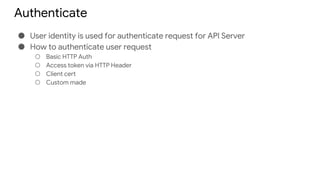
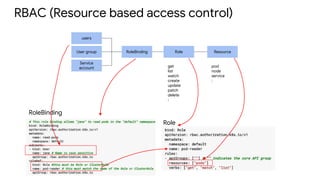
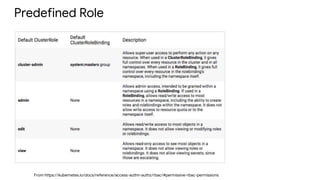
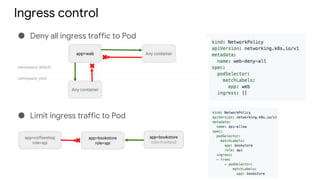
Kubernetes security involves authentication and authorization of users and service accounts, network policies to control ingress and egress traffic, security contexts to configure permissions and capabilities, and best practices like container image scanning, resource quotas, and network segmentation. The document outlines these Kubernetes security features and provides examples of how to implement authentication, define roles and permissions, set security contexts, and configure network policies and quotas. It recommends limiting direct access to nodes, regularly updating container images, and building a log cluster to analyze logs.




















![Network control
● Implement network segmentation
POST /apis/net.alpha.kubernetes.io/v1alpha1/namespaces/tenant-a/networkpolicys
{
"kind": "NetworkPolicy",
"metadata": {
"name": "pol1"
},
"spec": {
"allowIncoming": {
"from": [{
"pods": { "segment": "frontend" }
}],
"toPorts": [{
"port": 80,
"protocol": "TCP"
}]
},
"podSelector": {
"segment": "backend"
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kubernetes3-security-180525121434/85/Kubernetes-3-security-25-320.jpg)


