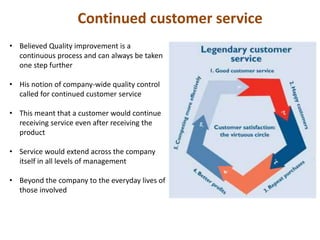
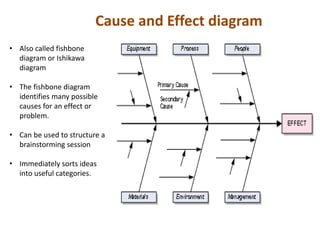
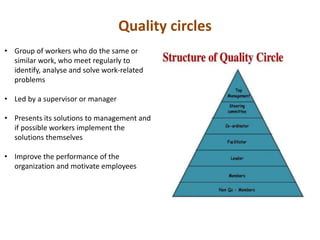
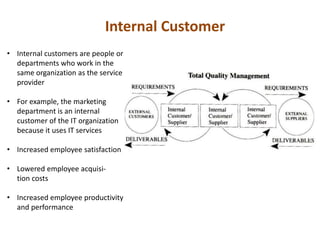
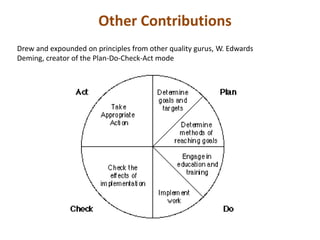
Dr. Kaoru Ishikawa was a Japanese quality control expert born in 1915 who made significant contributions to quality management. He joined the Japanese Union of Scientists and Engineers quality control research group in 1949 and helped drive Japan's quality improvement initiatives through mobilizing large groups. Ishikawa translated and expanded the management concepts of W. Edwards Deming and Joseph M. Juran, introducing tools like the cause-and-effect diagram, quality circles, and a focus on continuous improvement and internal/external customers. He died in 1989 after making Japan a leader in quality management.