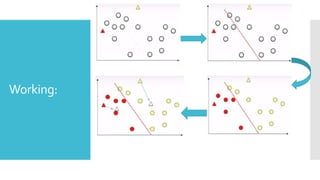
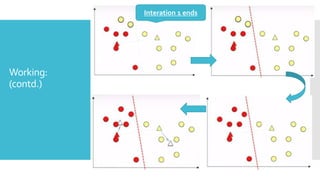
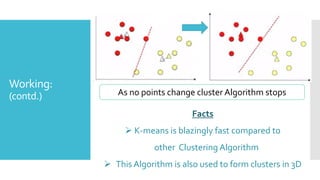
K-means clustering is an algorithm that groups data points into k clusters based on their similarity, with each point assigned to the cluster with the nearest mean. It works by randomly selecting k cluster centroids and then iteratively assigning data points to the closest centroid and recalculating the centroids until convergence. K-means clustering is fast, efficient, and commonly used for vector quantization, image segmentation, and discovering customer groups in marketing. Its runtime complexity is O(t*k*n) where t is the number of iterations, k is the number of clusters, and n is the number of data points.

![Information:
(contd.)
Types Of Clustering:
1. Hierarchical: [find Successive Cluster]
Agglomerative (bottom-up)
Divisive (top-down)
2. Partitional: [Construct various partition and evaluate]
K-means Clustering
Fuzzy c-means
QT clustering
The centroid is (typically) the mean of the points in the cluster.
Similarity is measured by Euclidean distance, Manhattan
Distance
NOTE: UsedWhen data is numeric not when categorical or boolean.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/k-meansclusteringalgorithm-190124172445/85/K-means-clustering-algorithm-3-320.jpg)