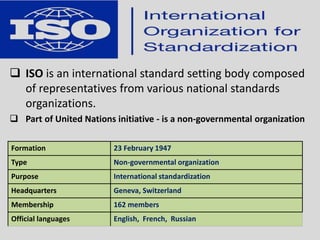
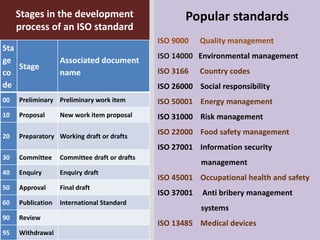
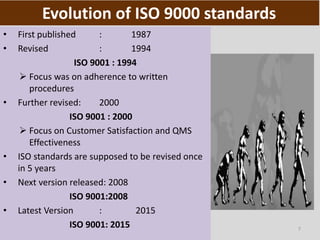
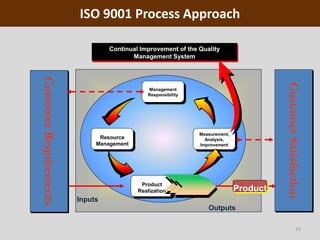
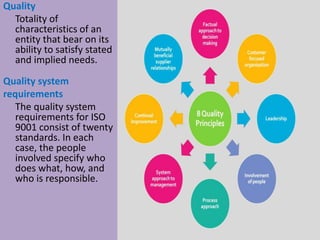
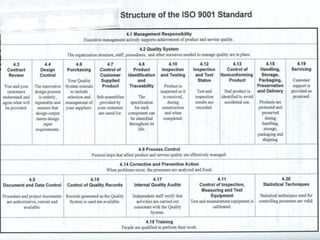
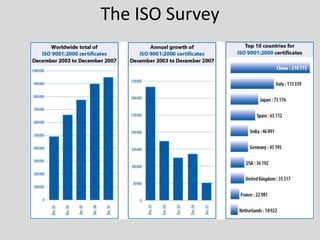
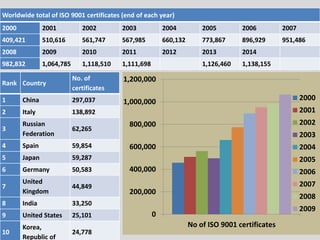
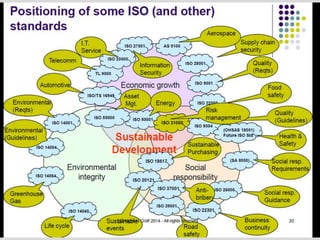
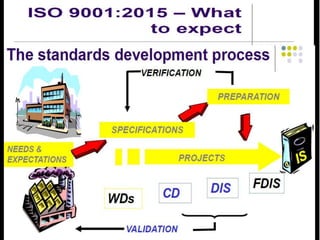
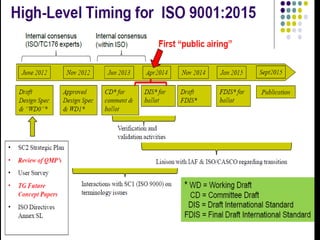
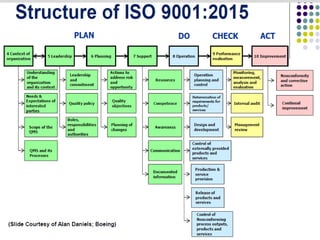
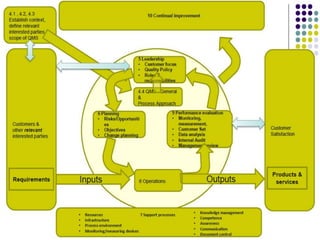
This document provides an overview of ISO 9001, an international standard for quality management systems. It discusses the history and development of ISO 9001, including the various versions that have been published. Key requirements of ISO 9001 are outlined, including demonstrating the ability to consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements. The document also summarizes ISO 9001's process approach and lists some of its main elements. Global statistics on ISO 9001 certifications are presented, with China having the most. Videos are also included that compare ISO 9001:2008 to the latest ISO 9001:2015 version.