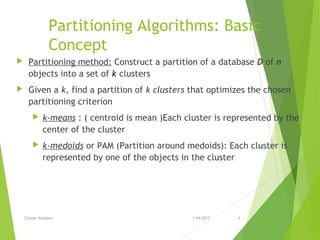
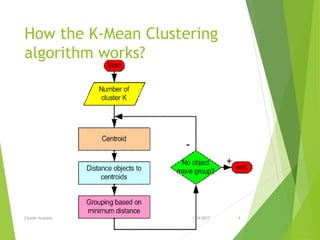
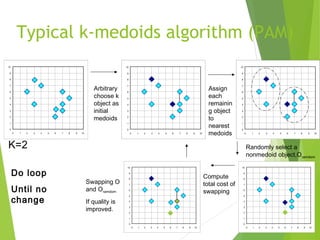
This document discusses various clustering analysis methods including k-means, k-medoids (PAM), and CLARA. It explains that clustering involves grouping similar objects together without predefined classes. Partitioning methods like k-means and k-medoids (PAM) assign objects to clusters to optimize a criterion function. K-means uses cluster centroids while k-medoids uses actual data points as cluster representatives. PAM is more robust to outliers than k-means but does not scale well to large datasets, so CLARA applies PAM to samples of the data. Examples of clustering applications include market segmentation, land use analysis, and earthquake studies.