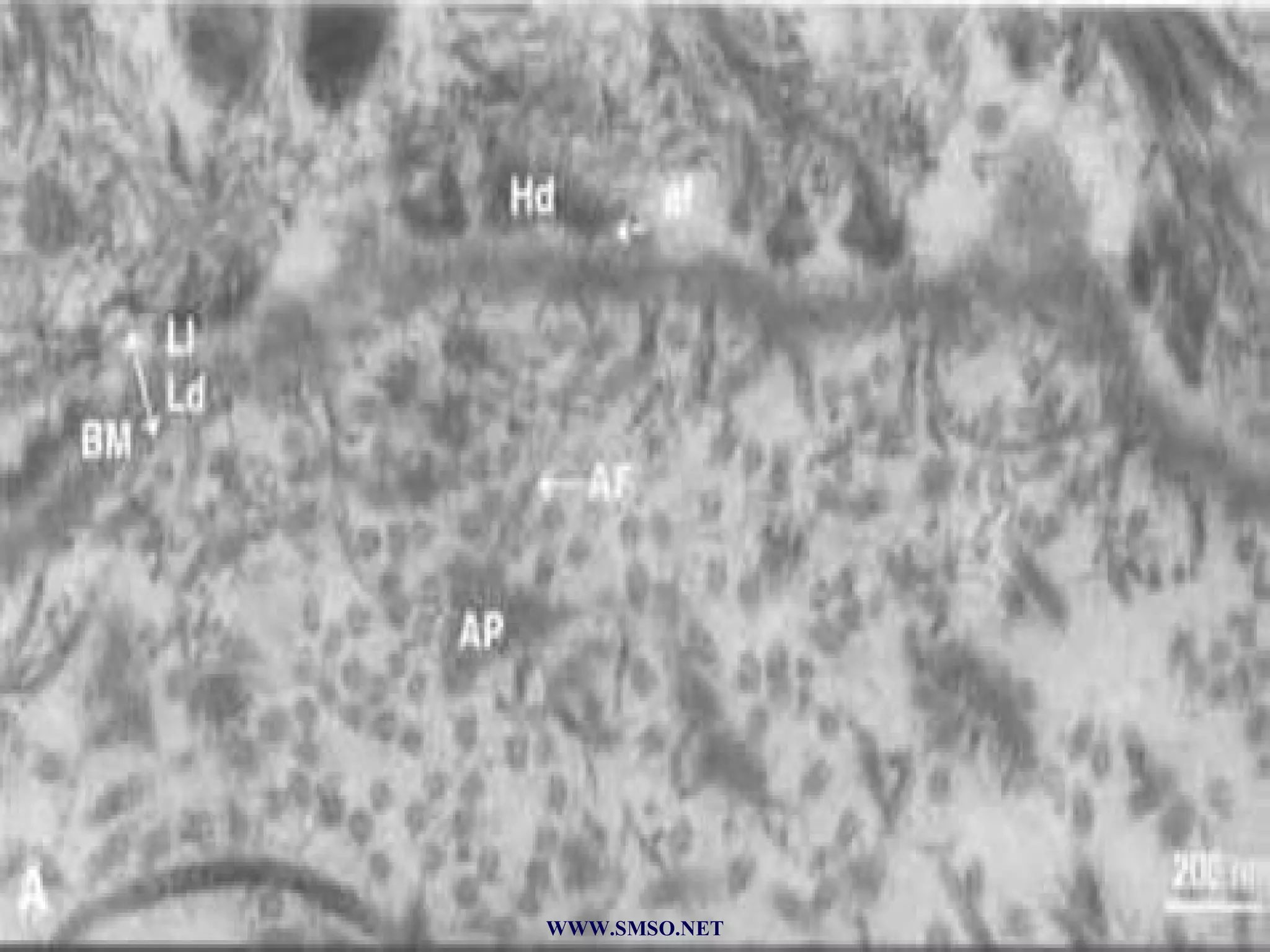
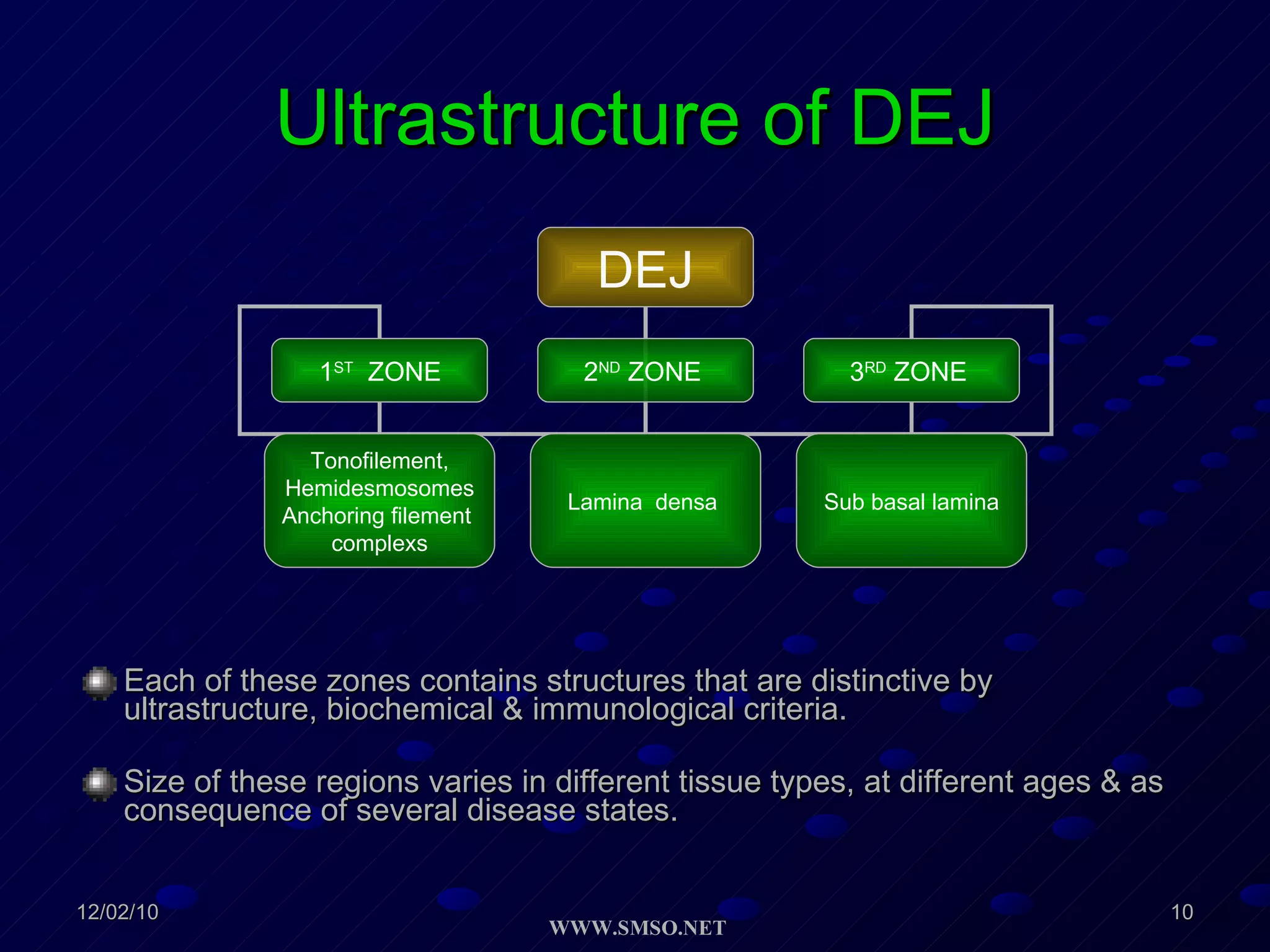
