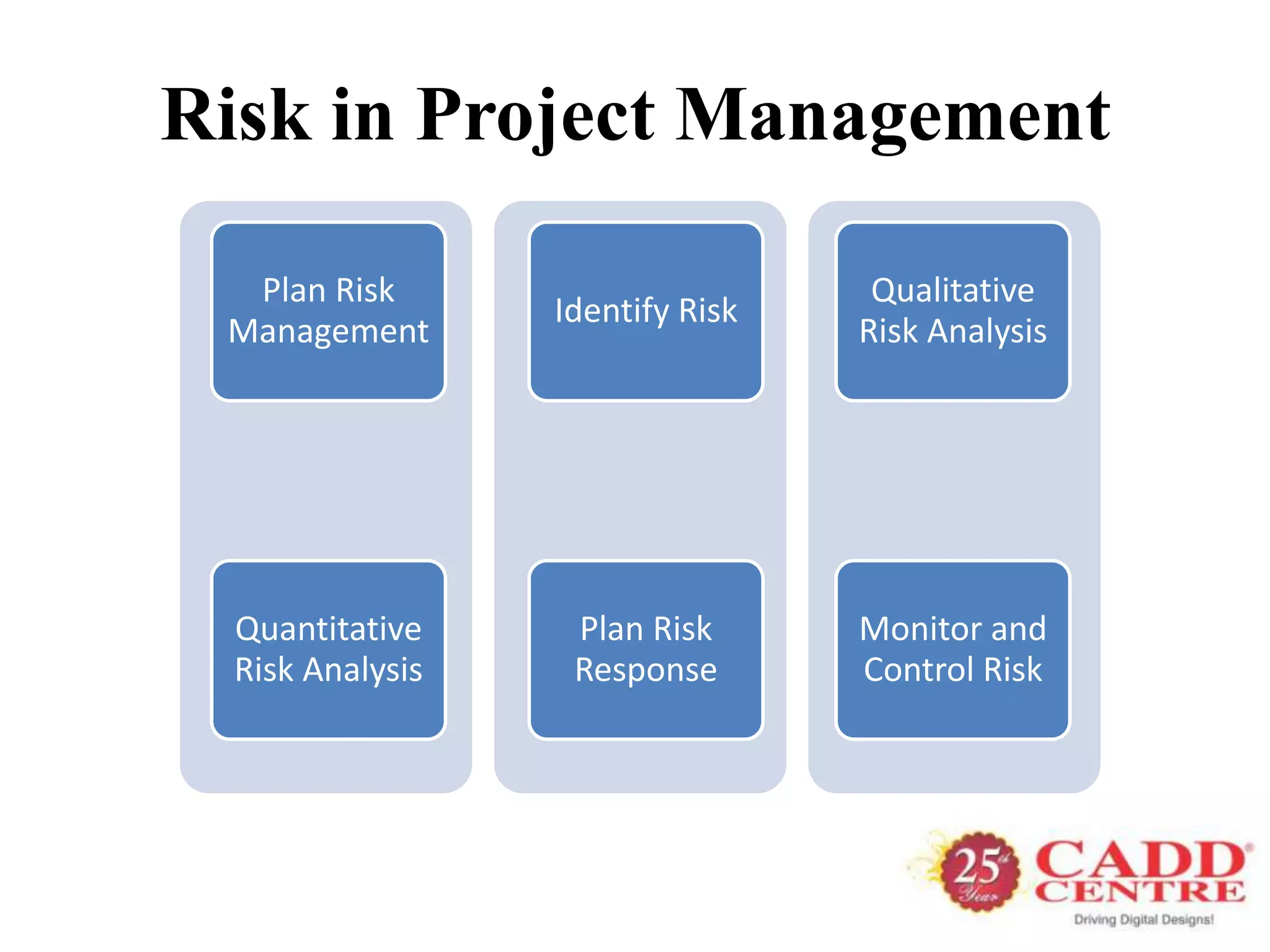
Risk management is the process of identifying and mitigating risks that may have a positive or negative impact on a project. It includes risk management planning, identification, analysis, response planning, and monitoring and control. Analyzing risks qualitatively and quantitatively helps prioritize them so appropriate responses can be developed, such as avoiding, transferring, mitigating, or accepting risks. Monitoring risks ensures new risks are identified and risk responses remain effective over the project lifecycle. The benefits of effective risk management include more efficient resource use, continuous improvement, fewer failures, and enhanced communication and accountability.