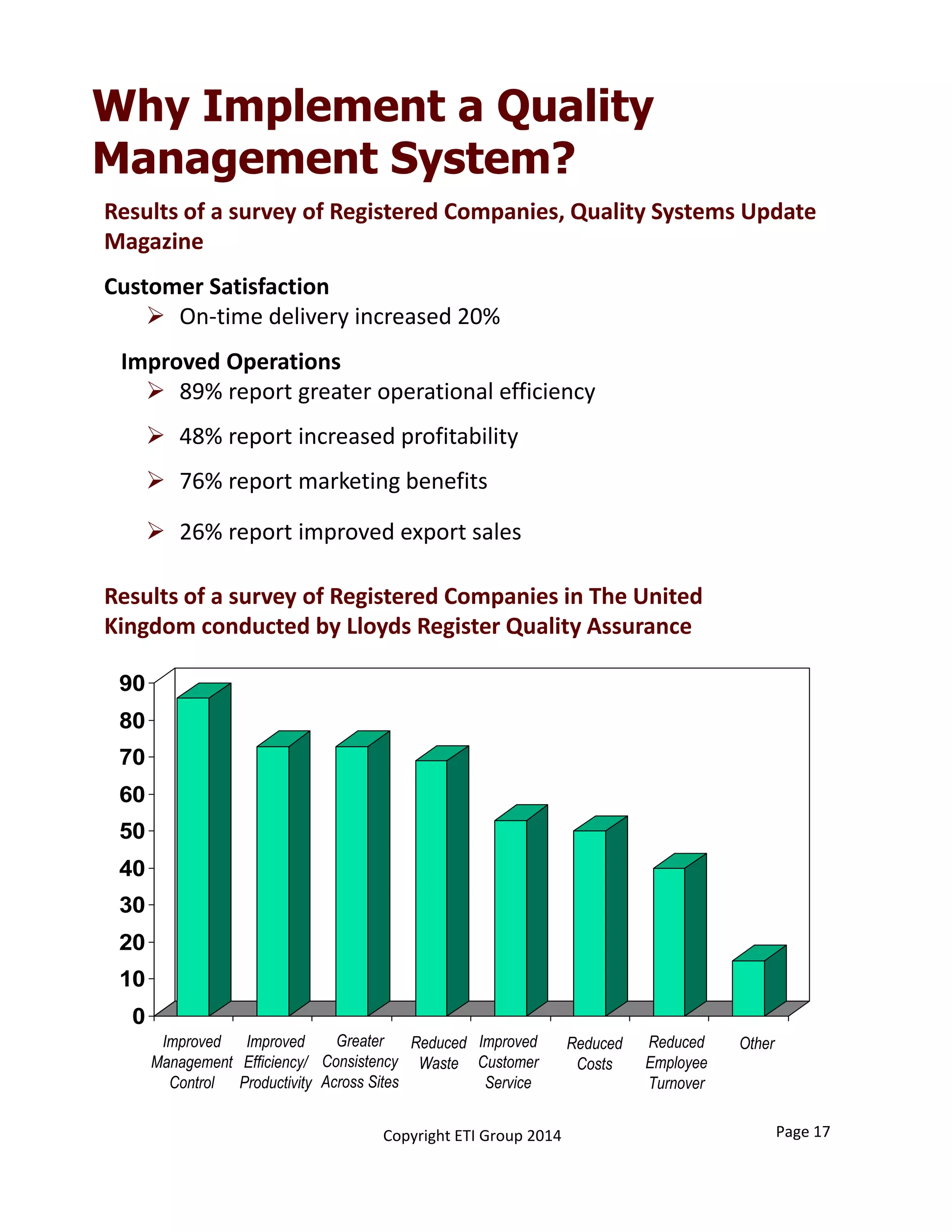
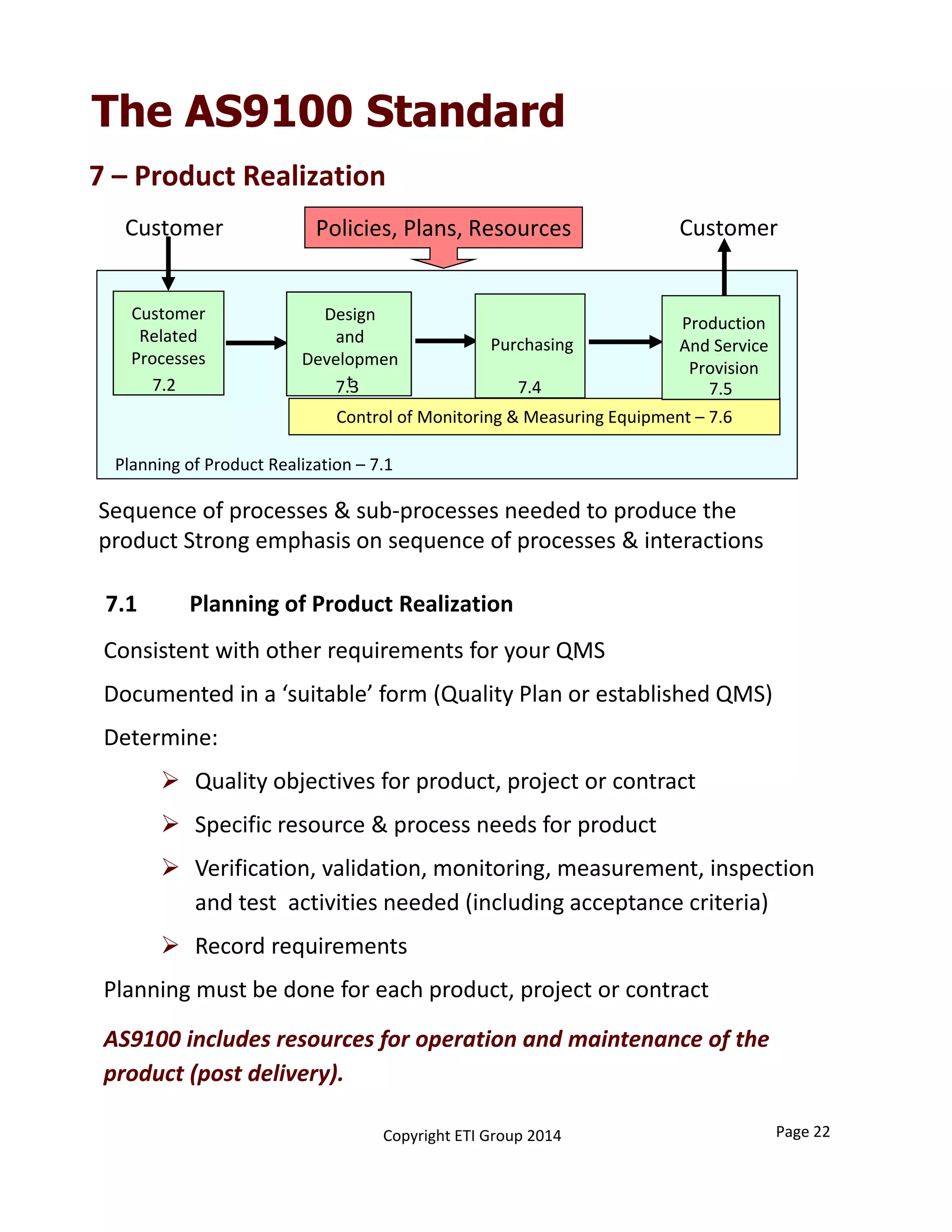
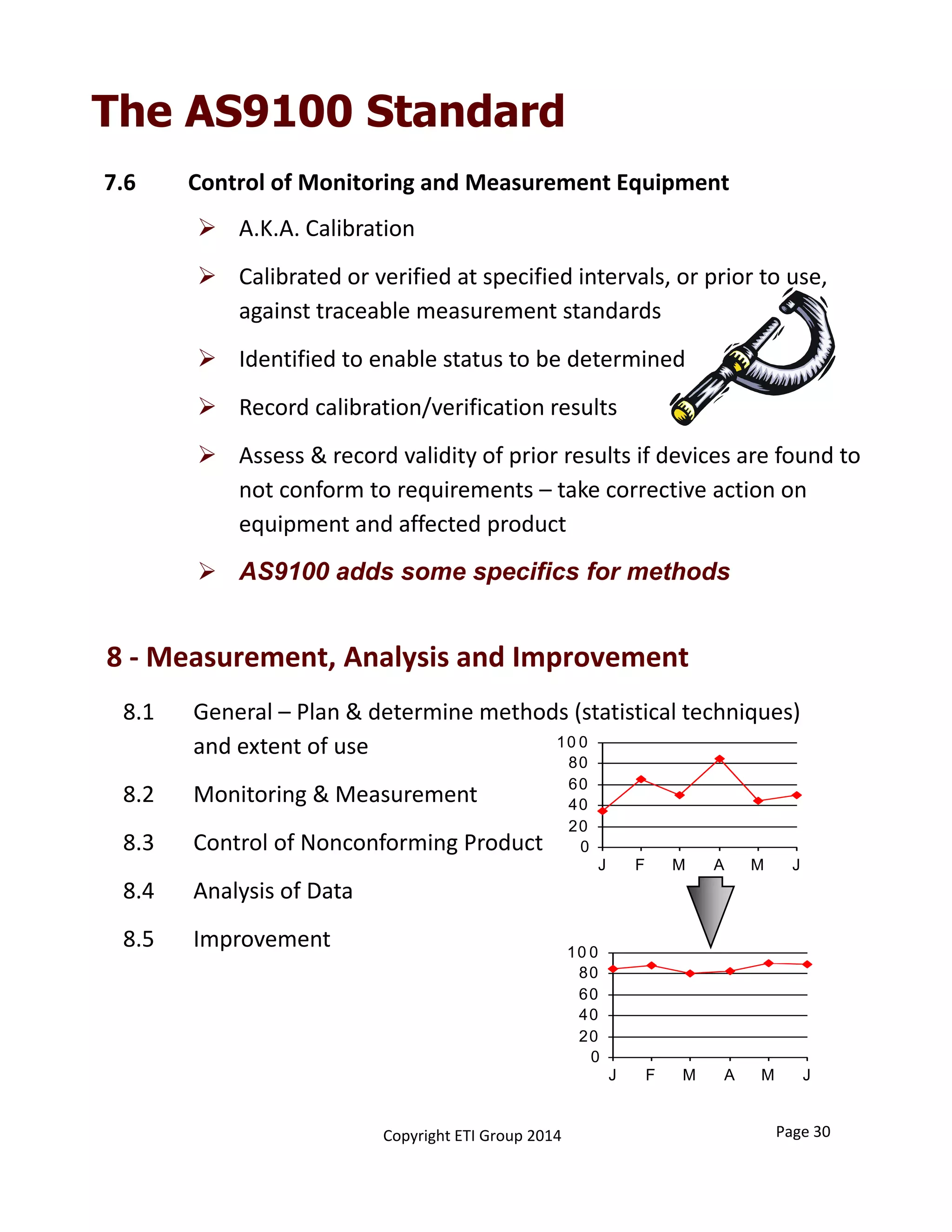
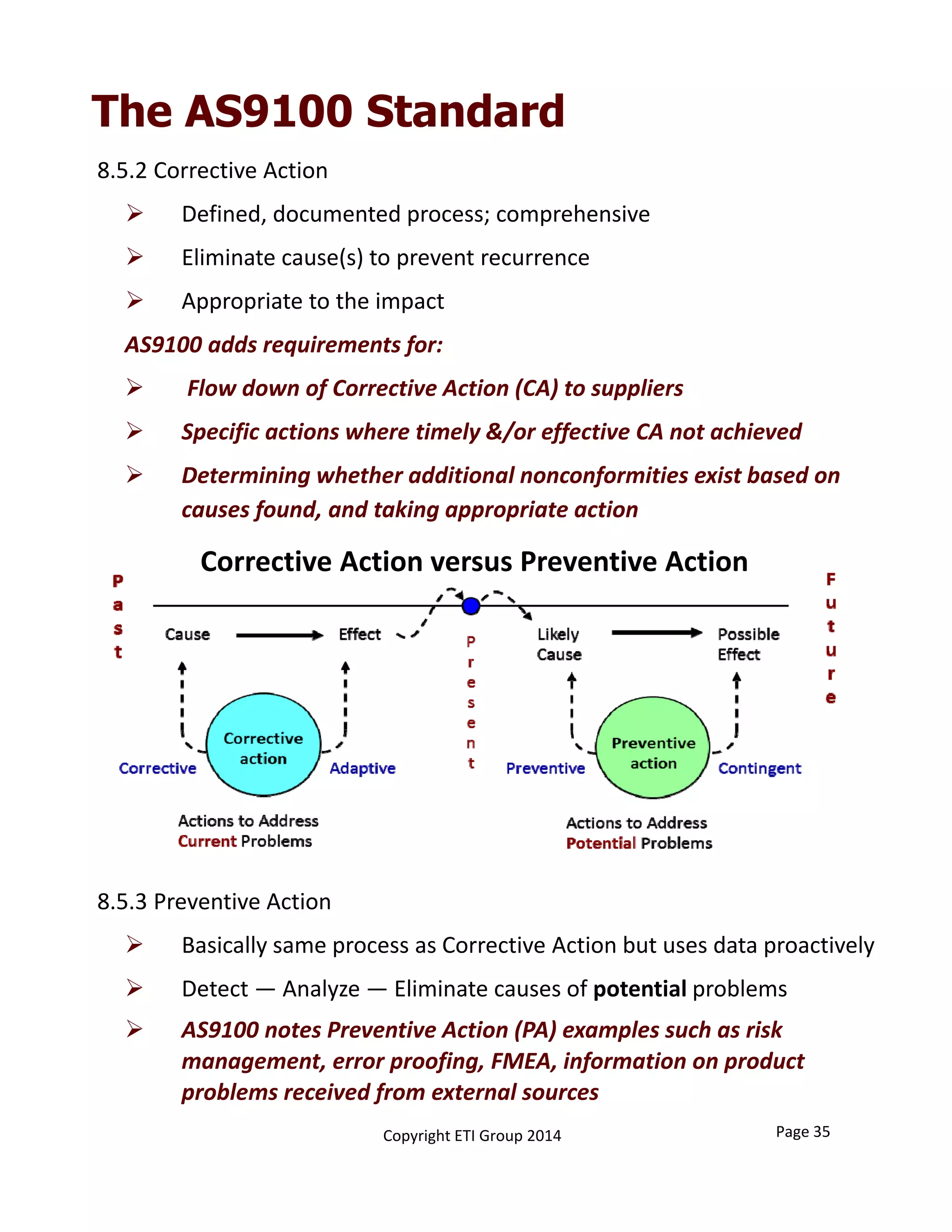
