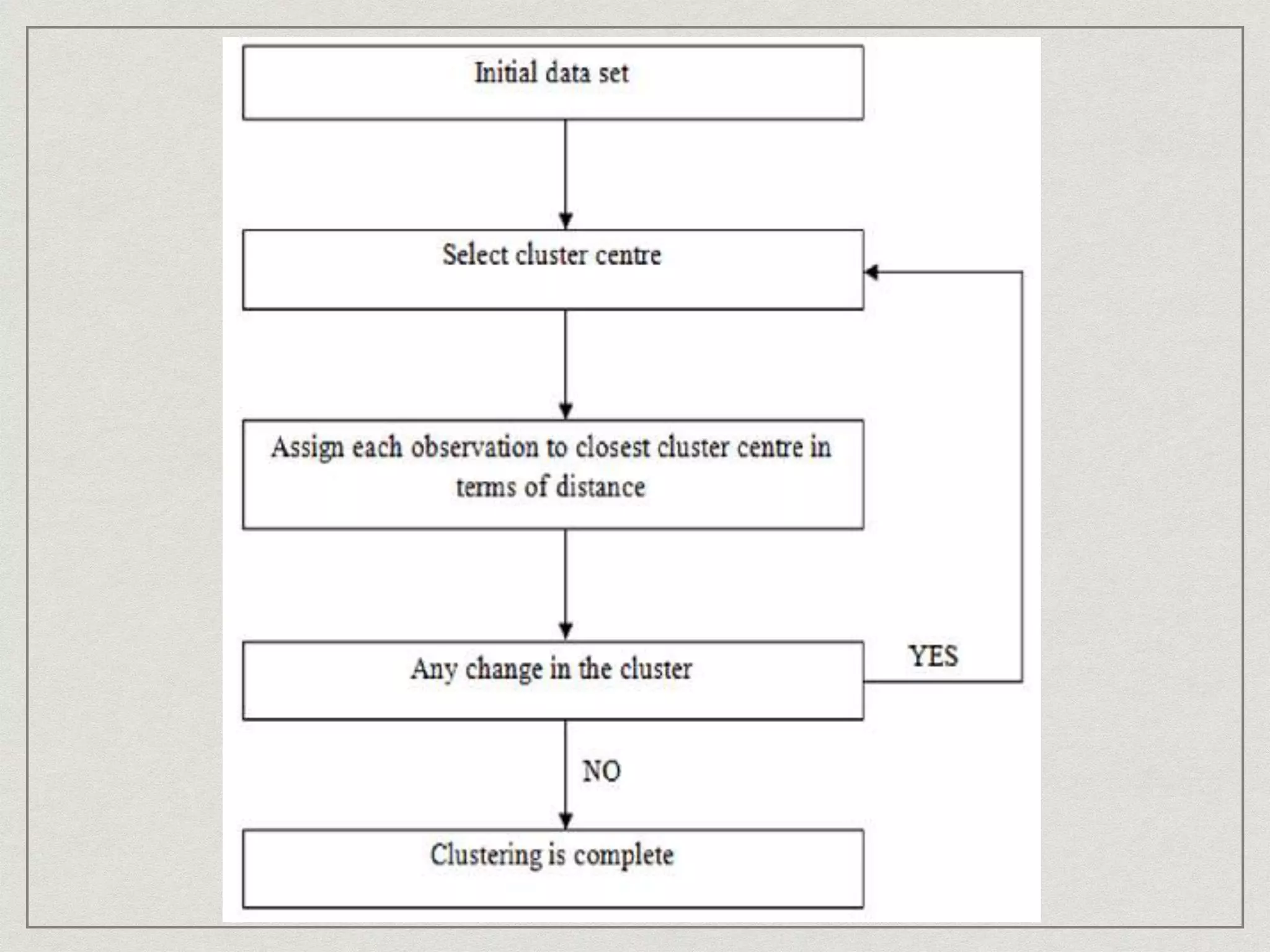
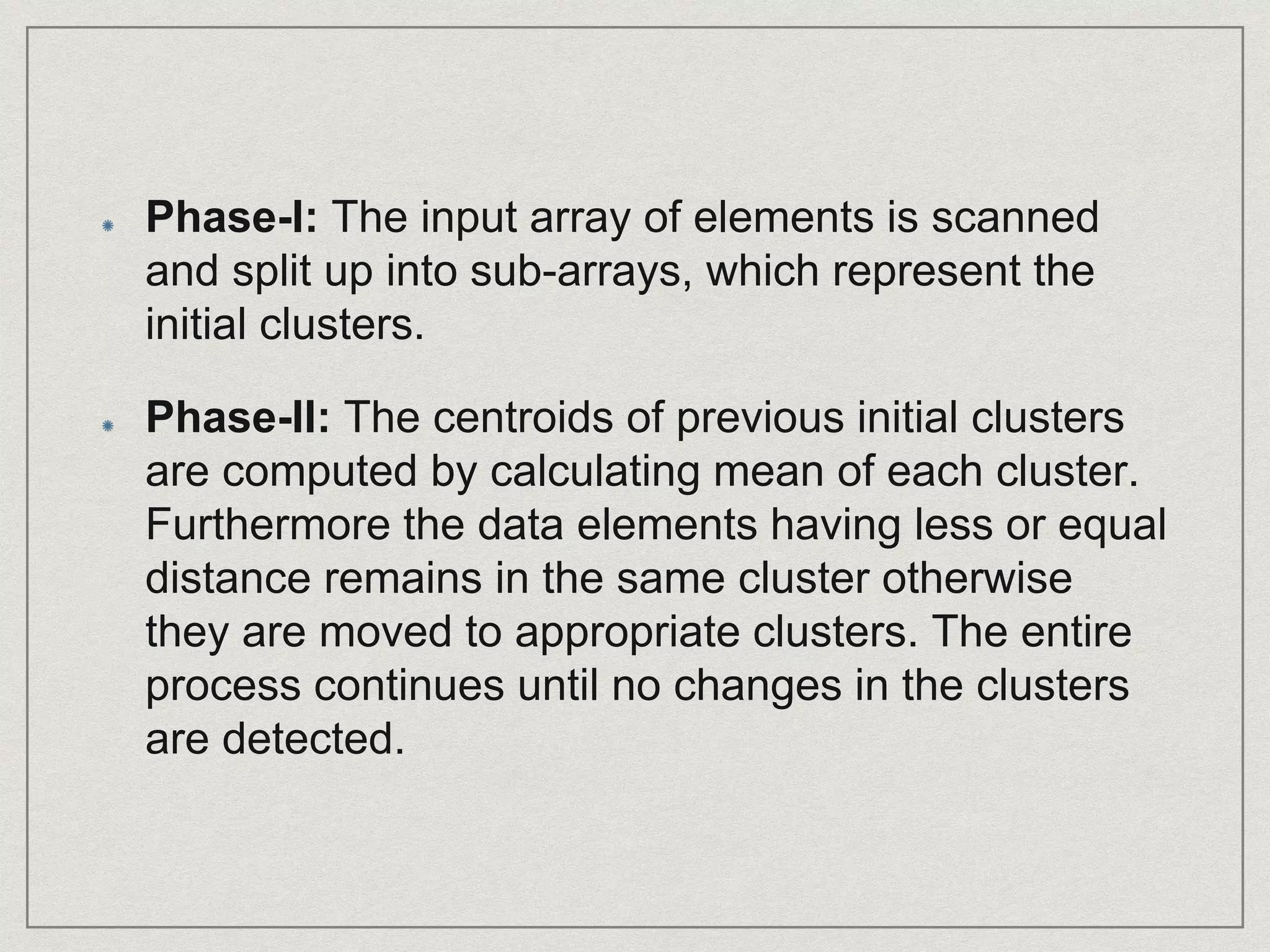
The document discusses the k-means algorithm used for clustering data points into 'k' clusters based on similarity measures, highlighting its dependence on the selection of initial centroids. It proposes an improved method for determining initial centroids to enhance clustering quality and reduce complexity through a two-phase process. The application of this improved algorithm includes rating-based clustering systems in e-commerce to optimize product organization and marketing strategies.