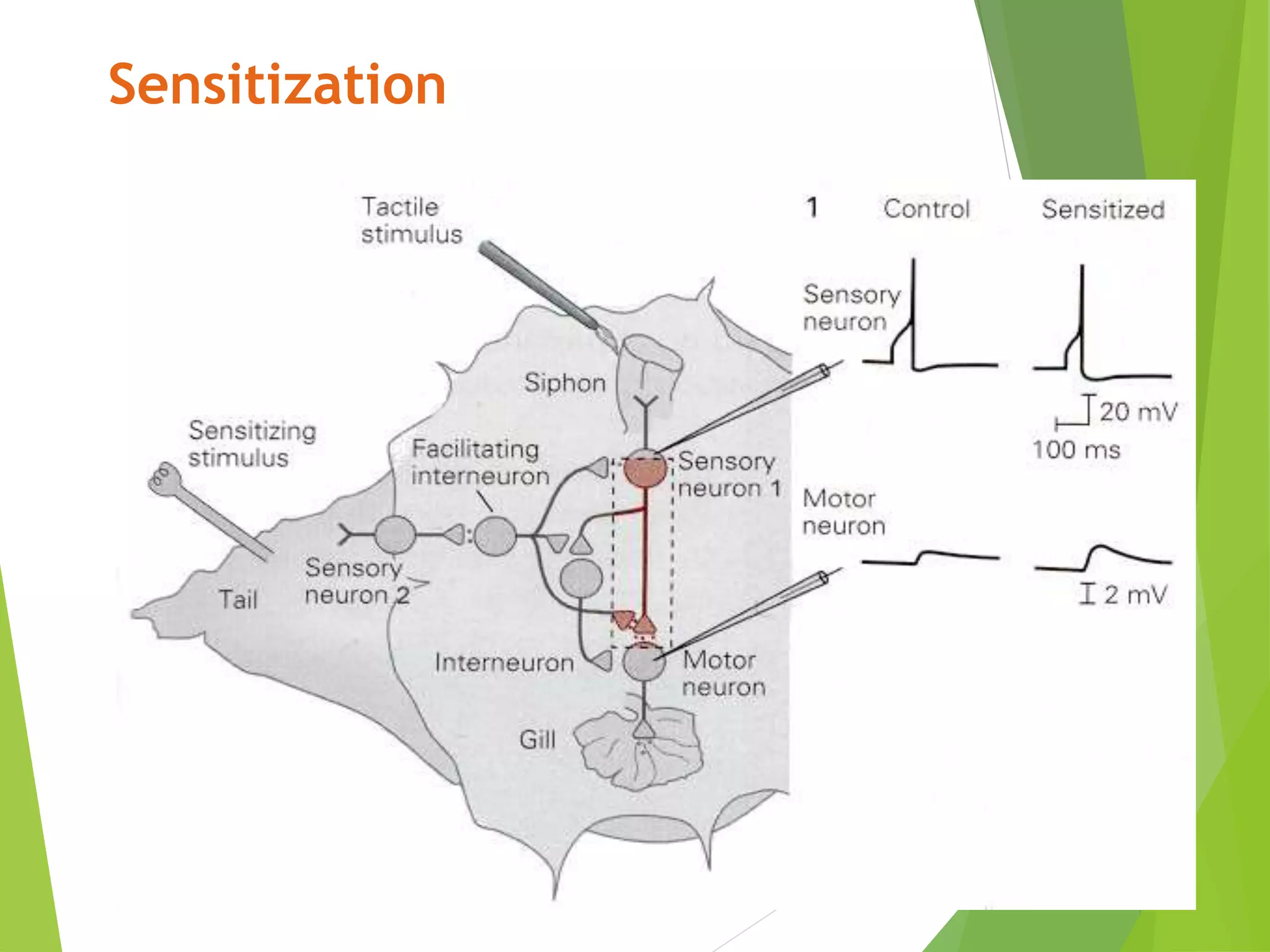
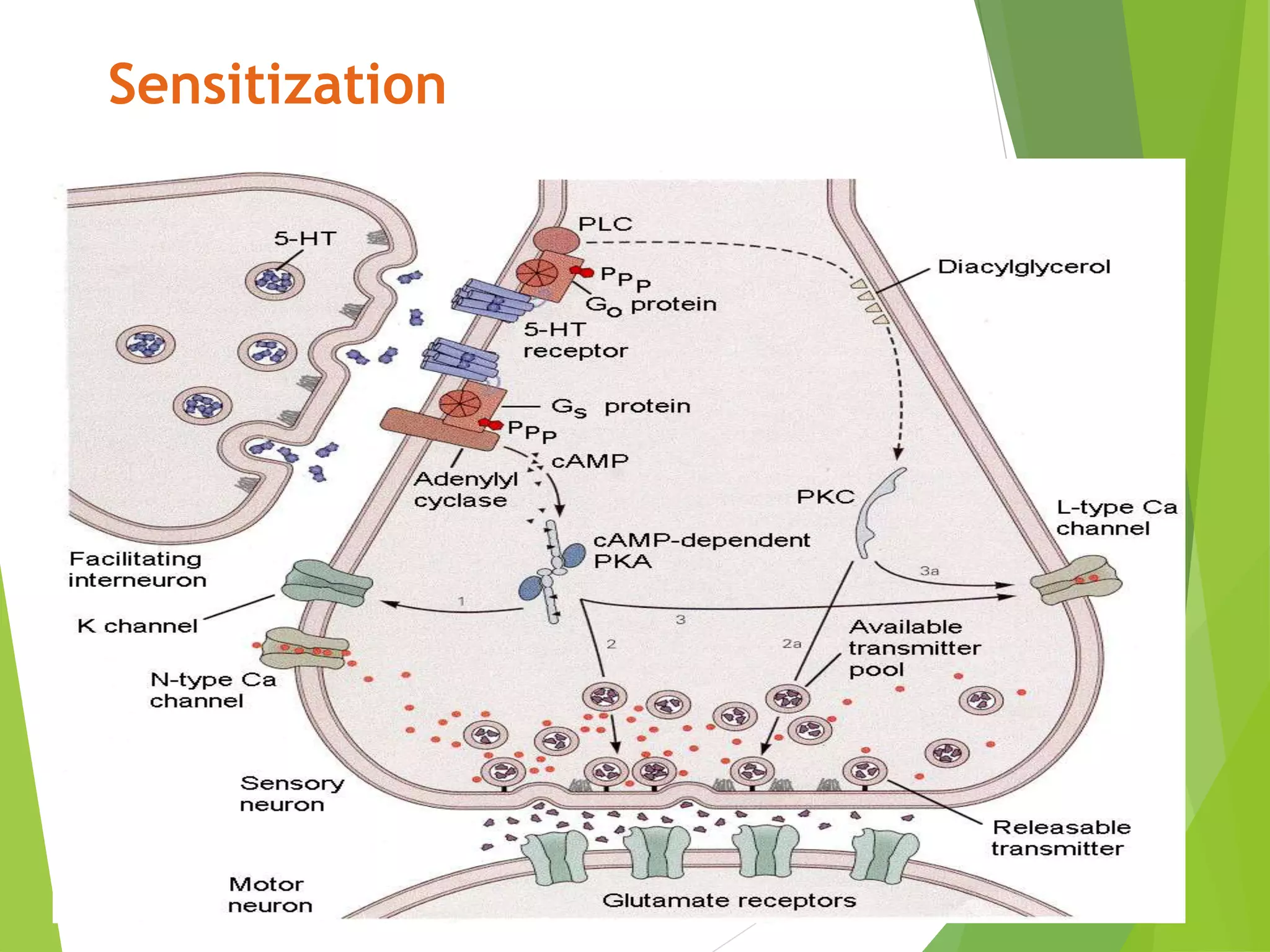
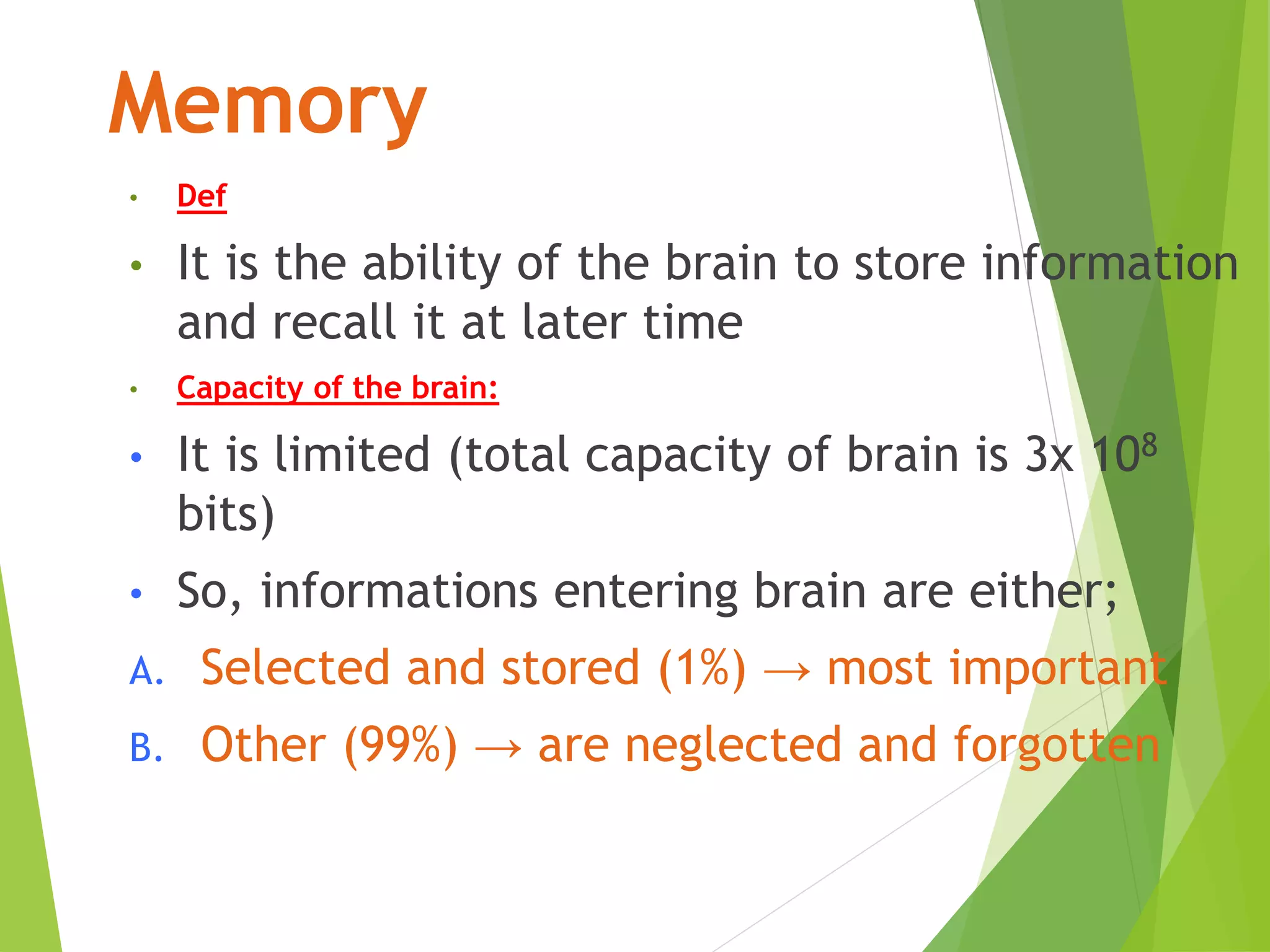
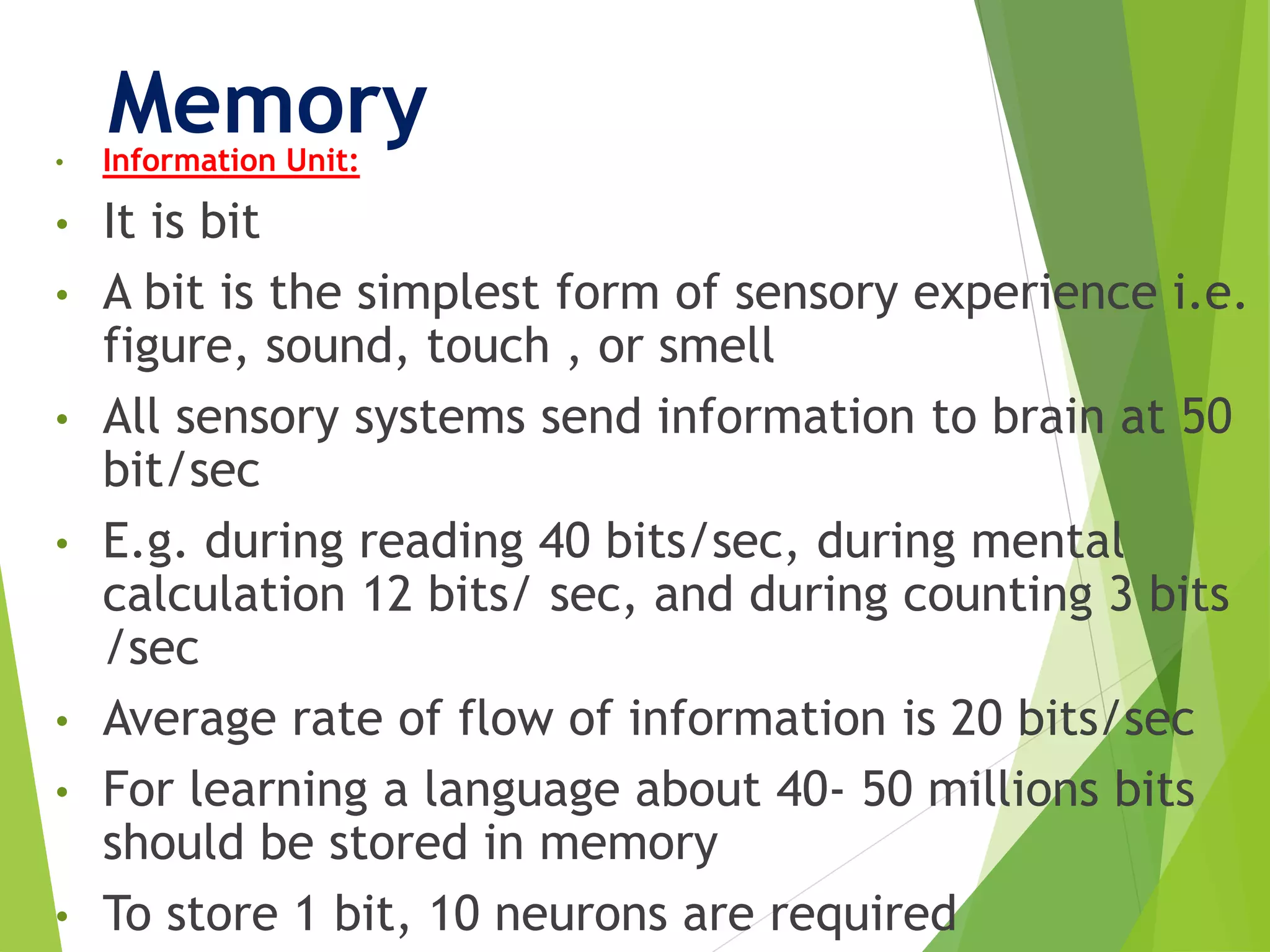
