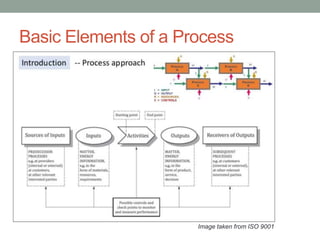
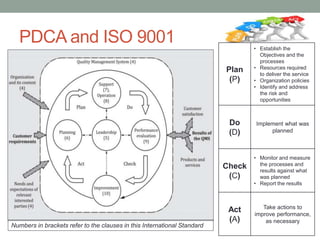
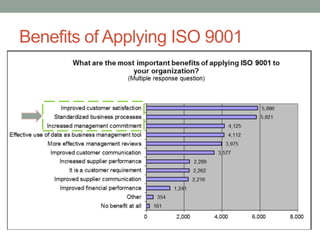
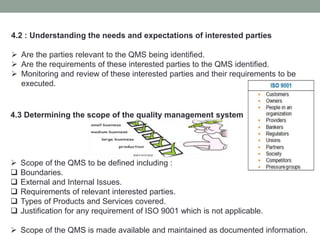
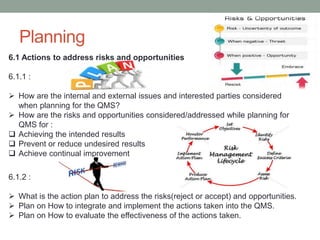
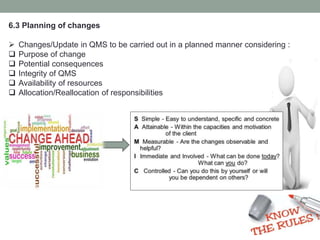
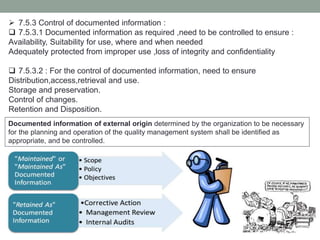
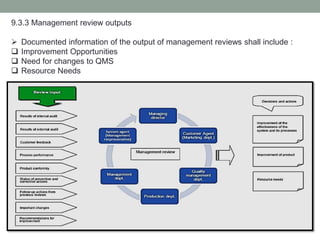
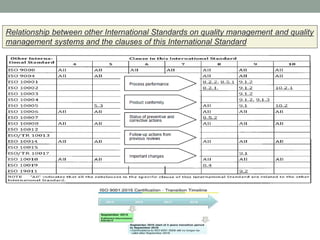
This document provides an overview of ISO 9001:2015 quality management system standard. It discusses the key principles such as customer focus, leadership, process approach, and continual improvement. The main clauses of ISO 9001:2015 are summarized, including context of the organization, leadership, planning, support, operation, performance evaluation, and improvement. Planning addresses risk management, quality objectives, and managing changes. Support covers resources, competence, awareness, communication, and documented information. The document emphasizes that ISO 9001 employs the PDCA cycle and risk-based thinking for continual improvement of processes and meeting customer requirements.