This document discusses different types of measurement scales used in scaling techniques:
- Nominal scale assigns labels or categories with no order or ranking. Examples include coding gender or subjects.
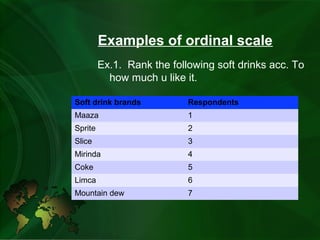
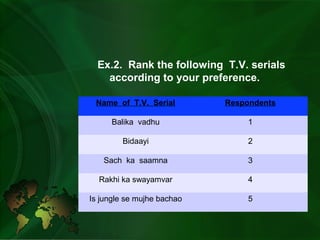
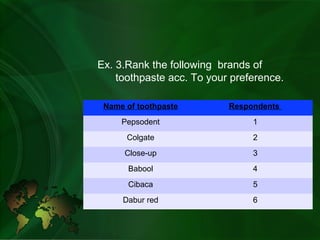
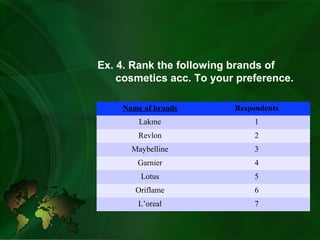
- Ordinal scale ranks items in logical order but does not specify differences between ranks. Examples include ranking preferences.
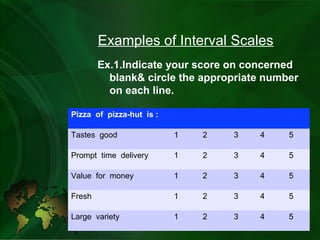
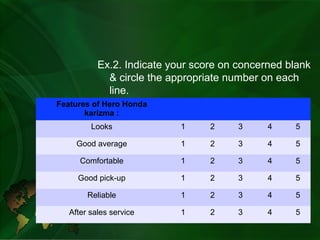
- Interval scale assigns equal intervals between units but with an arbitrary zero point. Examples include scoring attributes on a 1-5 scale.
- Ratio scale has a true absolute zero point and represents actual amounts, allowing for more precise measurements like percentages. Examples include allocating amounts of money.