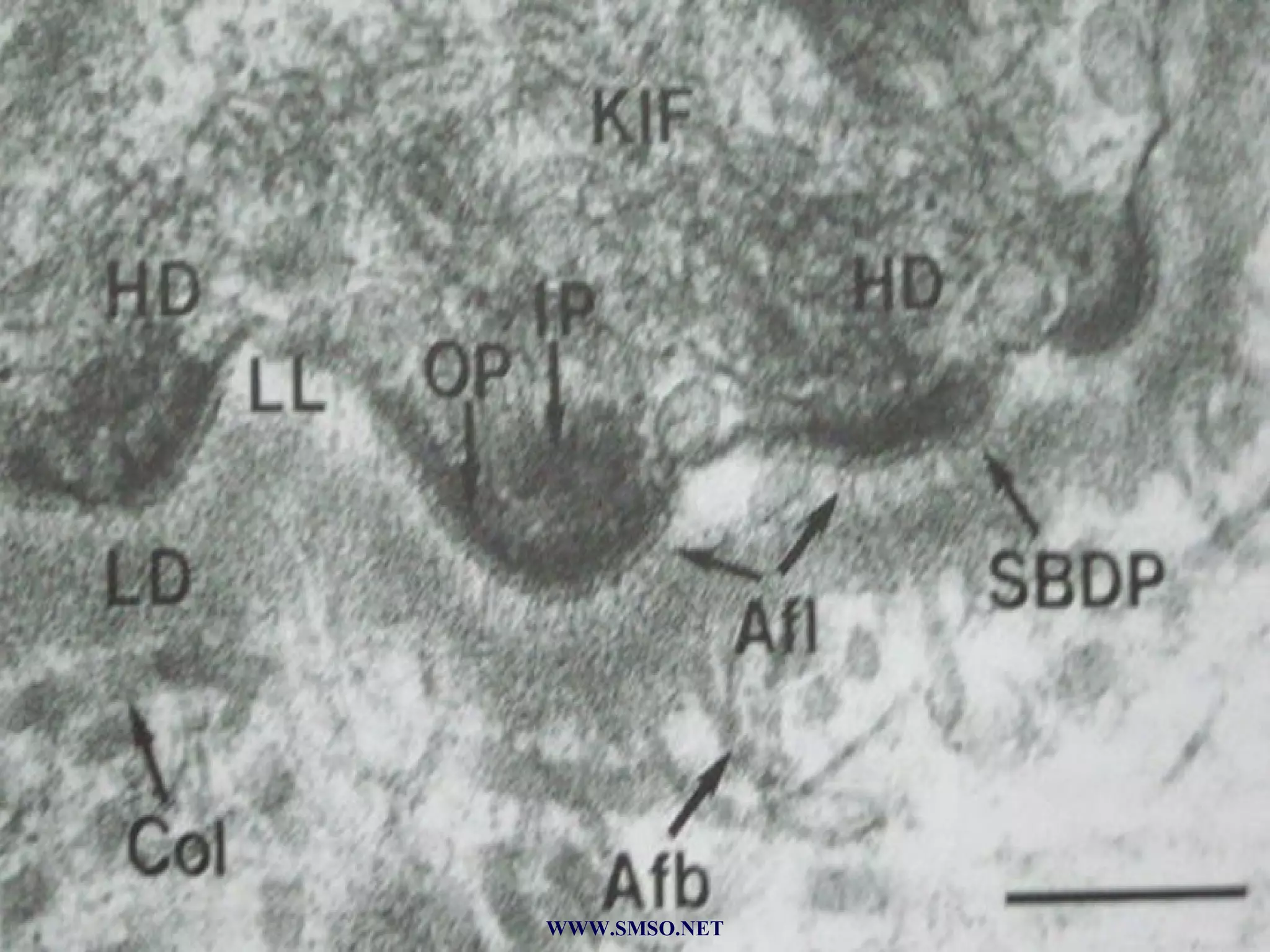
