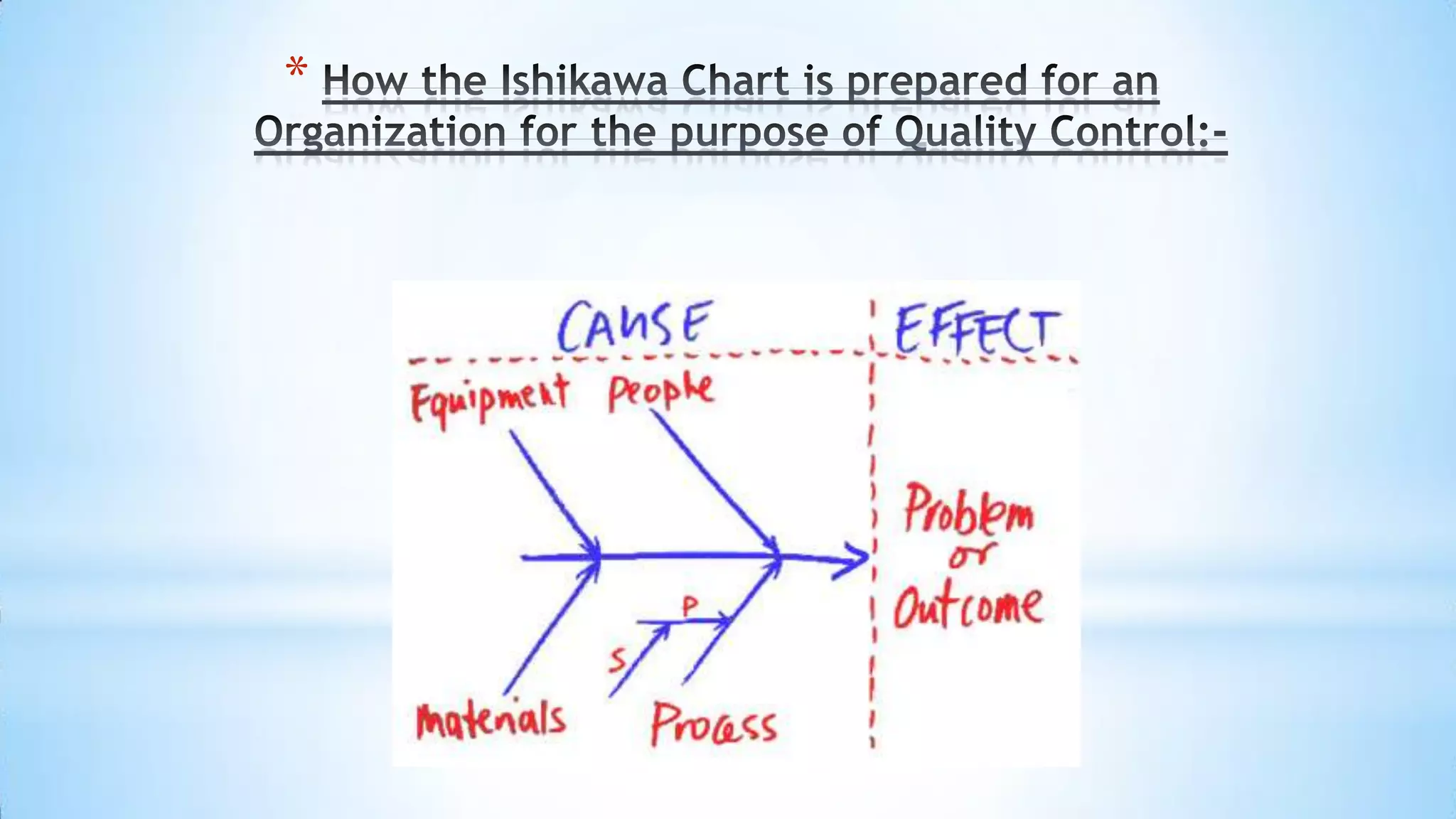
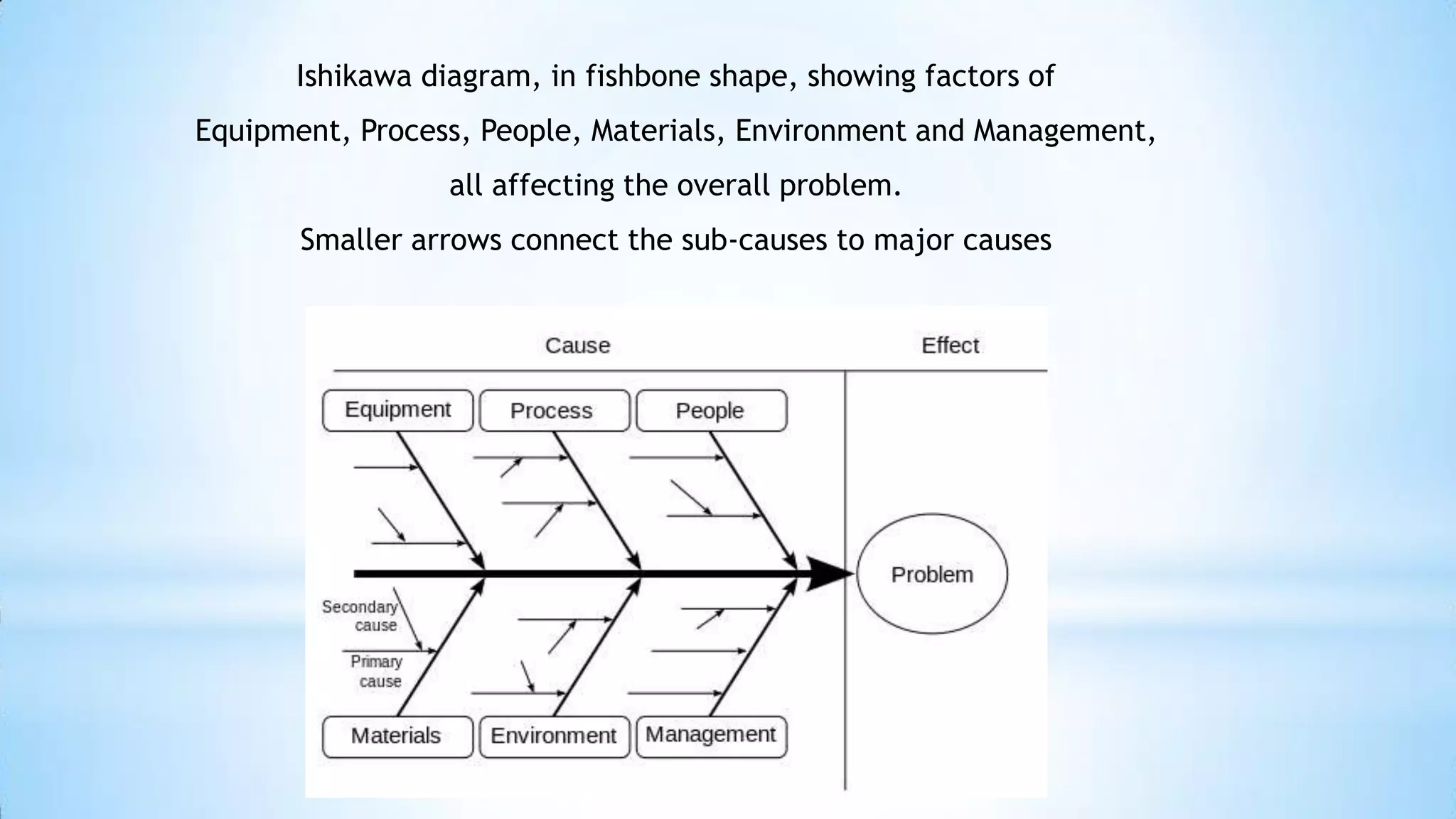
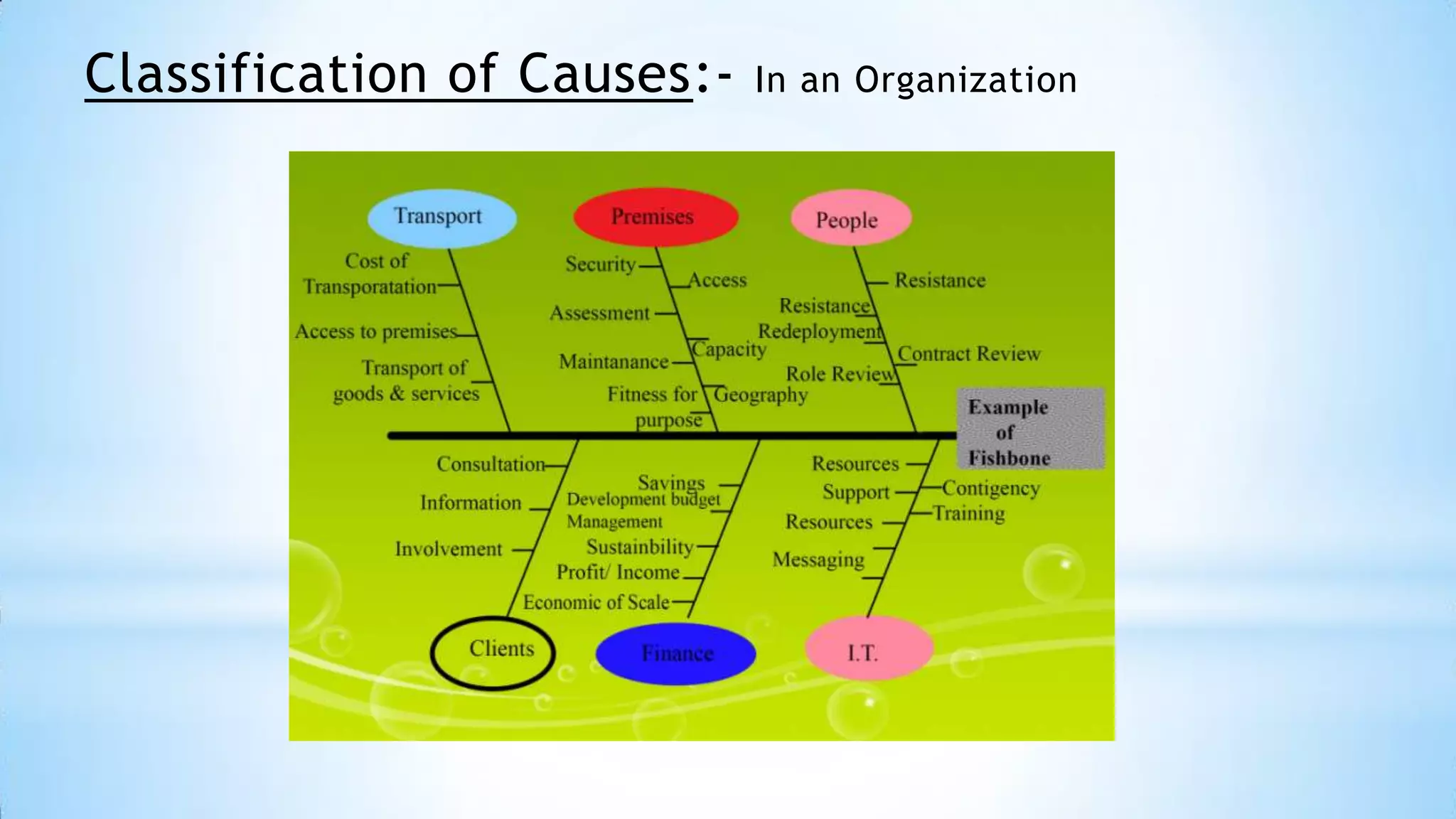
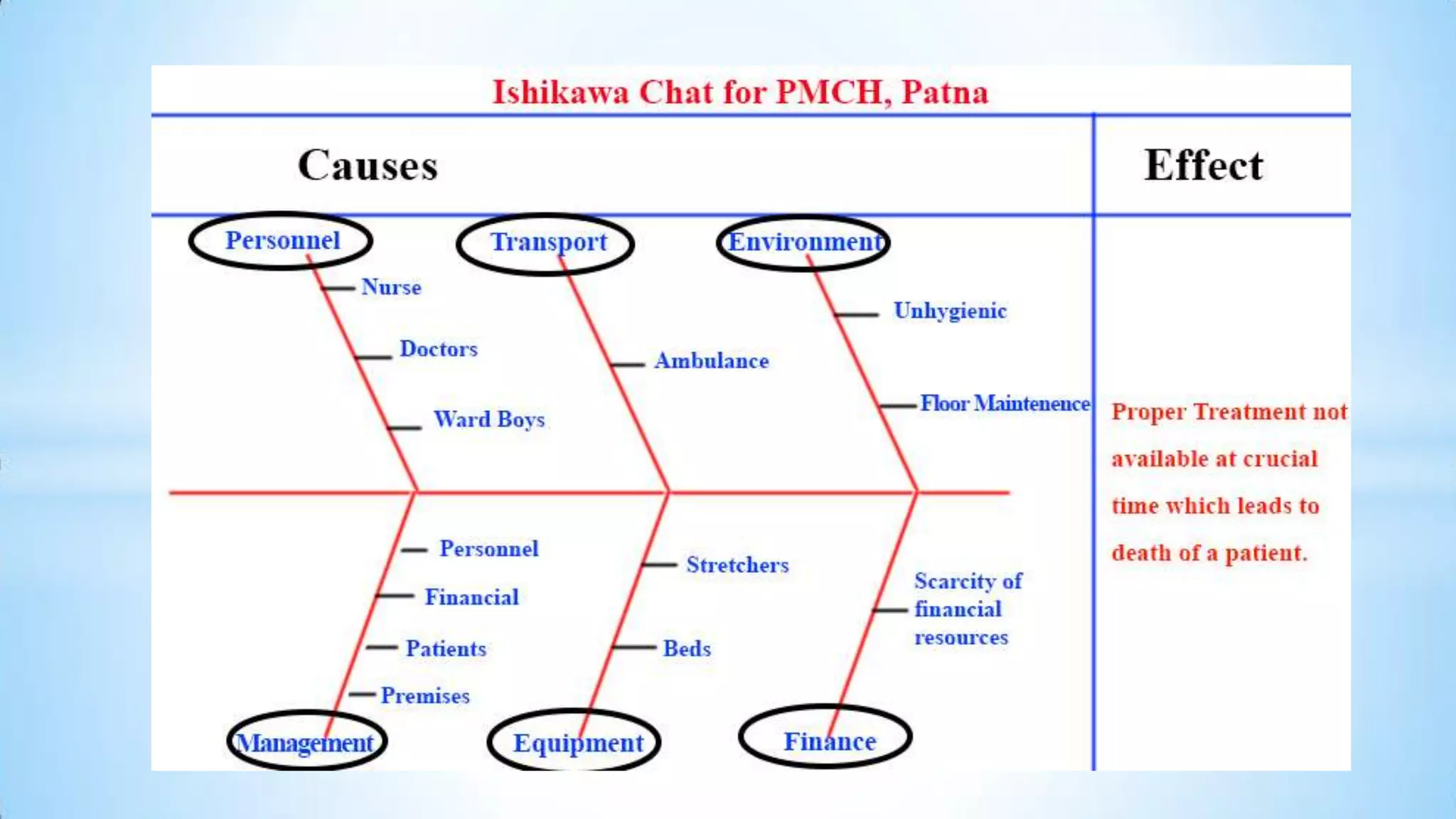
This document provides information about an Ishikawa diagram or fishbone diagram tool. It includes the steps to create an Ishikawa diagram, examples of typical categories used in the diagram, and different classification frameworks that can be used such as the 6Ms, 7Ps, and 5Ss. It also provides context that the tool was created by Kaoru Ishikawa in 1968 to help systematically identify and present all possible causes of a problem.