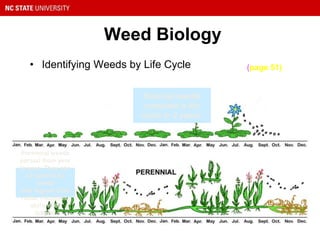
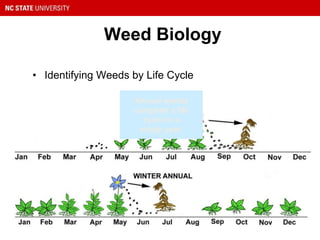
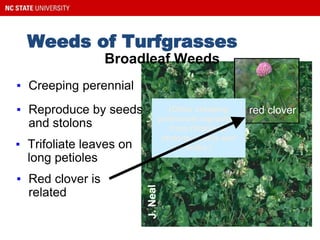
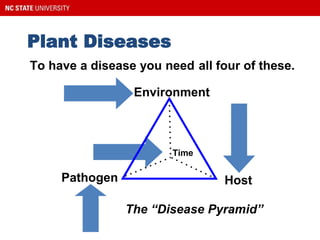
This document provides guidance on selecting and maintaining lawn grasses in North Carolina. It discusses choosing between warm-season and cool-season grasses based on climate, intended use, and site conditions. It then covers best practices for starting a new lawn, including soil preparation, planting methods, irrigation, mowing, fertilization, and weed and pest control. Key recommendations include selecting the right grass variety, maintaining proper soil pH and nutrient levels through testing and amendments, following best mowing practices, and identifying and managing common lawn weeds, insects and diseases. The document aims to help homeowners establish and care for healthy, sustainable lawns.