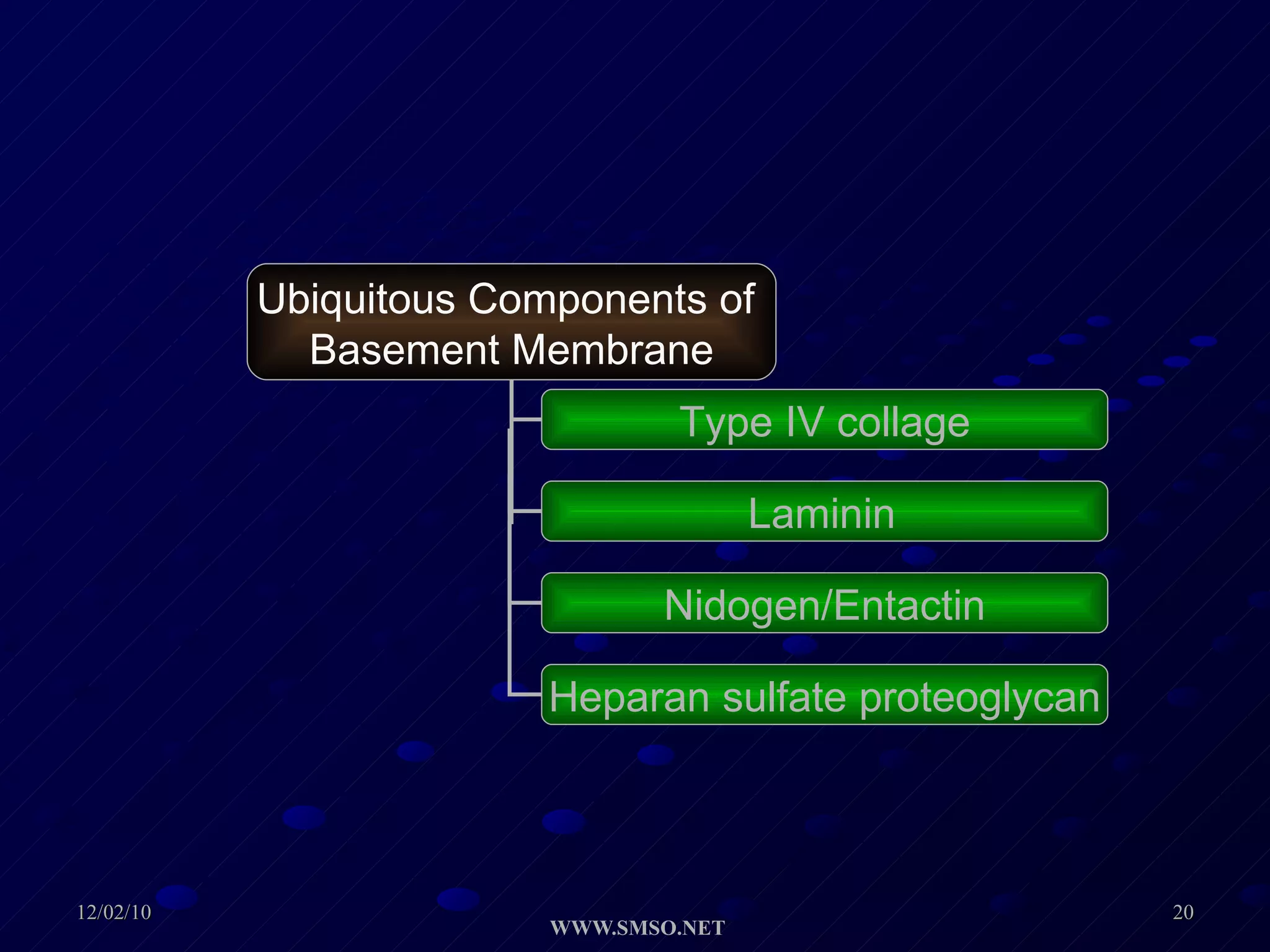
