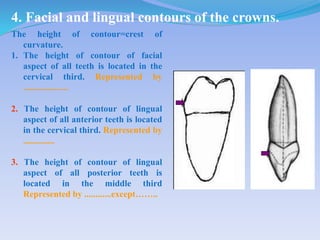
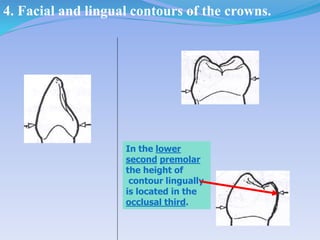
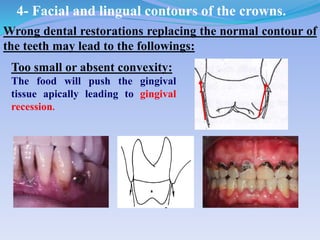
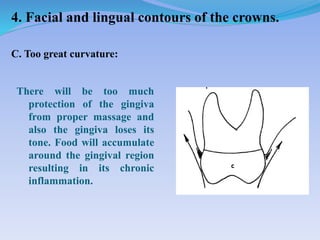
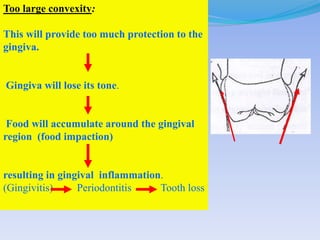
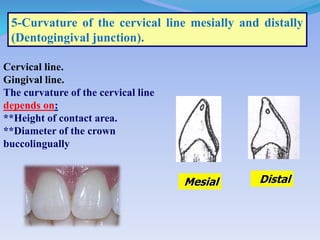
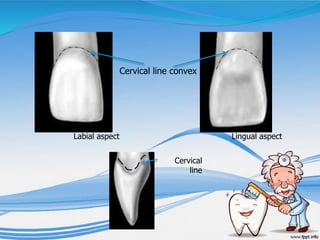
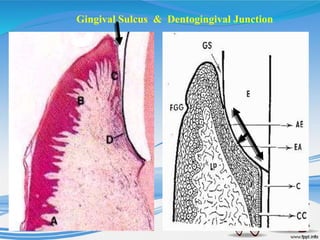
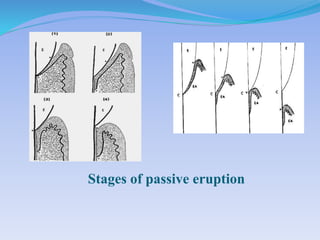
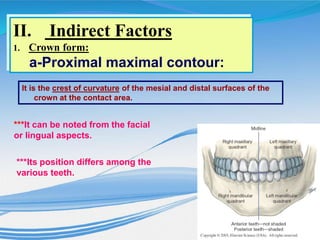
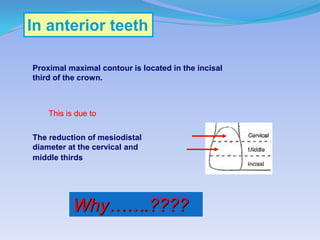
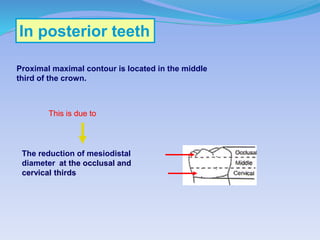
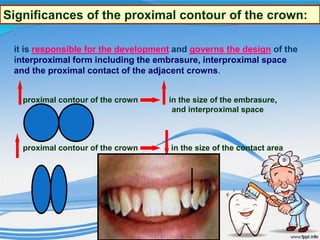
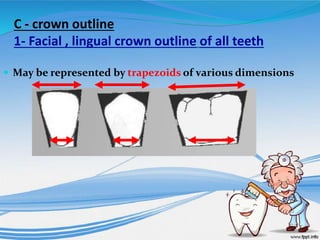
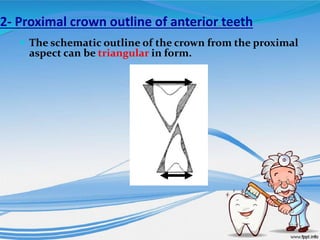
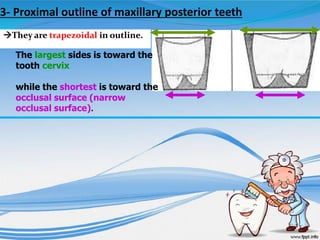
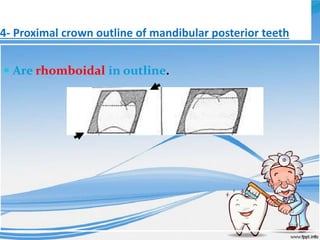
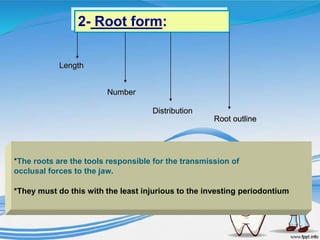
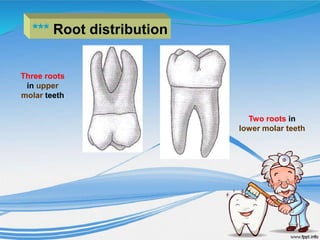
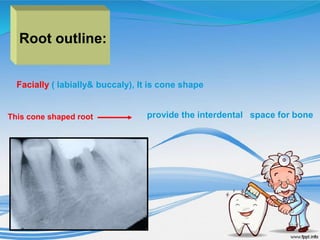
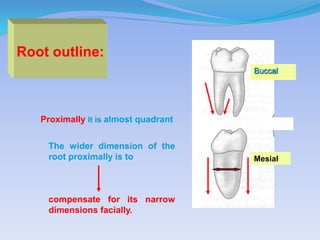
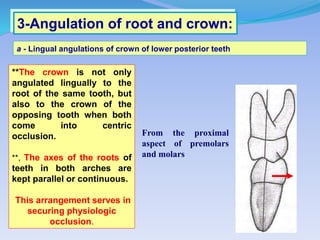
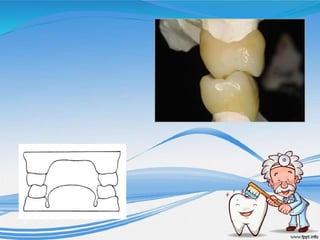
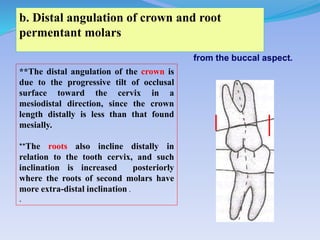
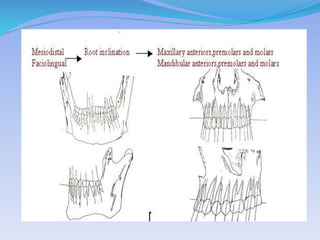
The document discusses several direct and indirect factors related to tooth morphology that influence periodontal health. The direct factors include proximal contact areas, interproximal spaces, embrasures, and facial and lingual contours of tooth crowns. Indirect factors involve crown form, root form, angulation of crowns and roots, self-cleaning ability, cusp form, and continuity of marginal ridges and central grooves. Specific anatomical features like proximal maximal contour, root outline, and lingual angulation of posterior crowns are described in detail due to their significance. Maintaining proper tooth morphology through these factors helps prevent periodontal issues.