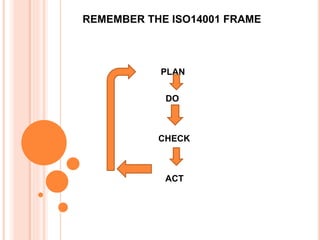
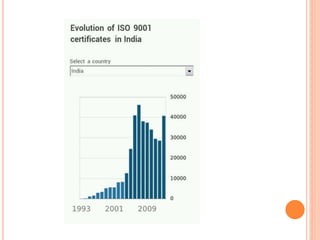
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. It was founded in 1947 and is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland. ISO establishes international standards in a wide range of industries to facilitate global trade and communication. Some key ISO standards include ISO 9000 for quality management, ISO 14000 for environmental management, and ISO 27001 for information security management.