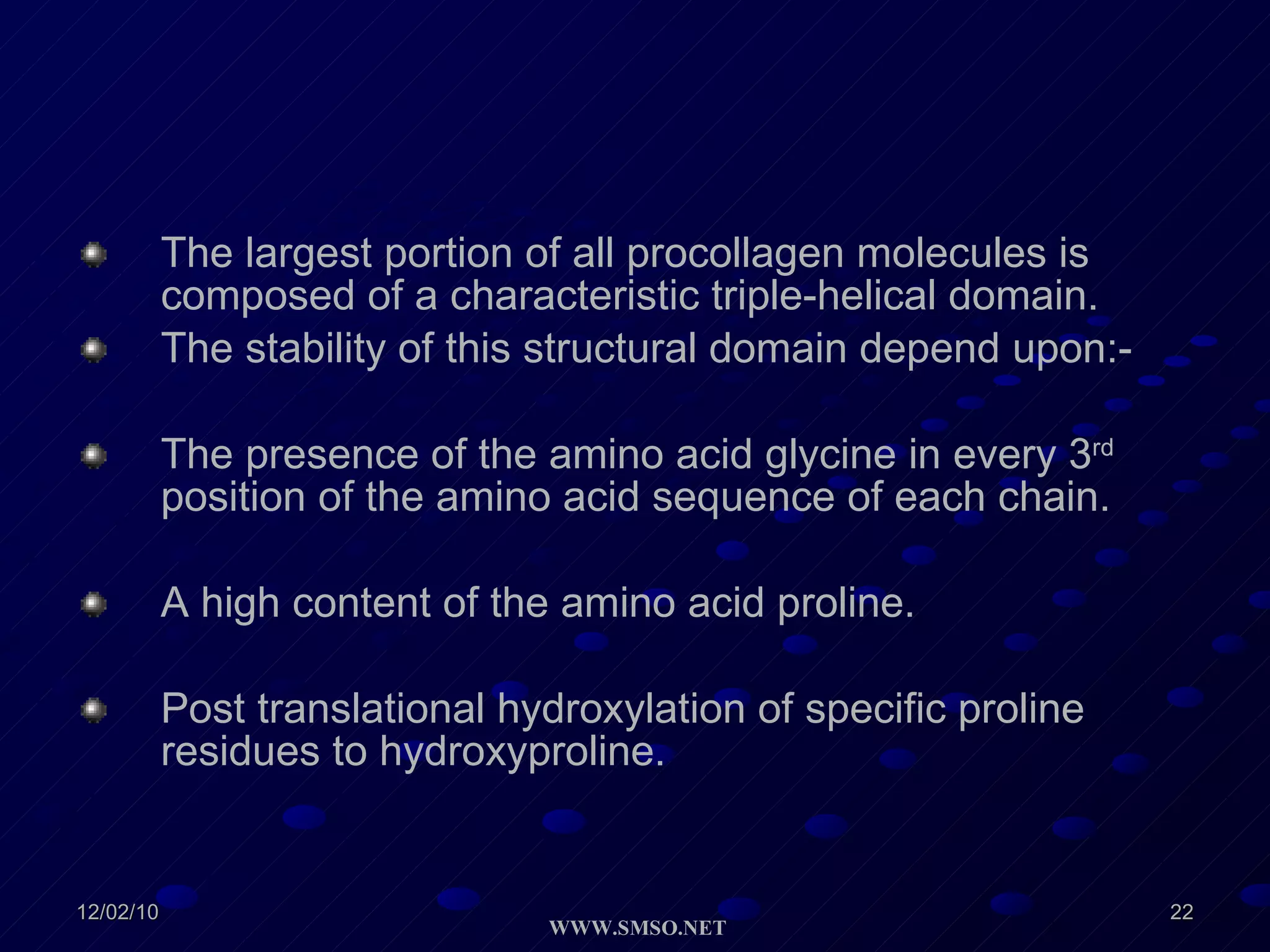
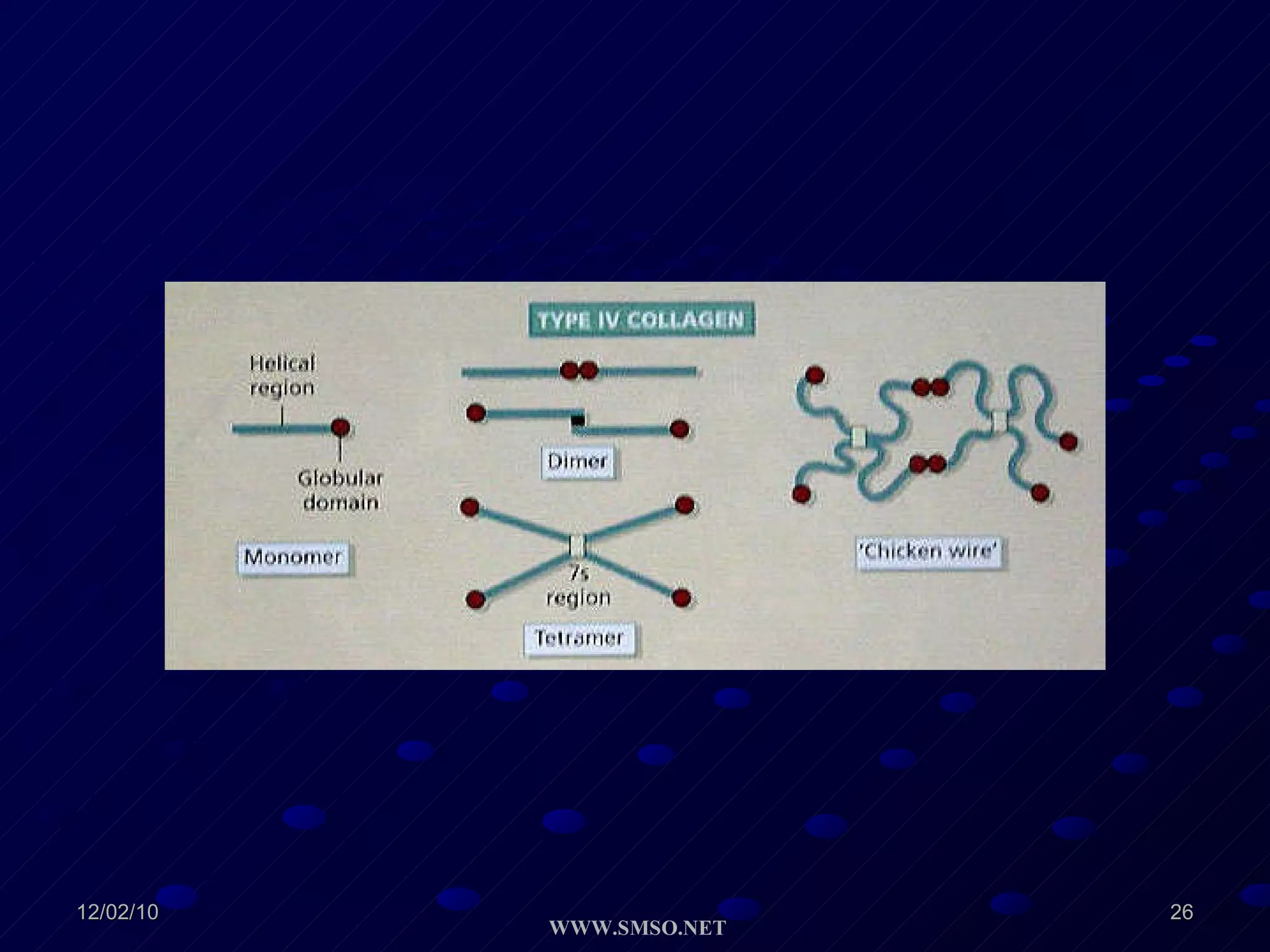
