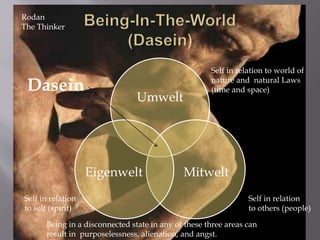
The document provides a biography and overview of the existential psychotherapy theories and philosophy of Rollo May. It discusses May's life experiences and influences, including his education and work as a therapist. May's approach was influenced by existentialism and phenomenology and focused on individuals' subjective experiences and responsibility for their own freedom and existence. He saw anxiety and meaning as important concepts and believed therapy should help people engage with their freedom.