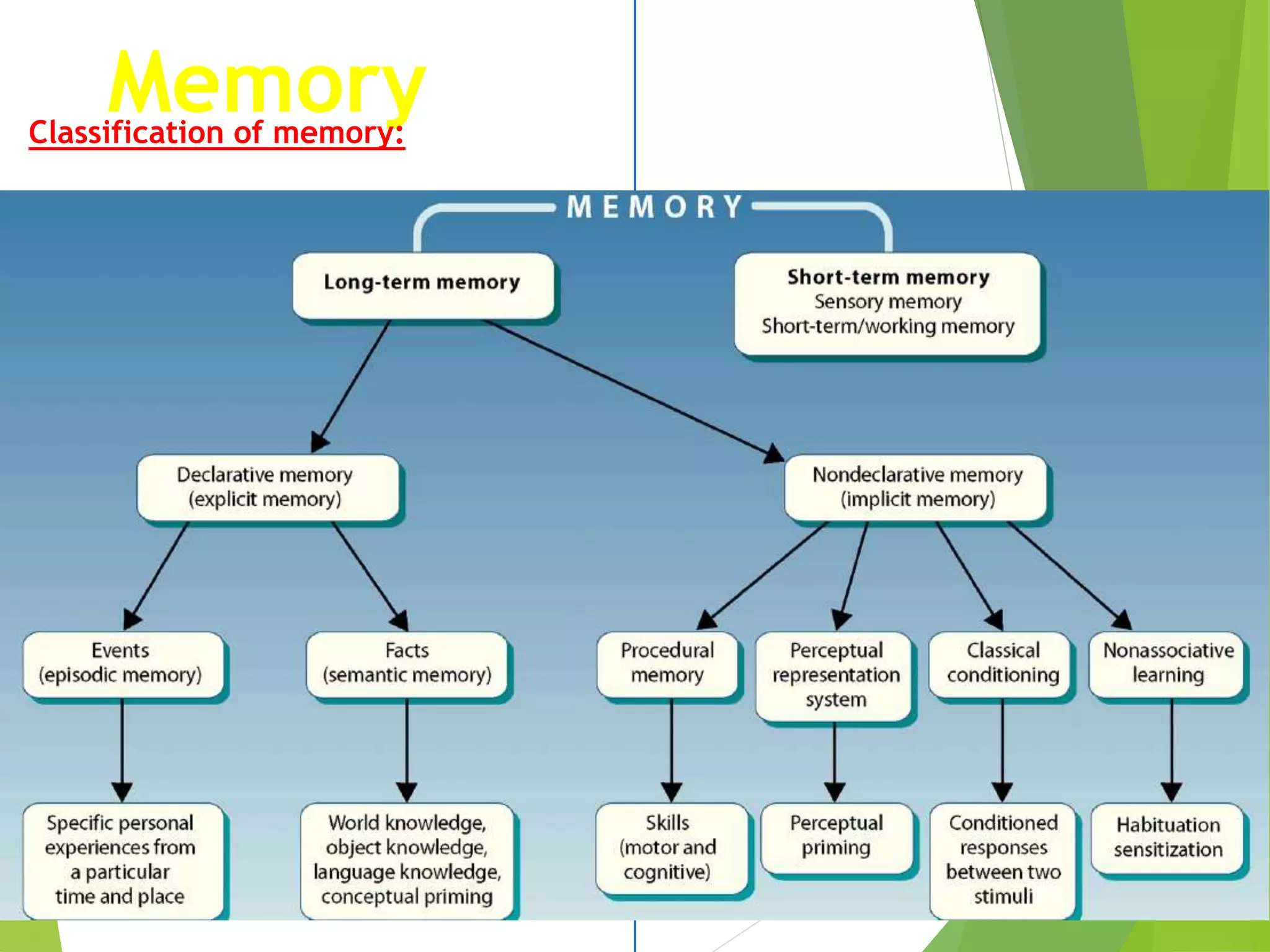
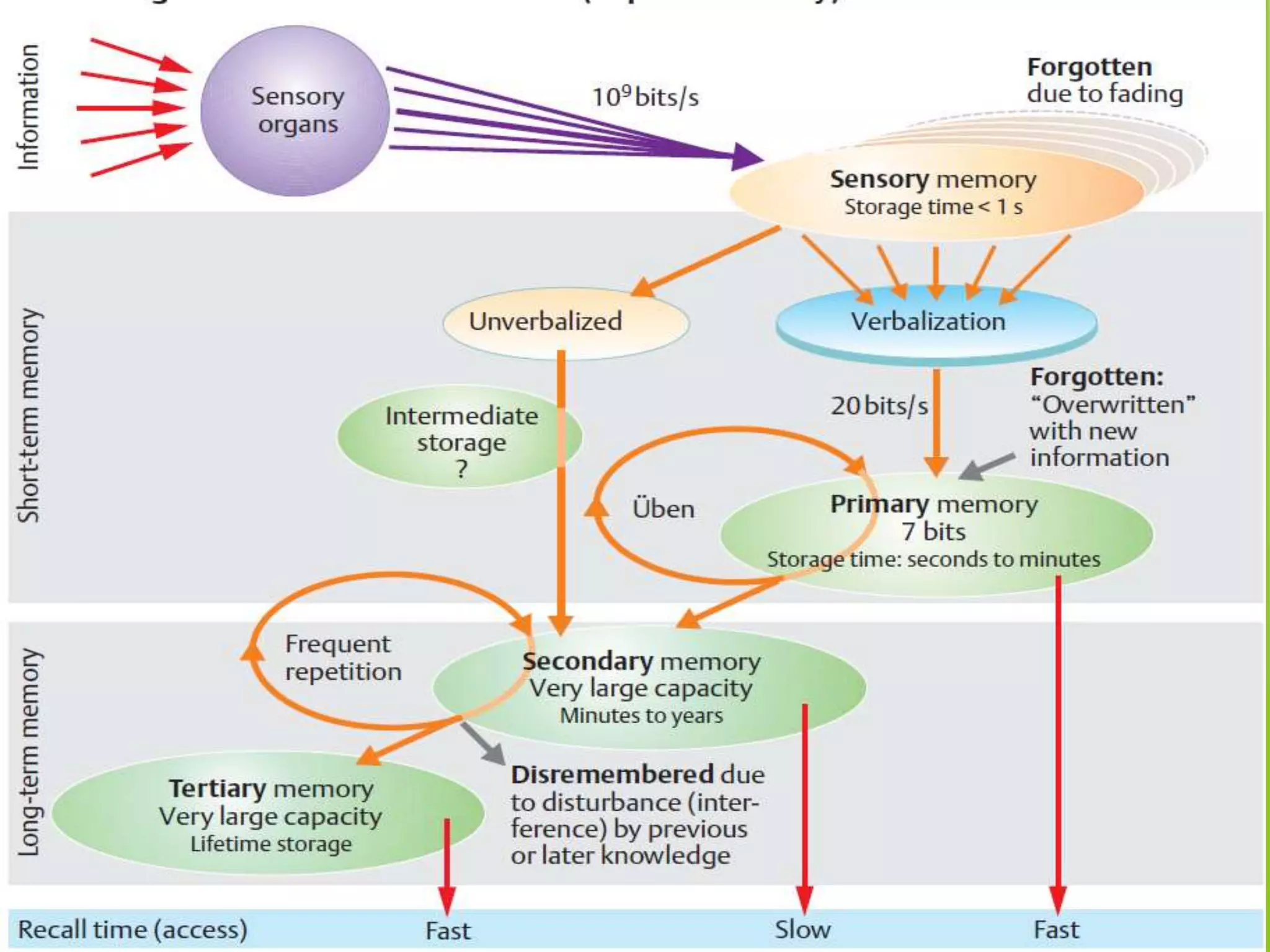
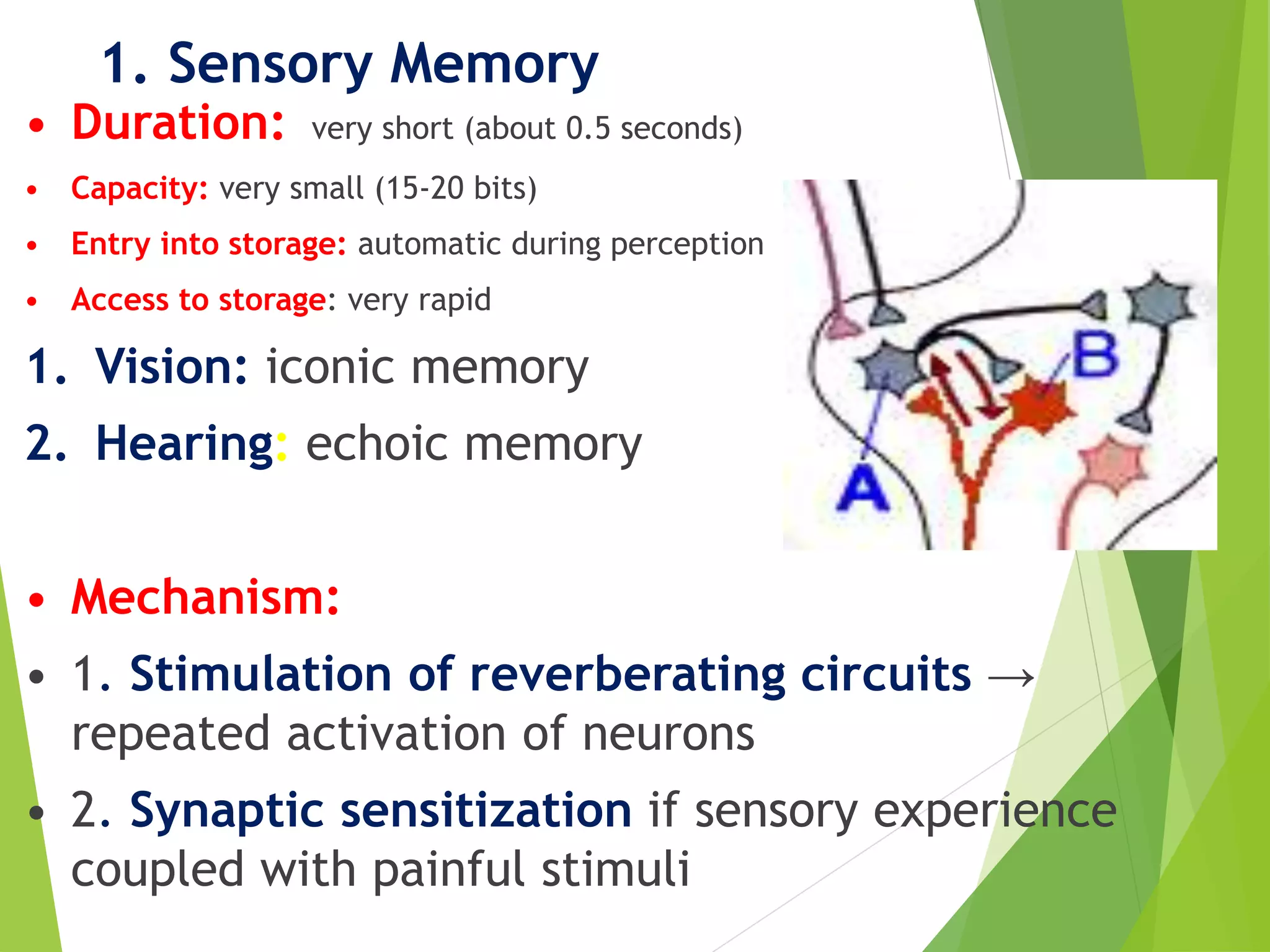
