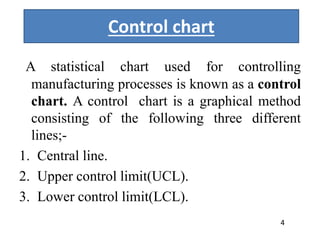
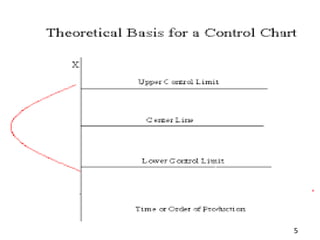
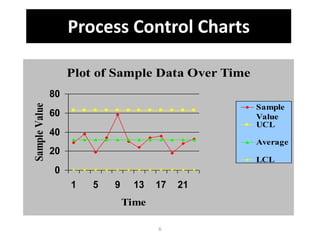
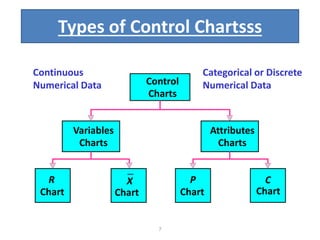
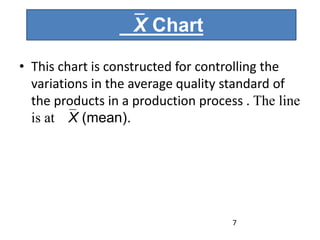
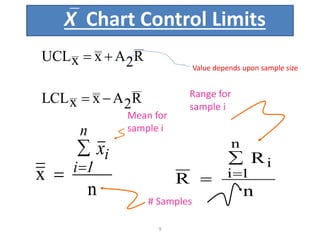
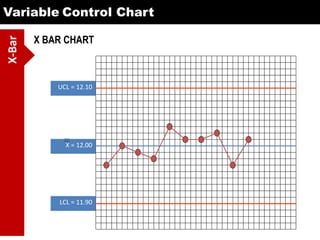
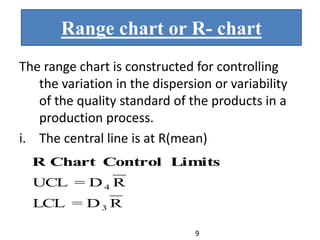
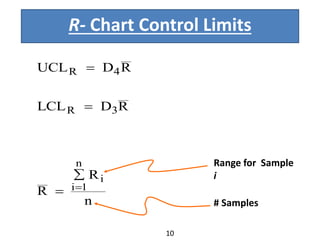
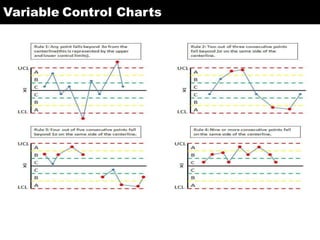
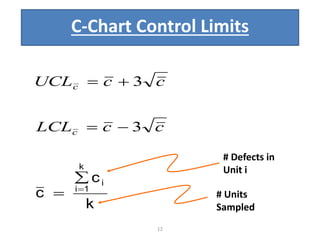
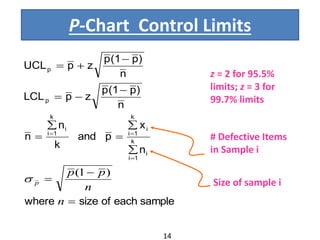
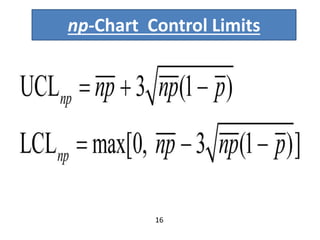
This document discusses various statistical quality control charts used to monitor manufacturing processes, including control charts, X-bar charts, R-charts, C-charts, P-charts, and NP-charts. A control chart is a graphical display that consists of a central line for the average and upper and lower control limits. X-bar and R-charts are used for continuous numerical data to control variations in average quality and dispersion. C-charts monitor the number of defects per unit while P-charts control the fraction defective. NP-charts simplify P-charts by plotting the number of defectives rather than the fraction. These statistical charts help maintain and improve quality throughout production.