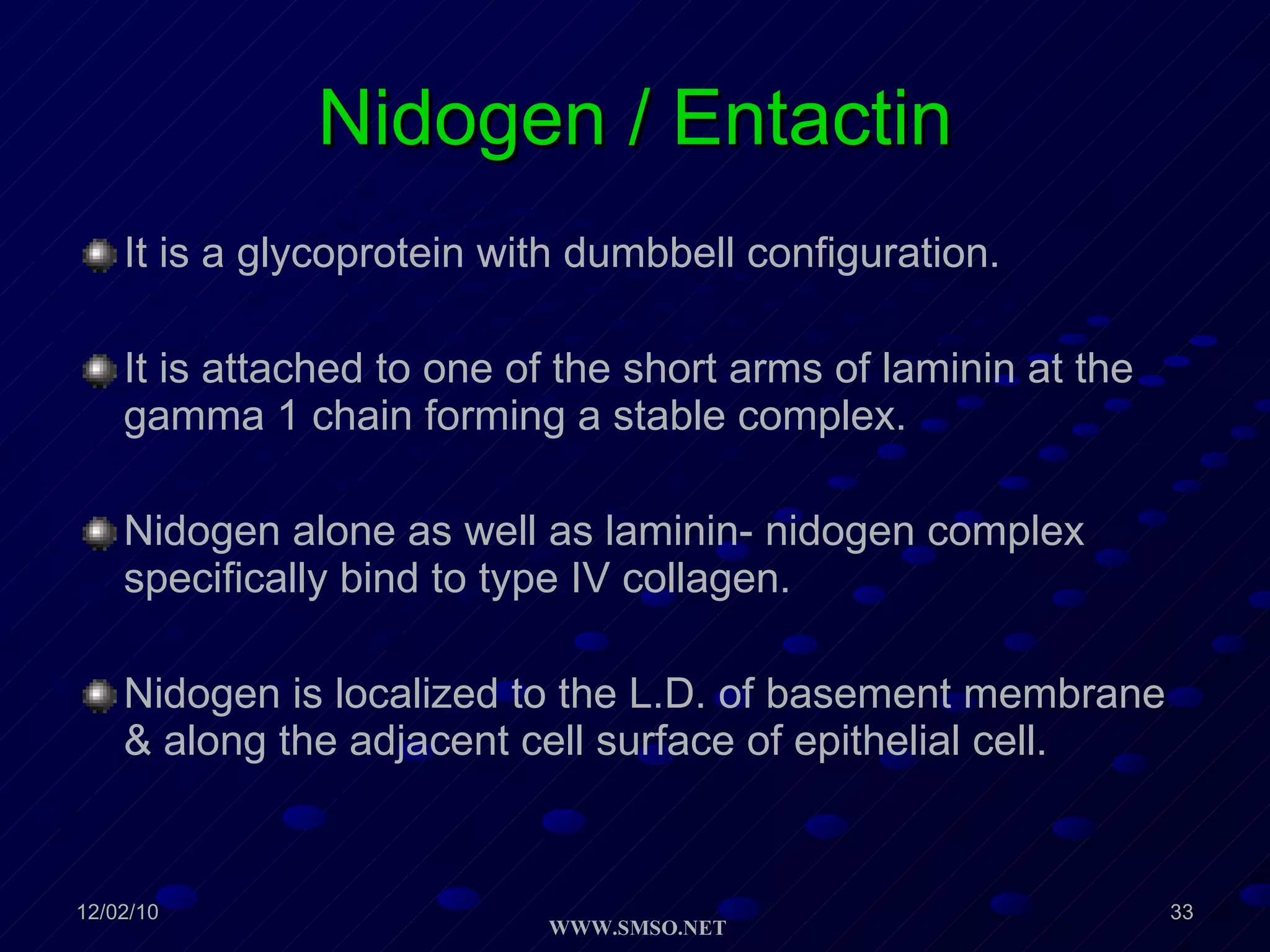
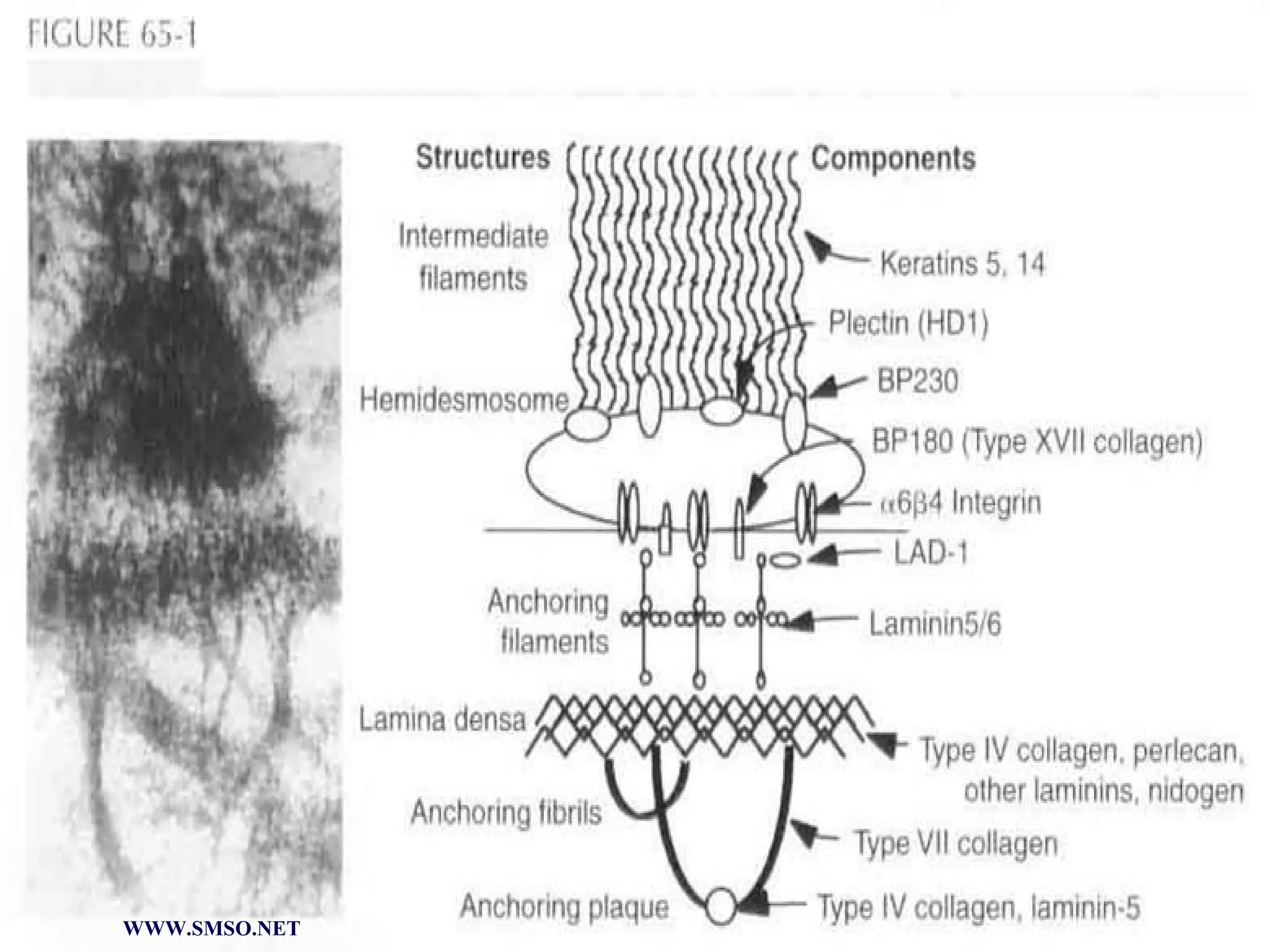