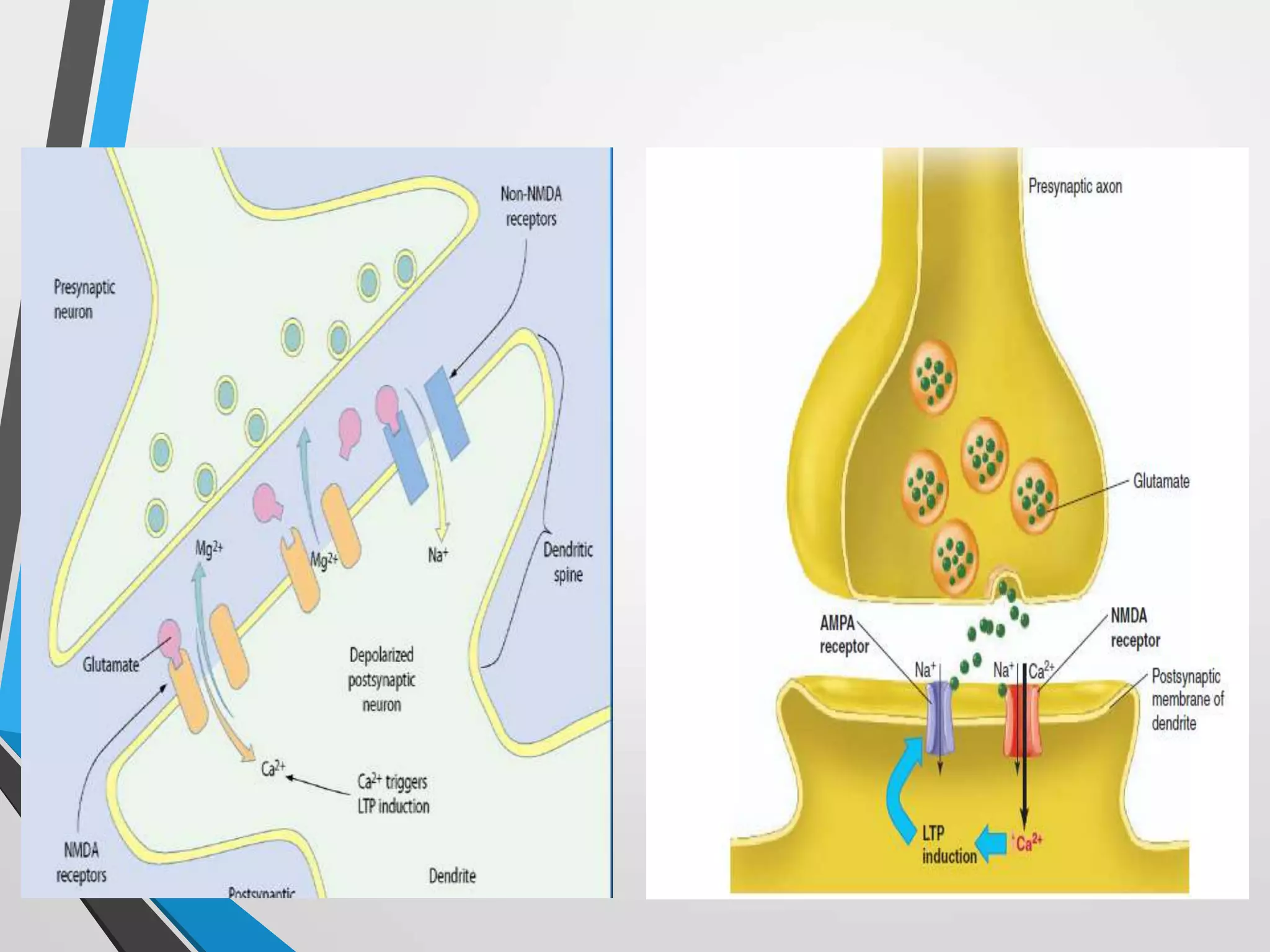
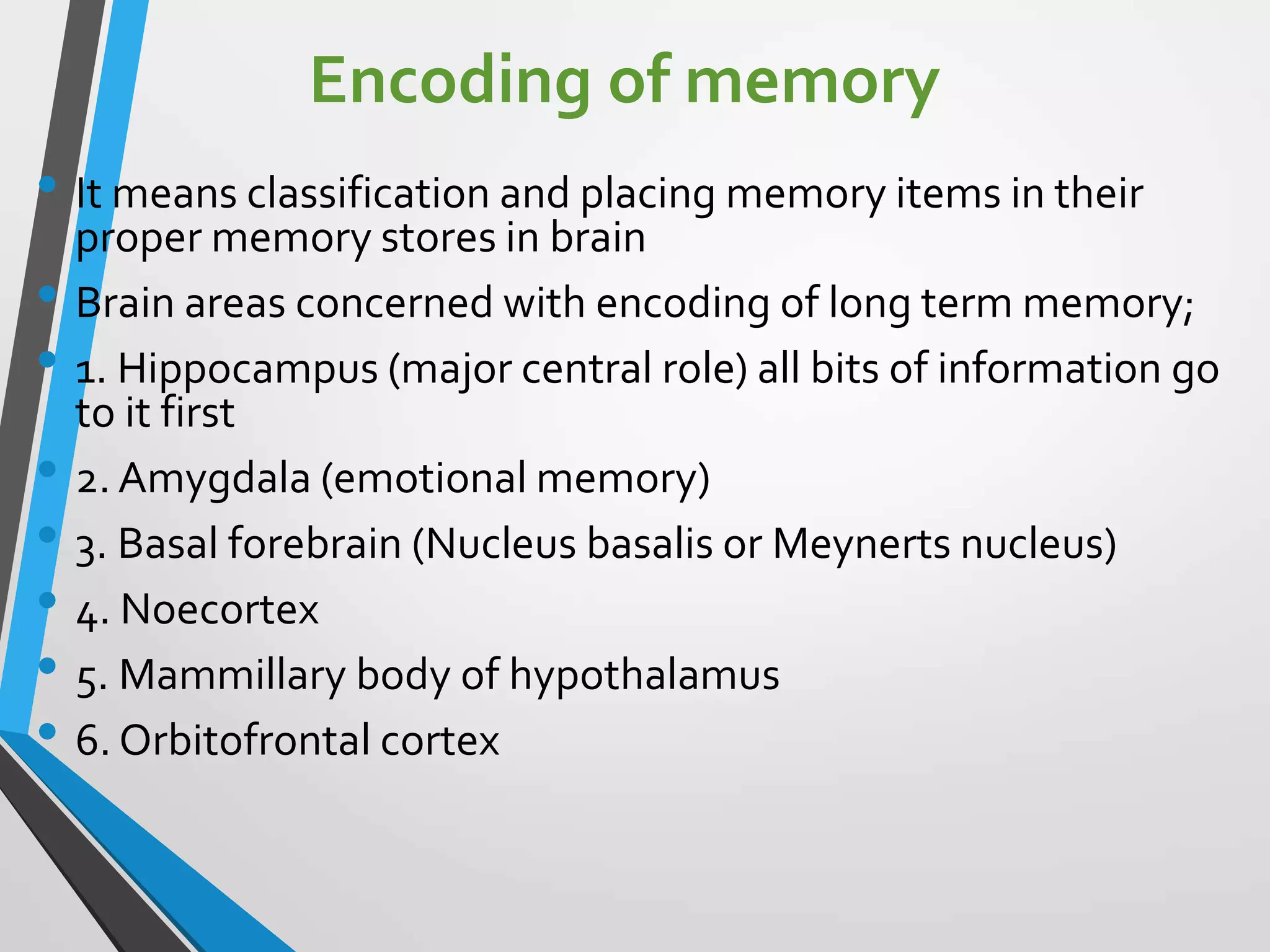
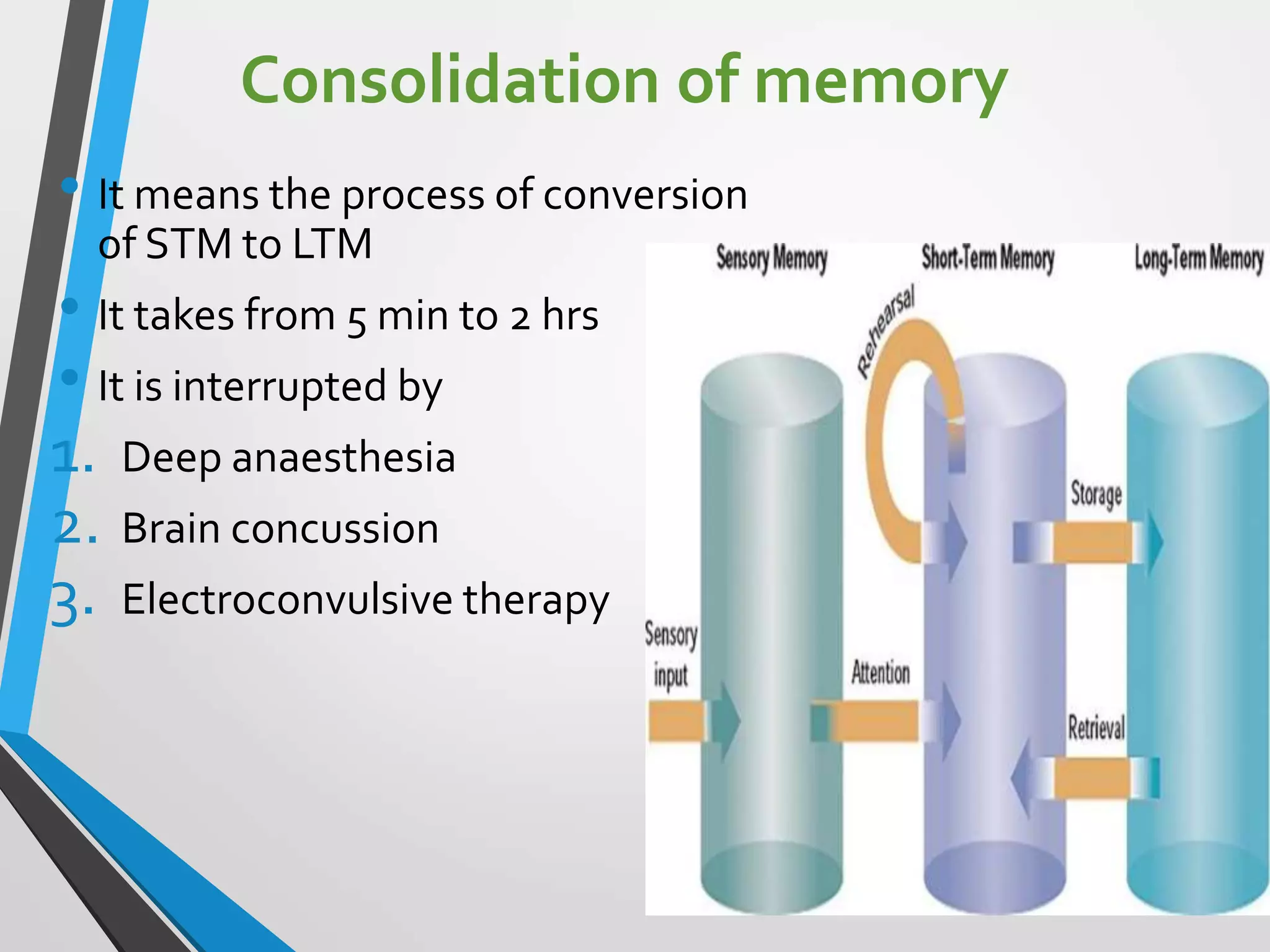
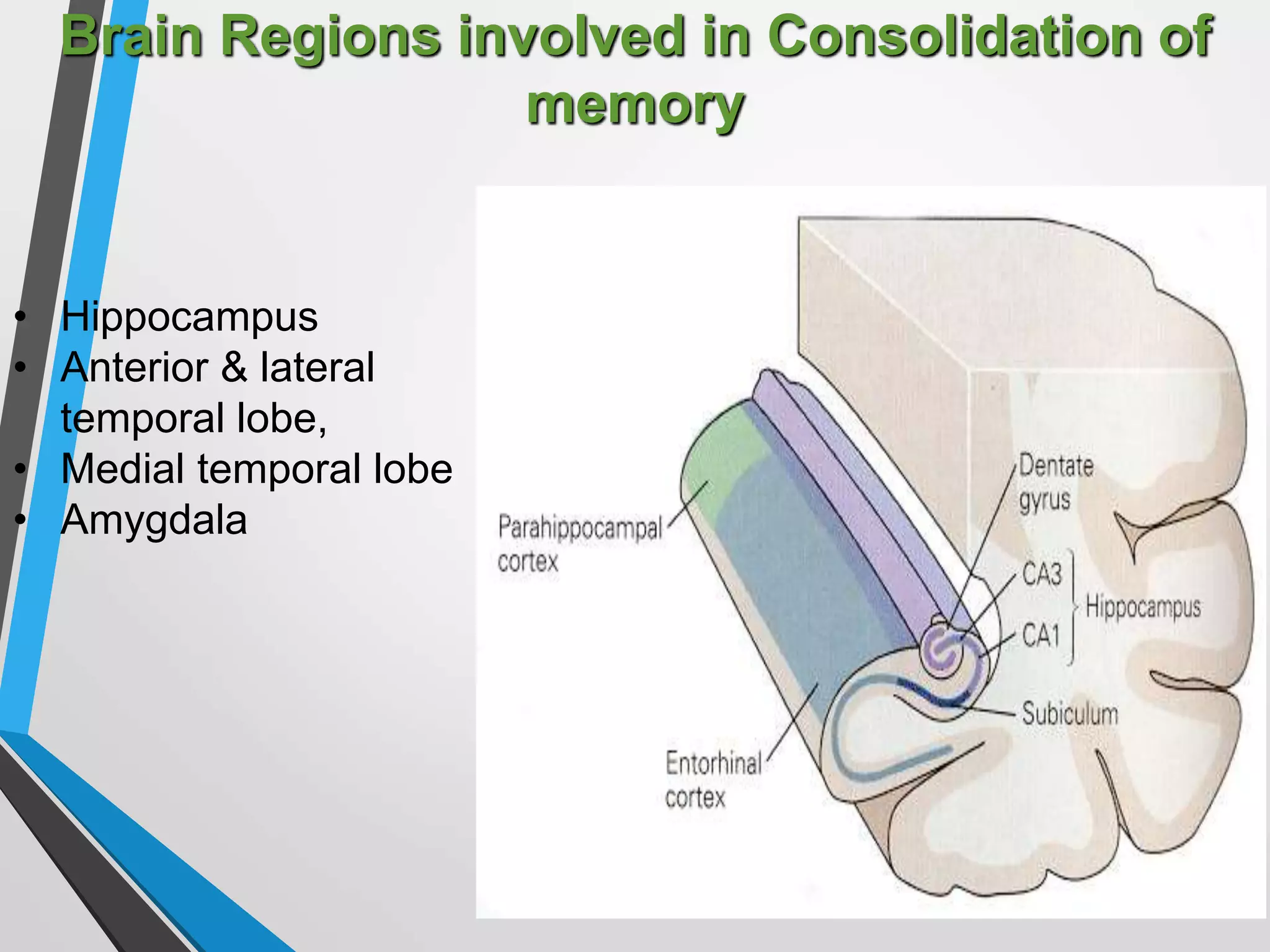
