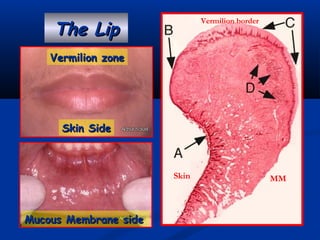
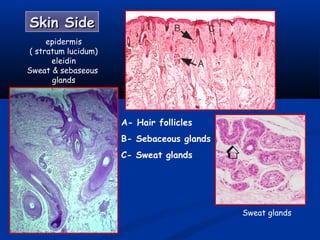
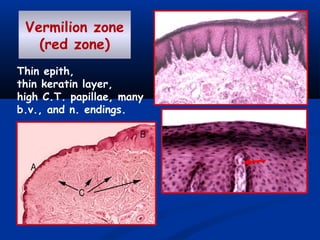
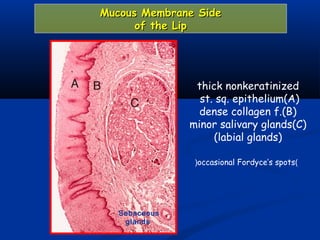
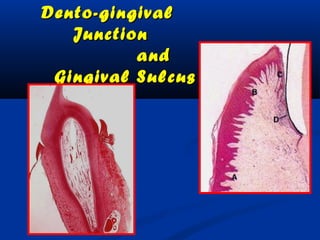
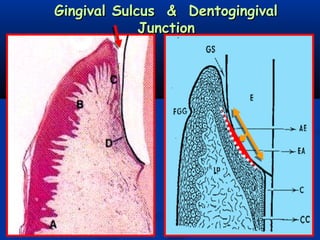
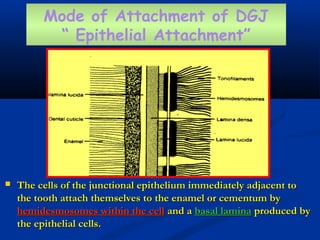
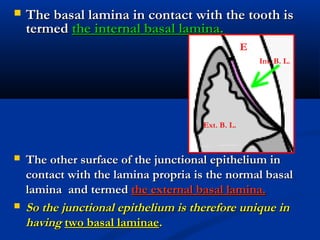
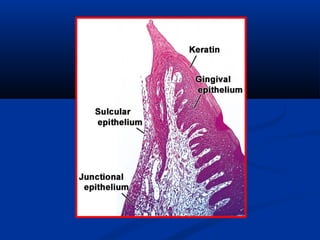
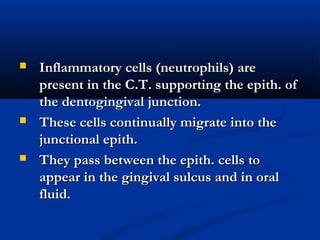
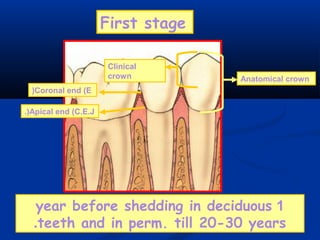
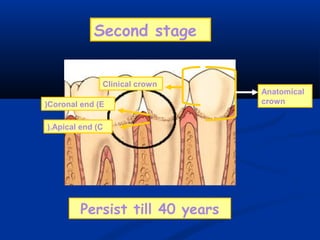
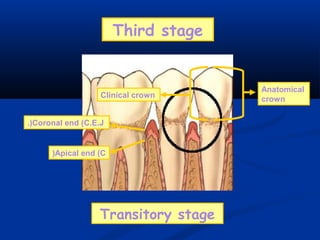
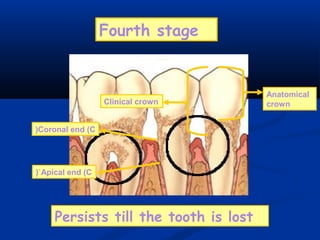
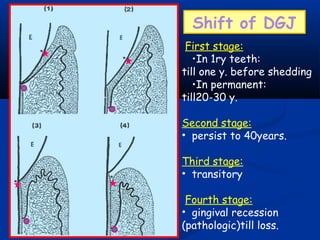
- There are three junctions in the oral mucosa: the mucocutaneous junction between the mucosa and skin, the mucogingival junction between the alveolar mucosa and attached gingiva, and the dentogingival junction between the tooth and gingiva.
- The mucocutaneous junction, also called the vermilion border, is the transitional zone between the lip skin and mucosa. It is characterized by long papillae, large blood vessels, and sensory nerve endings.
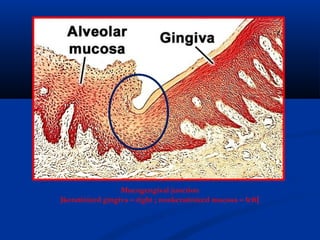
- The mucogingival junction can be identified clinically by the mucogingival groove and change in color from pink alveolar mucosa to pale gingiva. Histologically