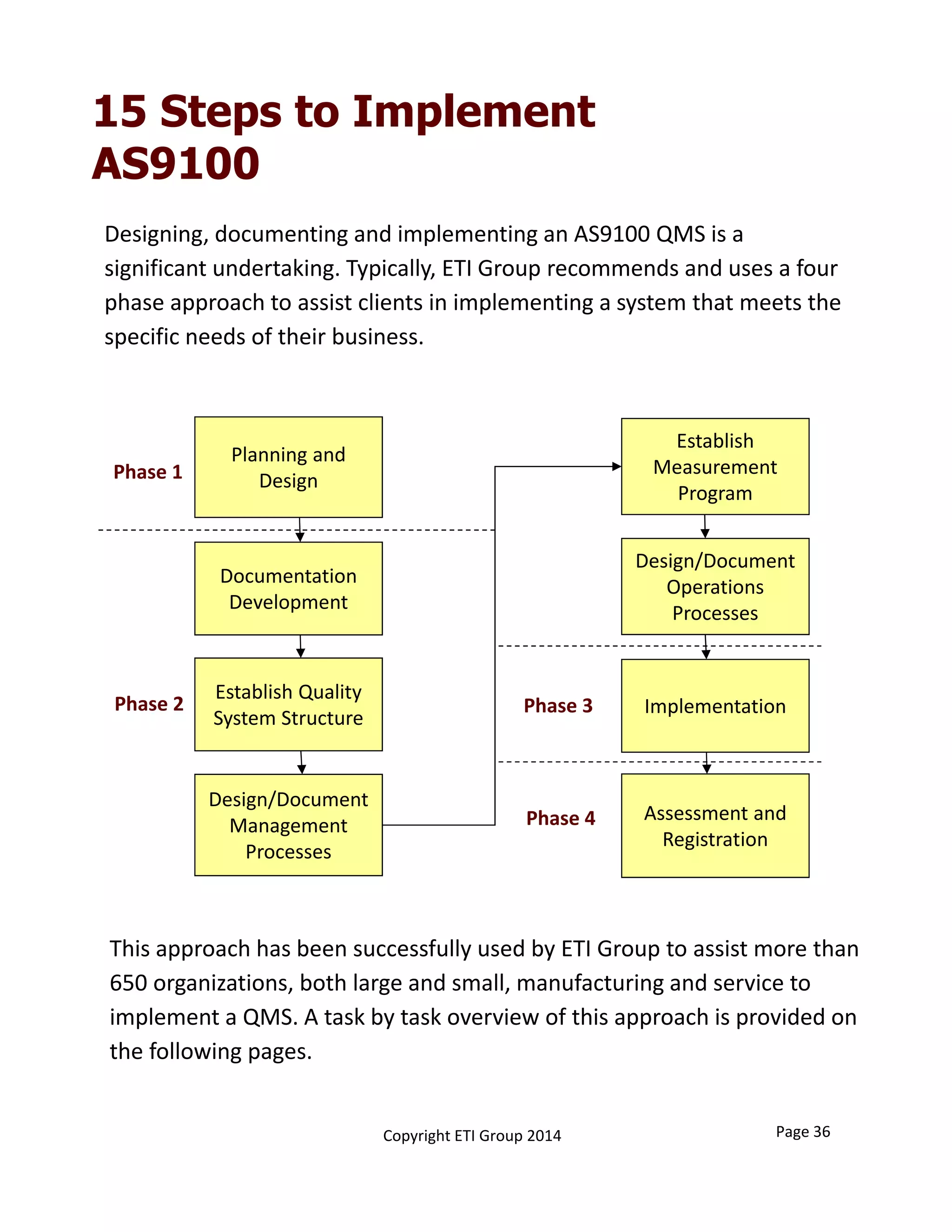
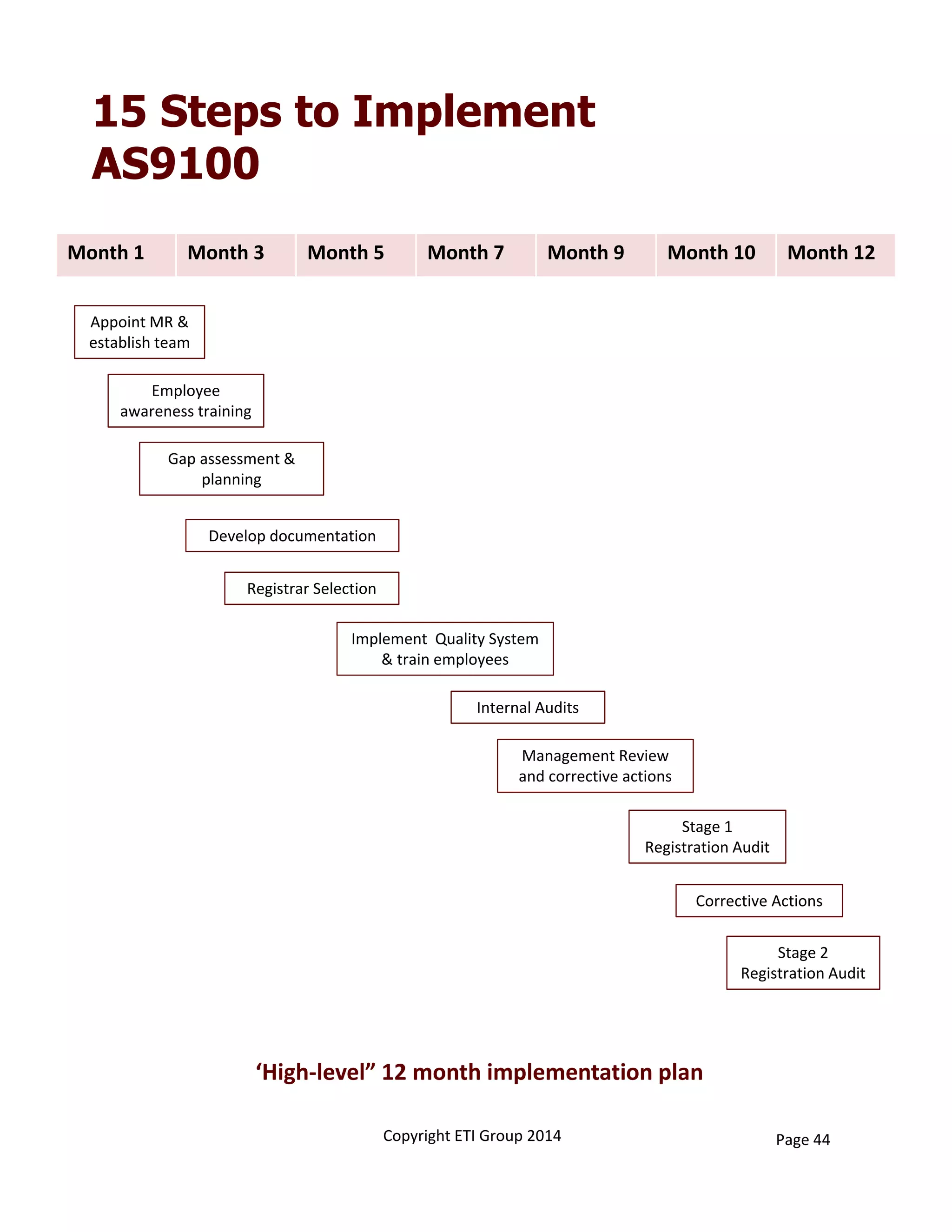
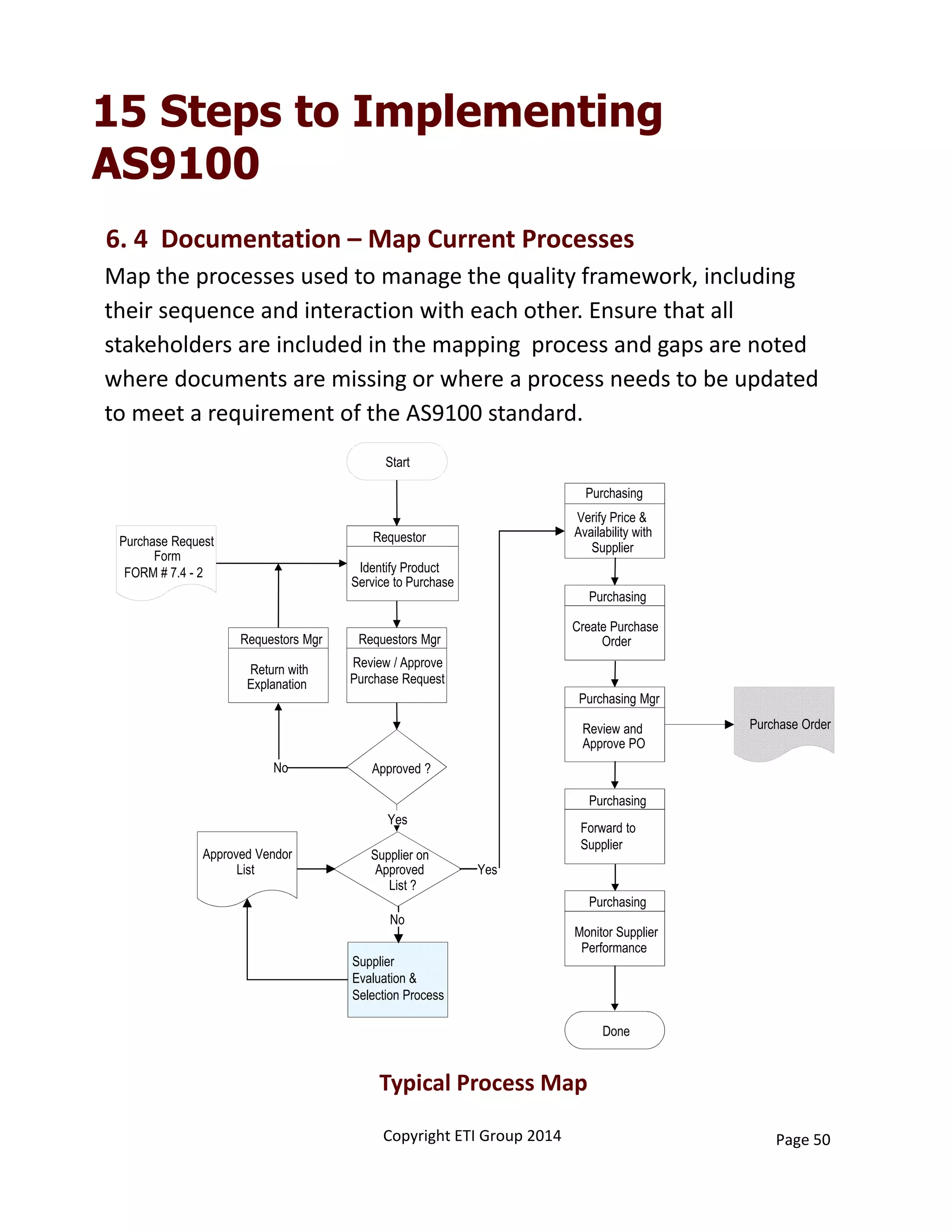
This document provides an overview of implementing an AS9100 quality management system. It discusses the benefits of implementing such a system, including helping win customers and improve internal processes. The document also describes the typical components of a quality management system, such as establishing documented processes, conducting internal audits, and continually improving processes based on audit findings. Finally, it outlines the 15 typical steps involved in implementing an AS9100 system, from planning and getting management support to achieving certification.