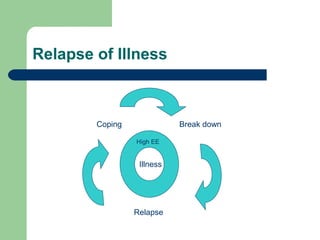
Expressed emotions refer to the amount and type of emotions that relatives express towards a family member with a psychological disorder when they are not present. There are two types - high expressed emotions, which are hostile, critical, or overly involved, and low expressed emotions, which are reserved and accepting. High expressed emotions can lead to increased relapse in the patient's disorder due to feelings of being trapped or dependent. Cultural and social factors can influence the level of expressed emotions.