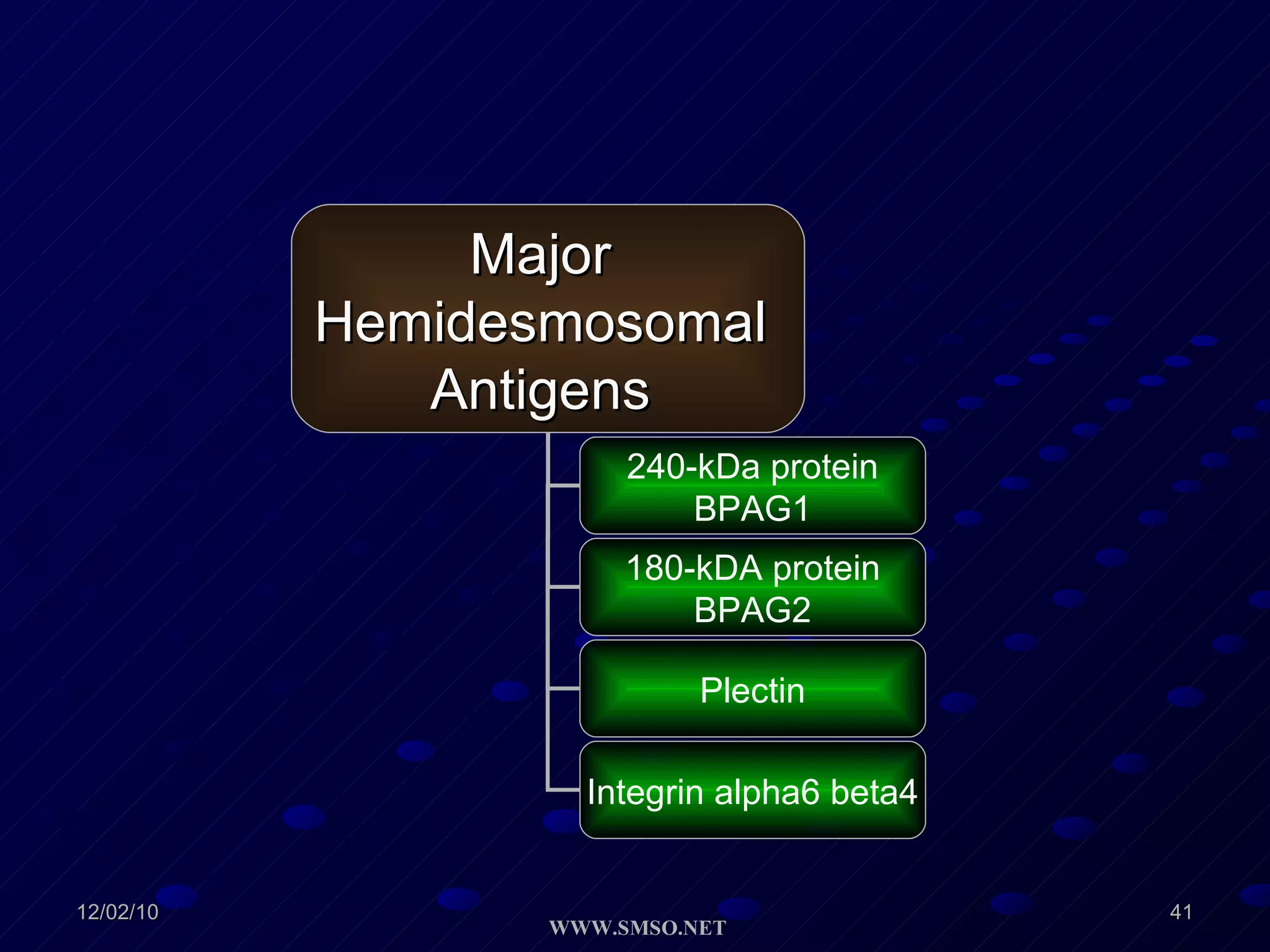
