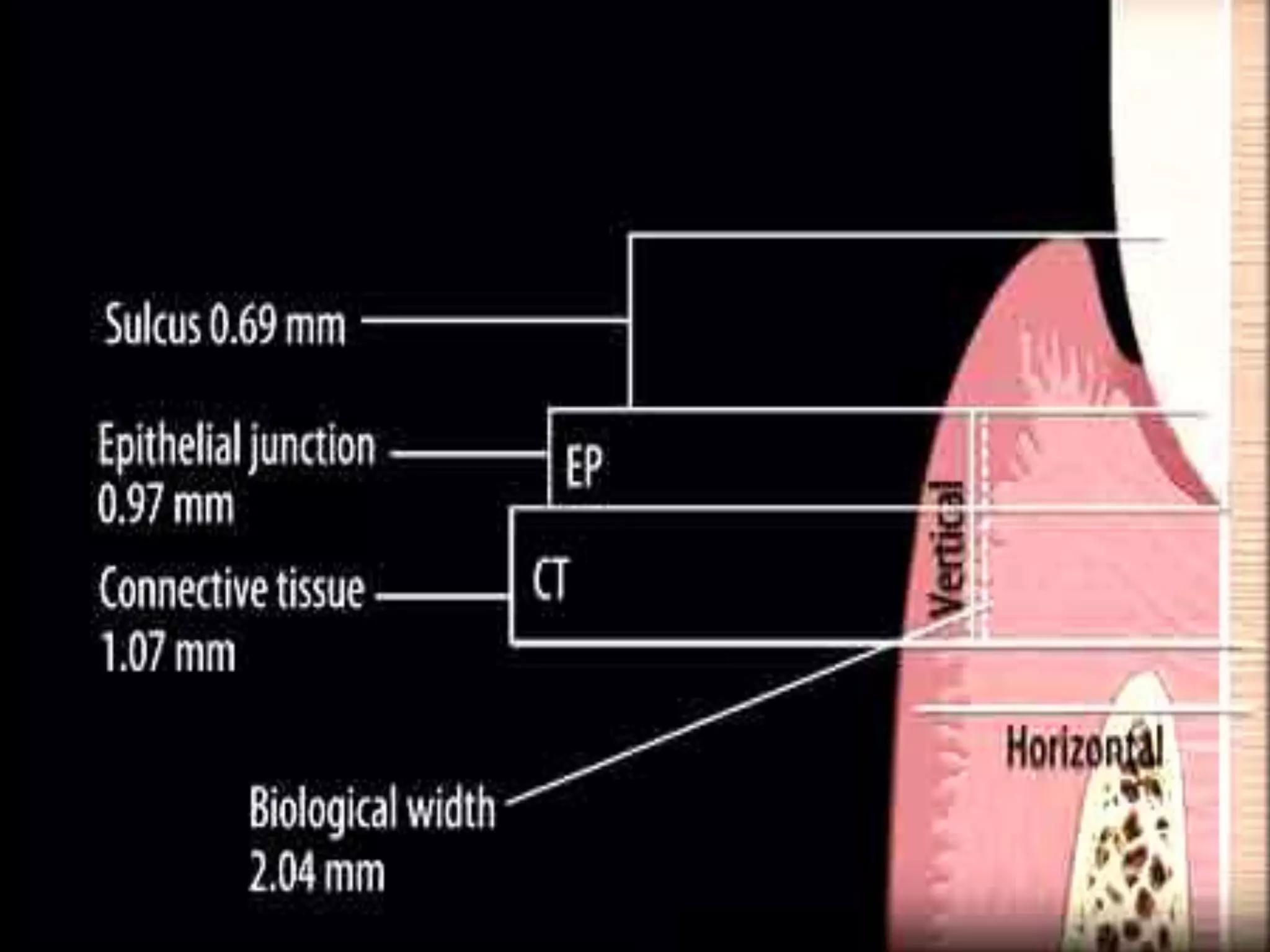
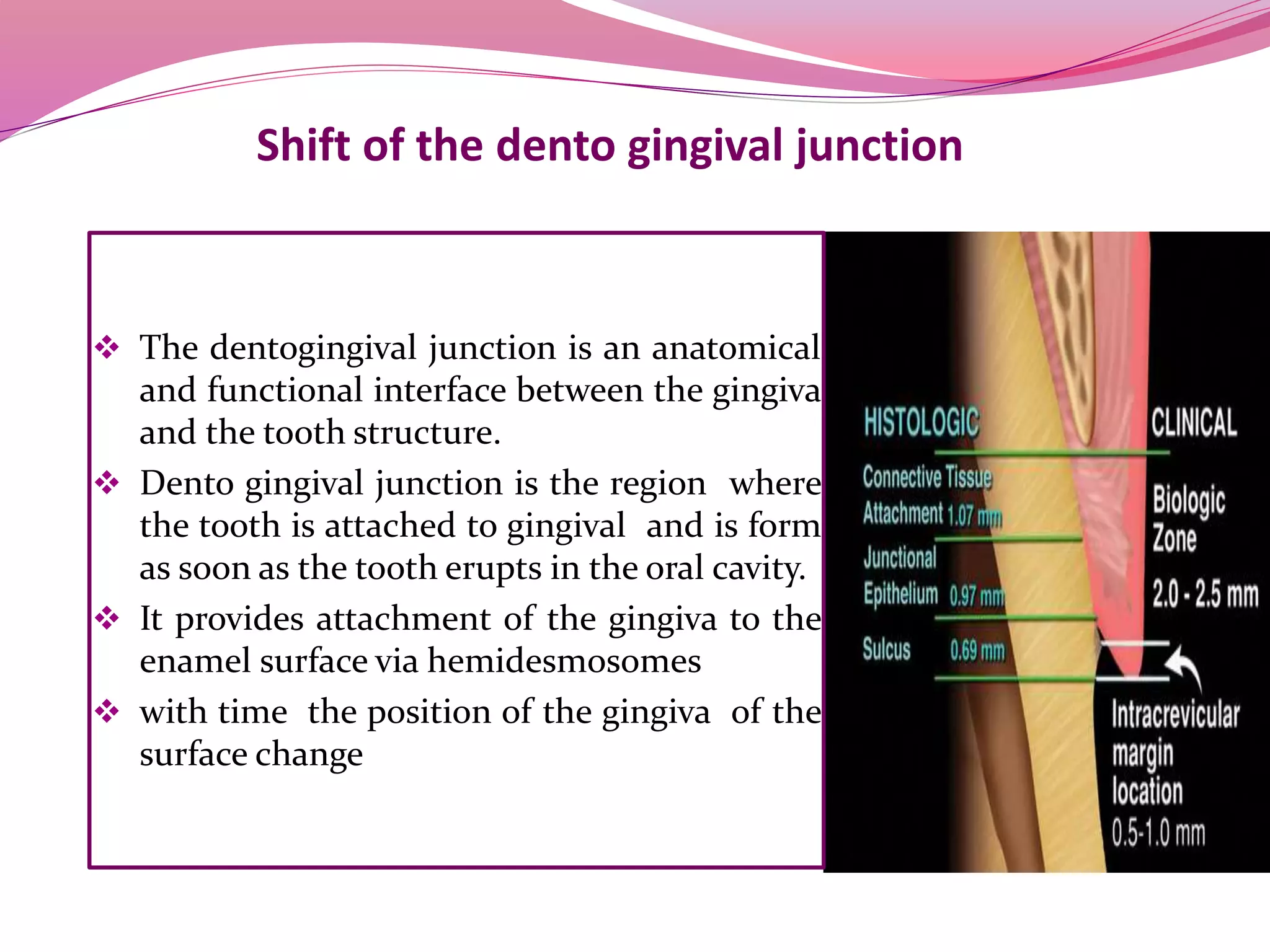
The dentogingival junction is the region where the tooth is attached to the gingiva. It initially forms with the emergence of the tooth into the oral cavity, with the enamel covered by epithelium. Over time, the junction shifts apically as the epithelium separates from the enamel surface in a process called passive eruption. The junctional epithelium, which is more permeable, eventually attaches at the cementoenamel junction. In unhealthy conditions, the junction and sulcus can shift further onto the root surface, forming a pathological periodontal pocket.