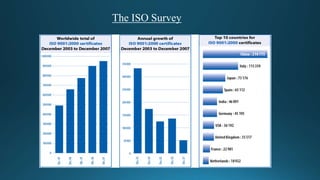
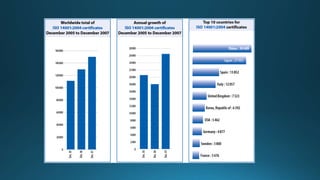
ISO establishes voluntary international standards to ensure quality, safety, and efficiency. ISO's most popular standards are ISO 9001 for quality management, ISO 14001 for environmental management, and ISO/IEC 27001 for information security. ISO 9001 focuses on meeting customer needs and continual improvement. ISO 14001 focuses on minimizing environmental impacts and conforming to regulations. Certification to ISO standards is done by independent auditors and provides benefits like improved operations, customer satisfaction, and international trade compliance.