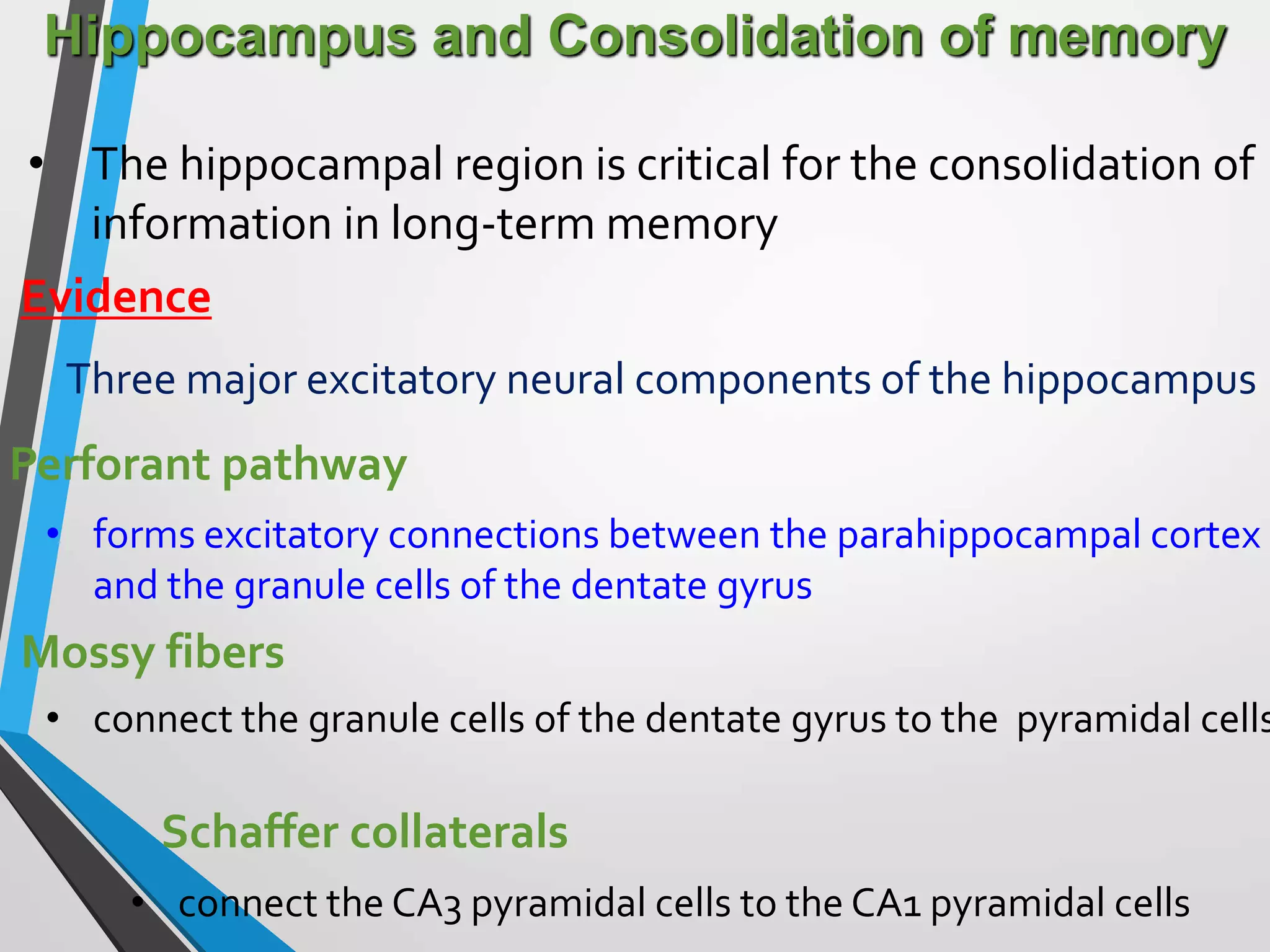
This document discusses physiology of memory and learning. It defines learning as a relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience, while memory is the ability to recall past events. There are two main types of learning - associative and non-associative. Associative learning involves associating stimuli, like in classical and operant conditioning. Non-associative learning does not require association of stimuli, and includes habituation and sensitization. Memory is classified into sensory, short-term, long-term and permanent memory based on duration. The hippocampus and surrounding areas are involved in consolidating memories by converting them from short-term to long-term storage through long-term potentiation.