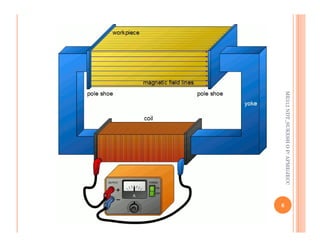
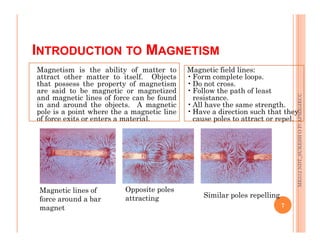
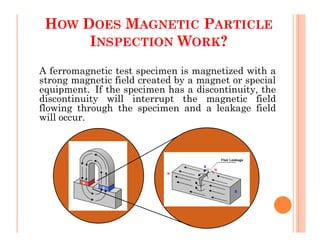
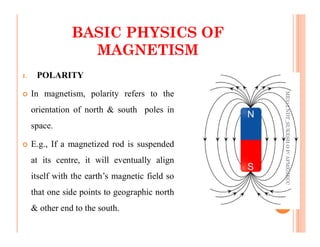
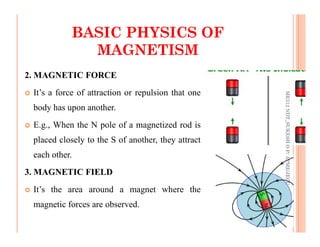
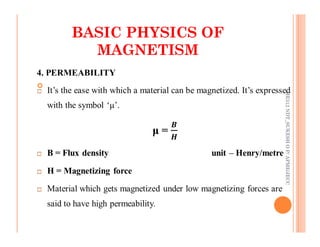
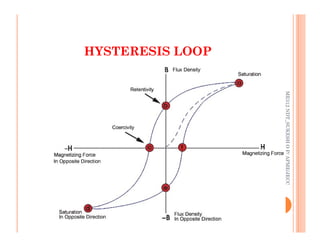
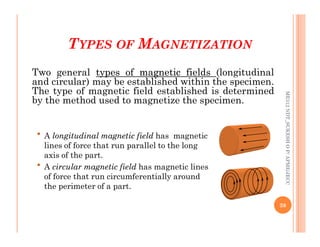
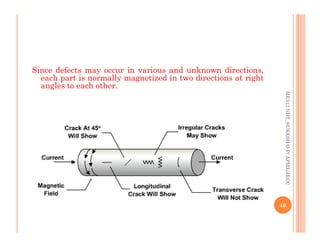
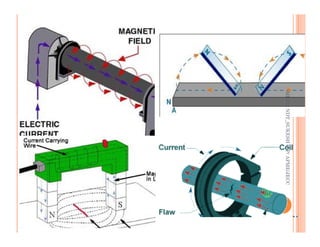
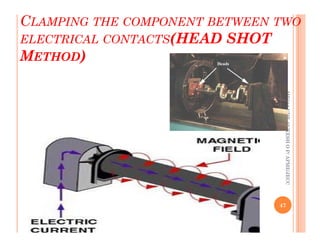
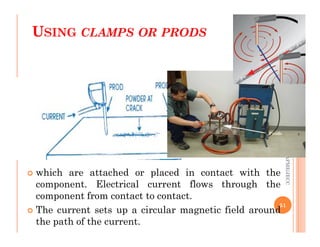
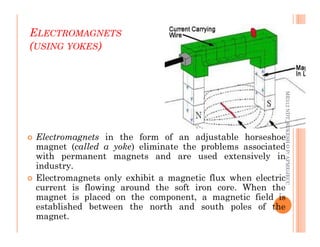
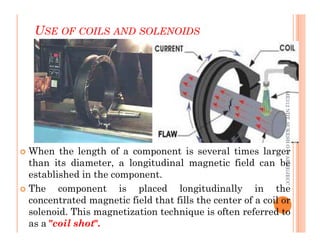
The document discusses magnetic particle inspection (MPI), a non-destructive testing method used to detect surface and near-surface flaws in ferromagnetic materials. MPI works by magnetizing the test specimen and applying iron particles coated with dye. Any discontinuities will cause magnetic leakage fields that attract and cluster the particles, revealing indications of flaws. The document covers the basic MPI procedure, types of magnetic particles, interpretation of indications, and examples of flaws found using MPI. It also provides background information on magnetism and ferromagnetic materials.