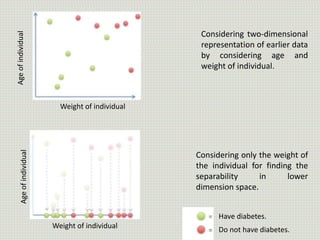
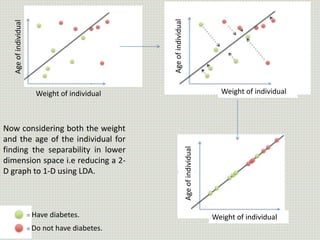
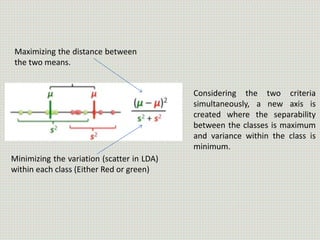
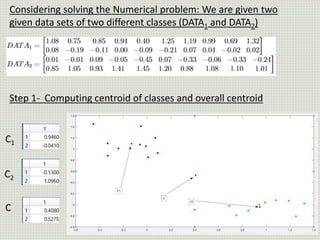
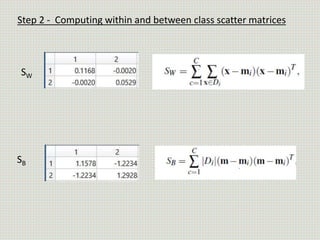
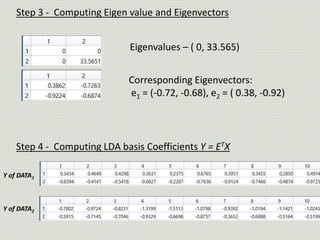
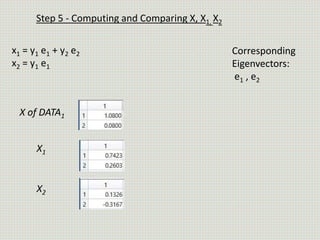
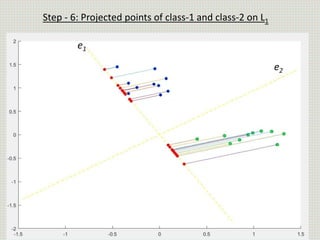
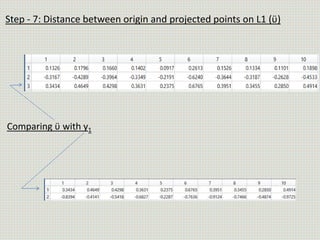
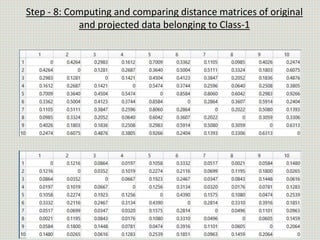
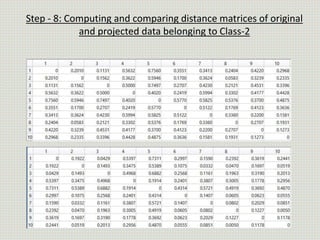
The document discusses the application of linear discriminant analysis (LDA) to determine an individual's propensity for diabetes based on their weight and age. It outlines the methodology for maximizing class separability and minimizing variance through scatter matrices and eigenvalue computation. The process includes several steps, including calculating centroids, projecting data onto a hyperplane, and comparing distances of original and projected data points for two different classes.