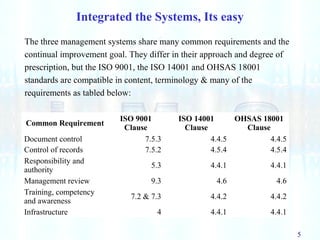
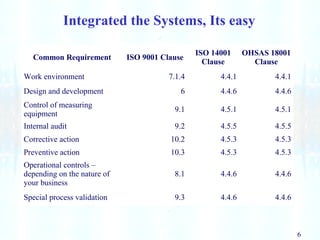
This document discusses integrated management systems (IMS), which integrate quality, environmental, and safety management systems into a single framework. An IMS allows an organization to work as a unified system toward shared objectives. The document outlines the common requirements and elements of ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and OHSAS 18001, and explains how integrating these systems can simplify processes and reduce costs. Implementing an IMS follows the PDCA (plan-do-check-act) cycle. Benefits include consistent objectives, reduced auditing and documentation, and easier management and evaluation across all related systems.











![14
OHSAS 18001
OHSAS 18001 is the International Occupational Health and Safety
Management Standard. It provides a framework for the effective management
of OH&S including all aspects of risk management and legal compliance. It
addresses occupational health and safety rather than any specific product
safety matters.]
OHSAS 18001 is not an ISO standard, It is British Standard (BS)
OHSAS Project Group published the OHSAS 18000 Series in 1999 and
BSI Group (UK’s national standards body) make the arrangements.
OHSAS 18000 series consisted of two specifications, 18001 provided
requirements for an OHS management system and 18002 gave
implementation guidelines.
OHSAS 18001 certification need to migrate to ISO 45001 to maintain
the validity of the certification.
ISO 45001 is expected to be published in February 2018.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/managementsystemsintegration-ims-170719220334/85/Management-systems-integration-ims-14-320.jpg)









