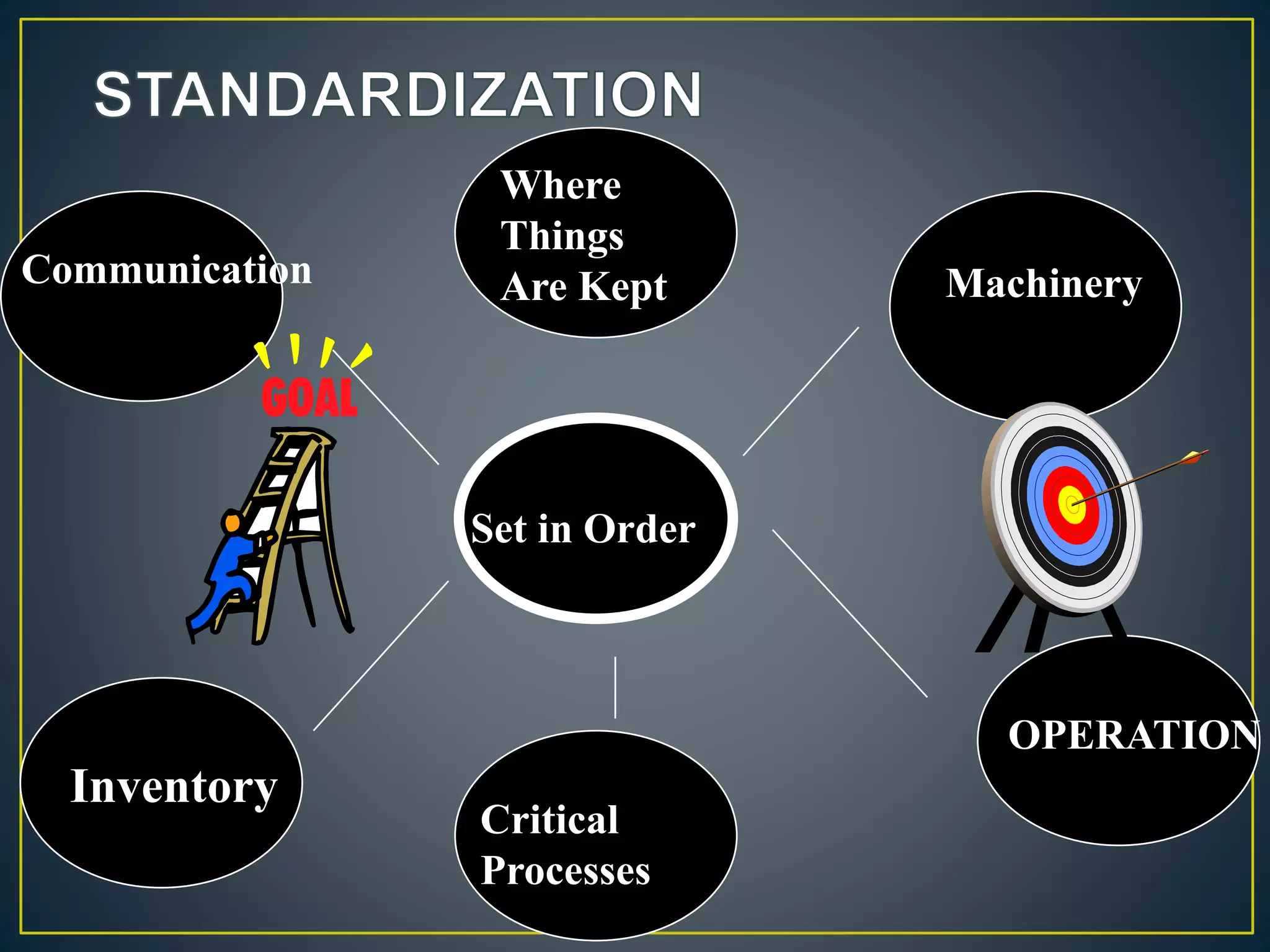
The document discusses 5S principles and the 8 disciplines of problem solving. 5S principles were developed in Japan and include Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain to create a better working environment and consistently high quality processes. The 8 disciplines of problem solving include Plan, Use a Team, Define the Problem, Develop Interim Containment, Determine Root Causes, Choose Permanent Corrections, Implement Corrective Actions, and Take Preventive Measures to identify, correct, and eliminate recurring problems following the PDCA cycle. Both methods aim to improve processes, productivity, and quality.