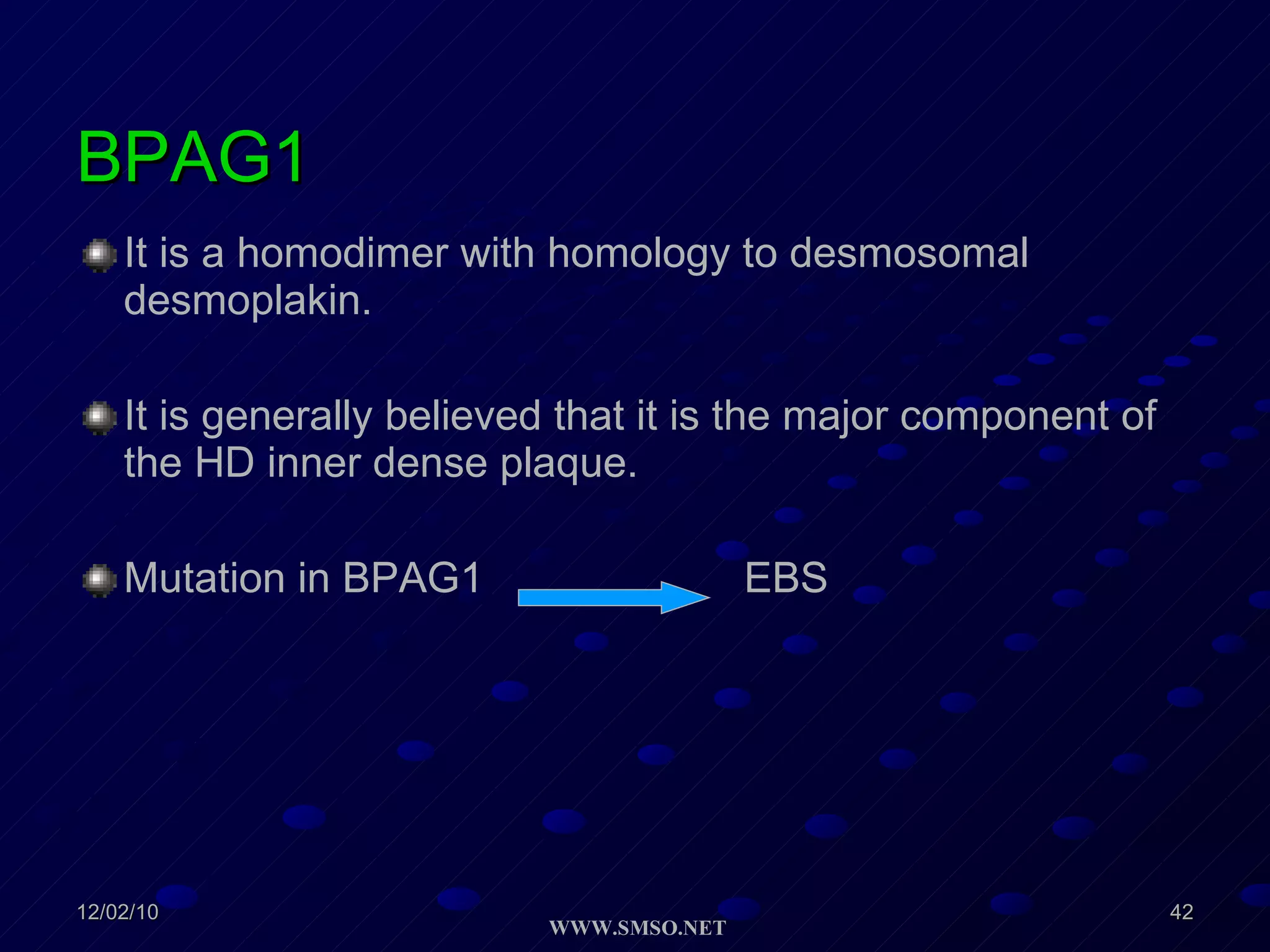
