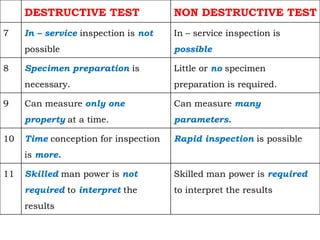
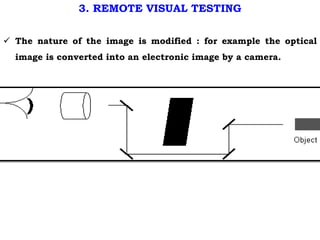
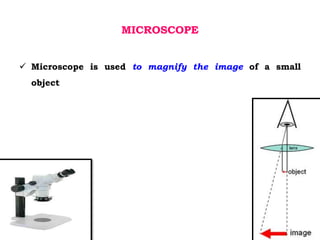
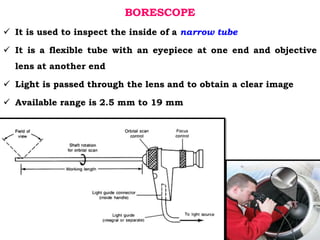
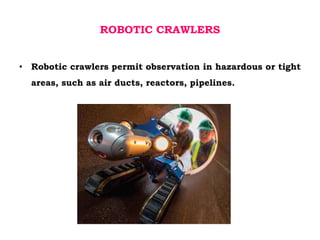
This document discusses non-destructive testing (NDT) methods, with a focus on visual inspection techniques. It defines NDT as examining materials and components without destroying them to find defects. Several NDT methods are described including visual inspection, liquid penetrant testing, magnetic particle testing, etc. Visual inspection can be unaided or aided using tools like magnifying mirrors, boroscopes, and robotic crawlers. Factors that influence visual testing like surface conditions, environment, and inspector fatigue are also covered. The document provides examples of visual inspection applications and lists advantages and limitations of various NDT methods.