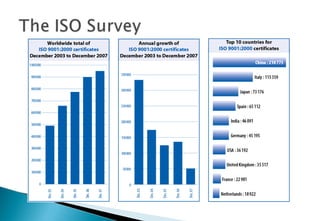
This document provides an overview of ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 standards for quality and environmental management systems. It discusses that ISO 9001 helps organizations implement quality management to satisfy customer requirements, while ISO 14001 helps with environmental management to minimize environmental impacts and improve performance. Both standards can be applied to any size or type of organization and provide a framework for managing key processes.