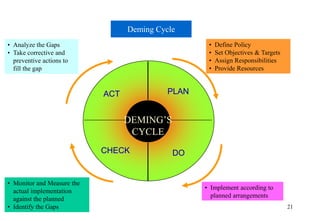
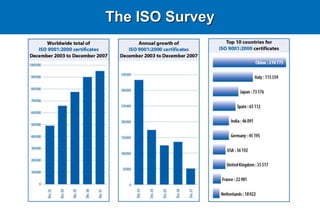
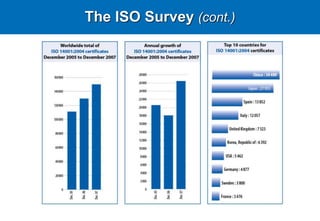
The document provides information about the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). It discusses that ISO is the world's largest developer and publisher of international standards, with members from 163 countries. ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 are two of ISO's most well-known standards for quality management and environmental management systems. The document provides details on the requirements and processes for organizations to implement ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 standards and become certified.