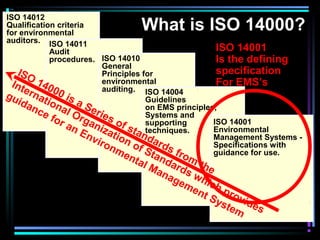
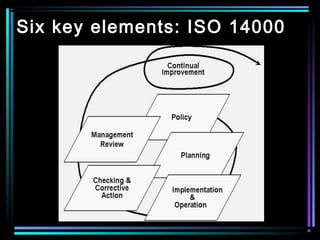
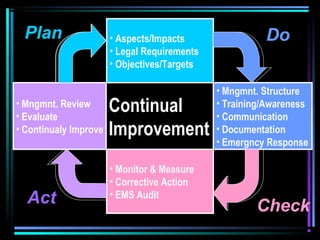
This document provides an overview of ISO 14000, which is a series of international standards for environmental management systems (EMS). It describes the key elements of an EMS according to ISO 14000, including establishing environmental aspects and impacts, legal requirements, objectives and targets, management structure and responsibilities, training, communication, documentation, monitoring, corrective action, audits, and management review to facilitate continual improvement. The goals of ISO 14000 and implementing an EMS are to minimize negative environmental impacts, comply with regulations, and improve environmental performance.