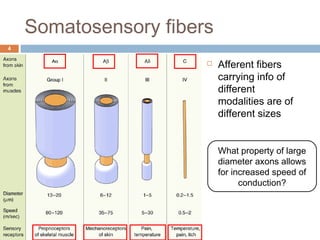
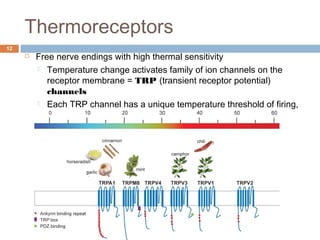
Here are the answers to your questions:
1a) A transection on the left side at T4 would impair fine touch, proprioception and vibration sense on the right side of the body below the level of the lesion.
1b) A transection on the left side at T4 would impair pain, temperature and crude touch sensation on the left side of the body below the level of the lesion.
2) In response to an increase in temperature from 35oC to 40oC: Cold receptors would increase their firing rate initially but then adapt to the new temperature. Warm receptors would increase their firing rate initially and maintain an elevated firing rate as long as the temperature is sustained at 40oC. Both receptor