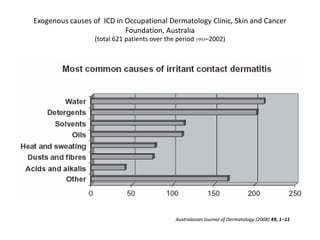
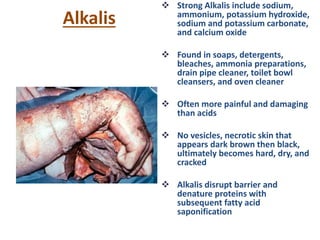
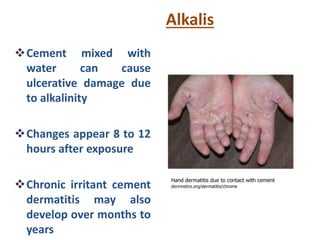
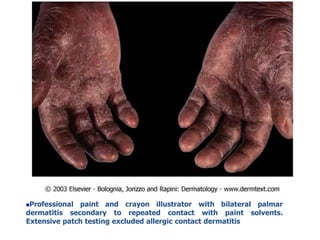
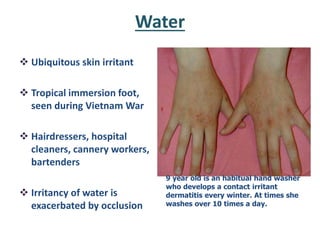
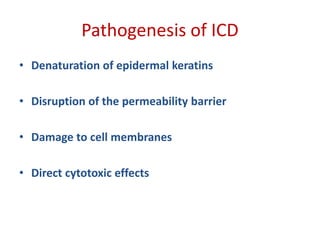
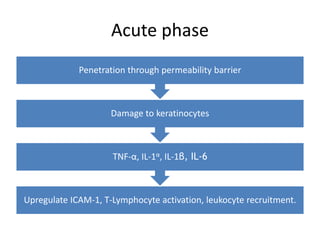
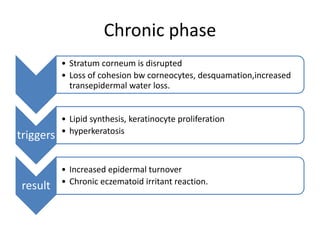
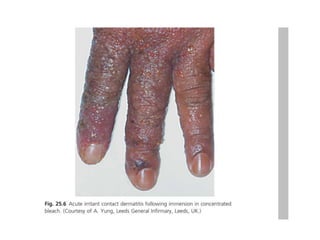
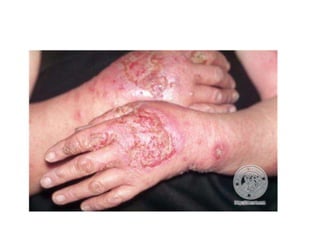
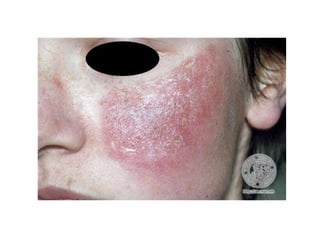
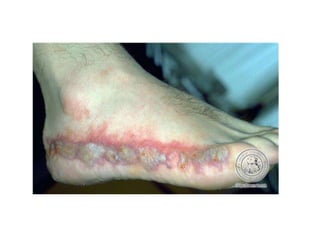
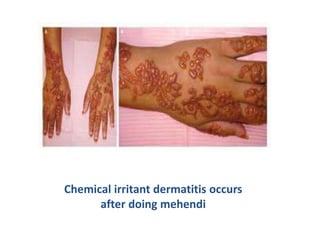
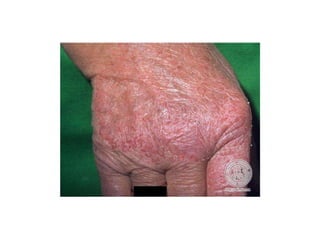
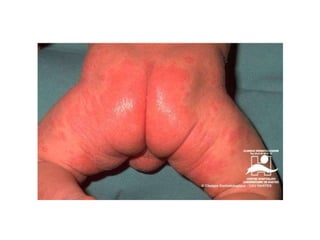
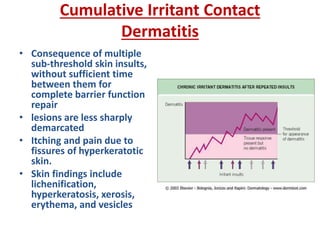
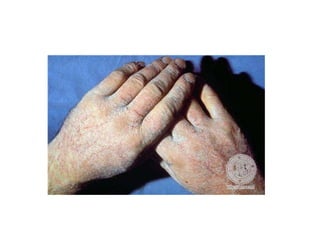
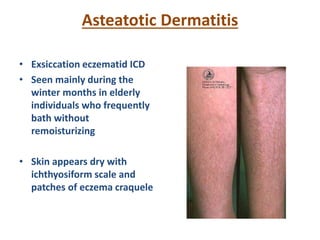
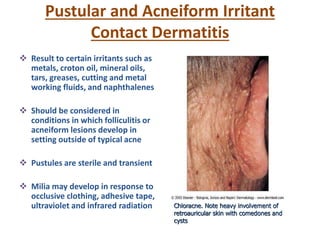
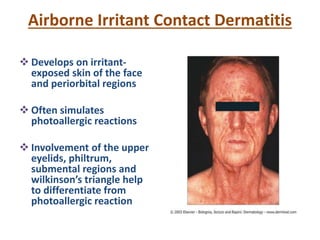
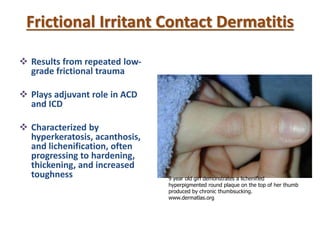
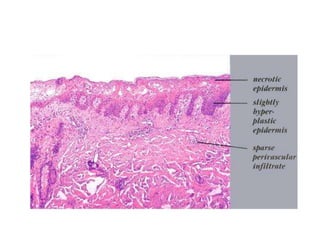
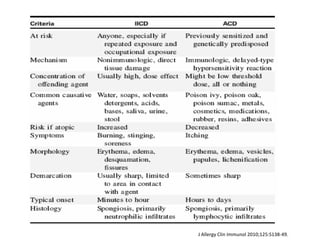
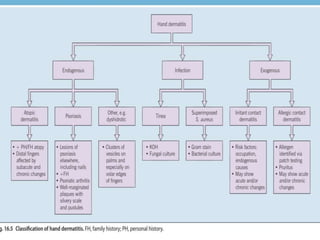
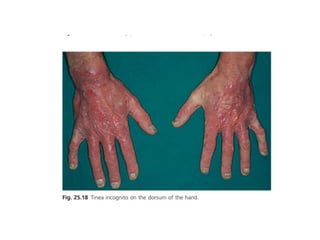
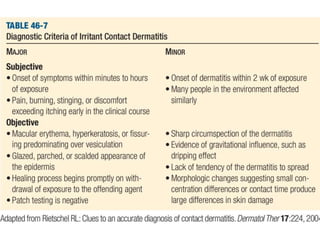
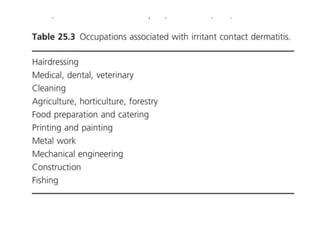
Irritant contact dermatitis (ICD) is caused by direct cytotoxic effects of physical or chemical irritants on the skin. Acute ICD presents with erythema, edema, vesiculation and erosion while chronic ICD shows lichenification, hyperkeratosis and fissures. ICD is commonly caused by occupational exposure to chemicals like acids, alkalis, metals, solvents, detergents and cleansers. Clinical features depend on properties of the irritant, host factors, and environment. Management involves avoiding irritants, using protective measures, and restoring the skin barrier with emollients and moisturizers.