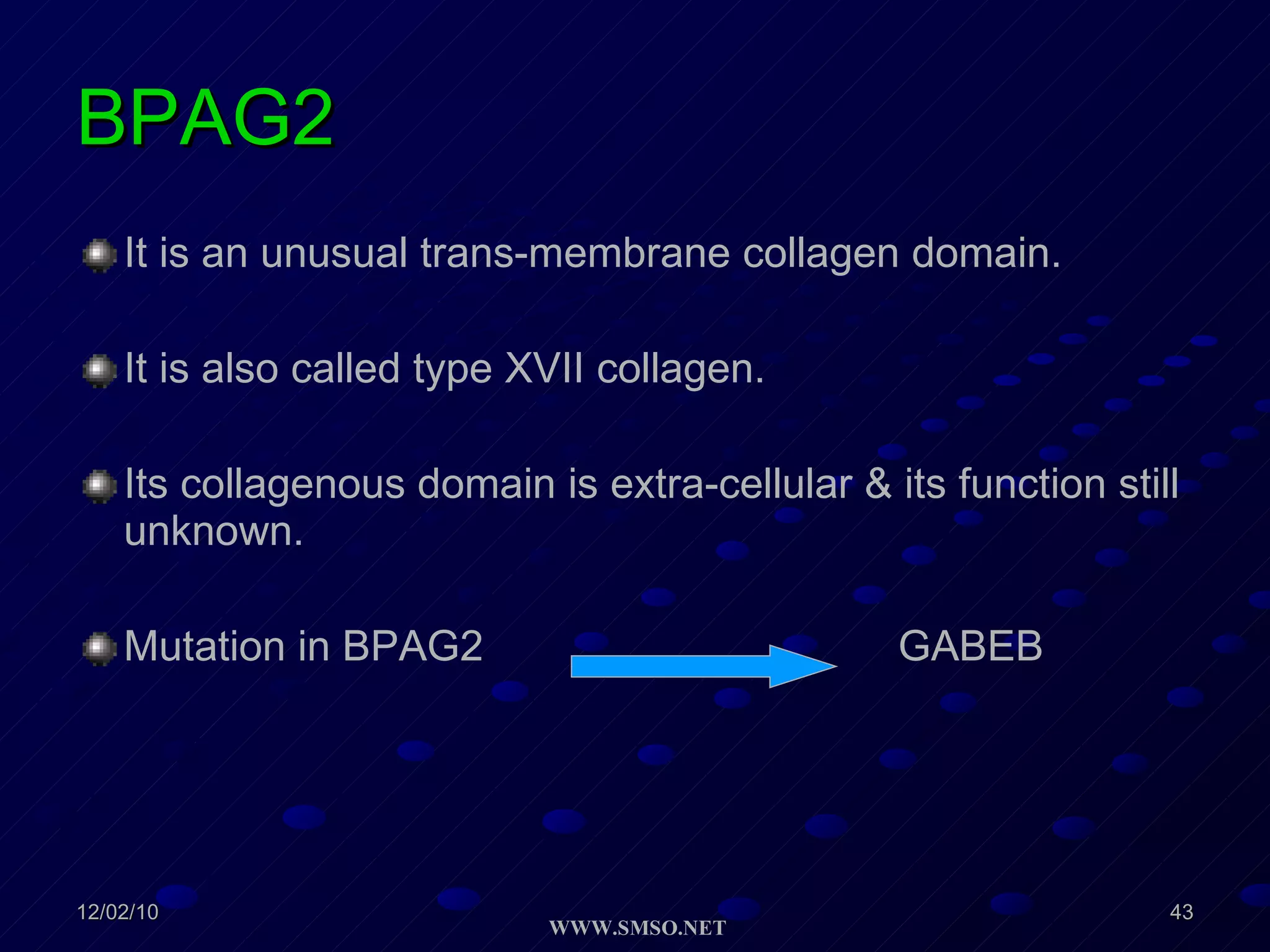
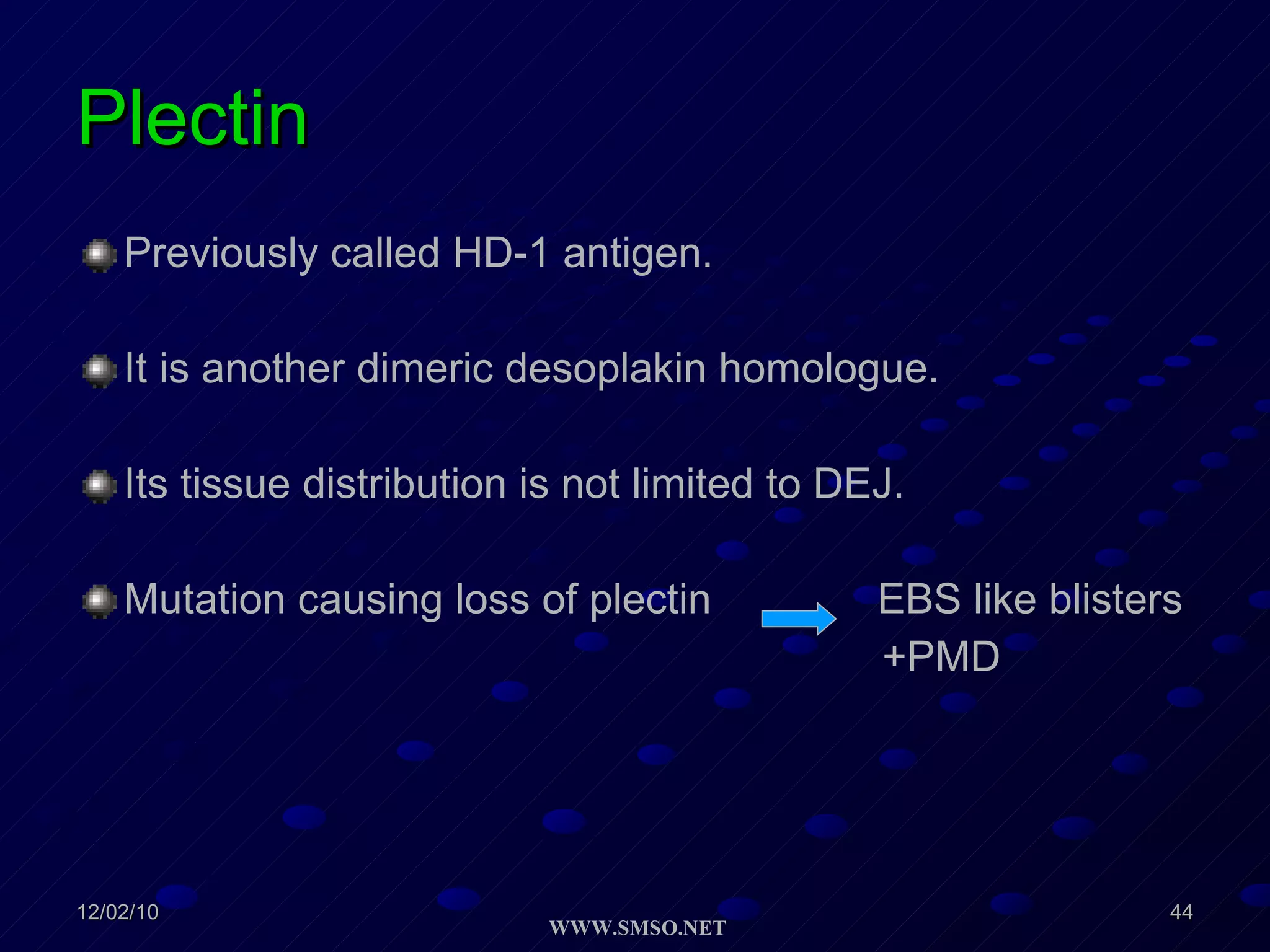
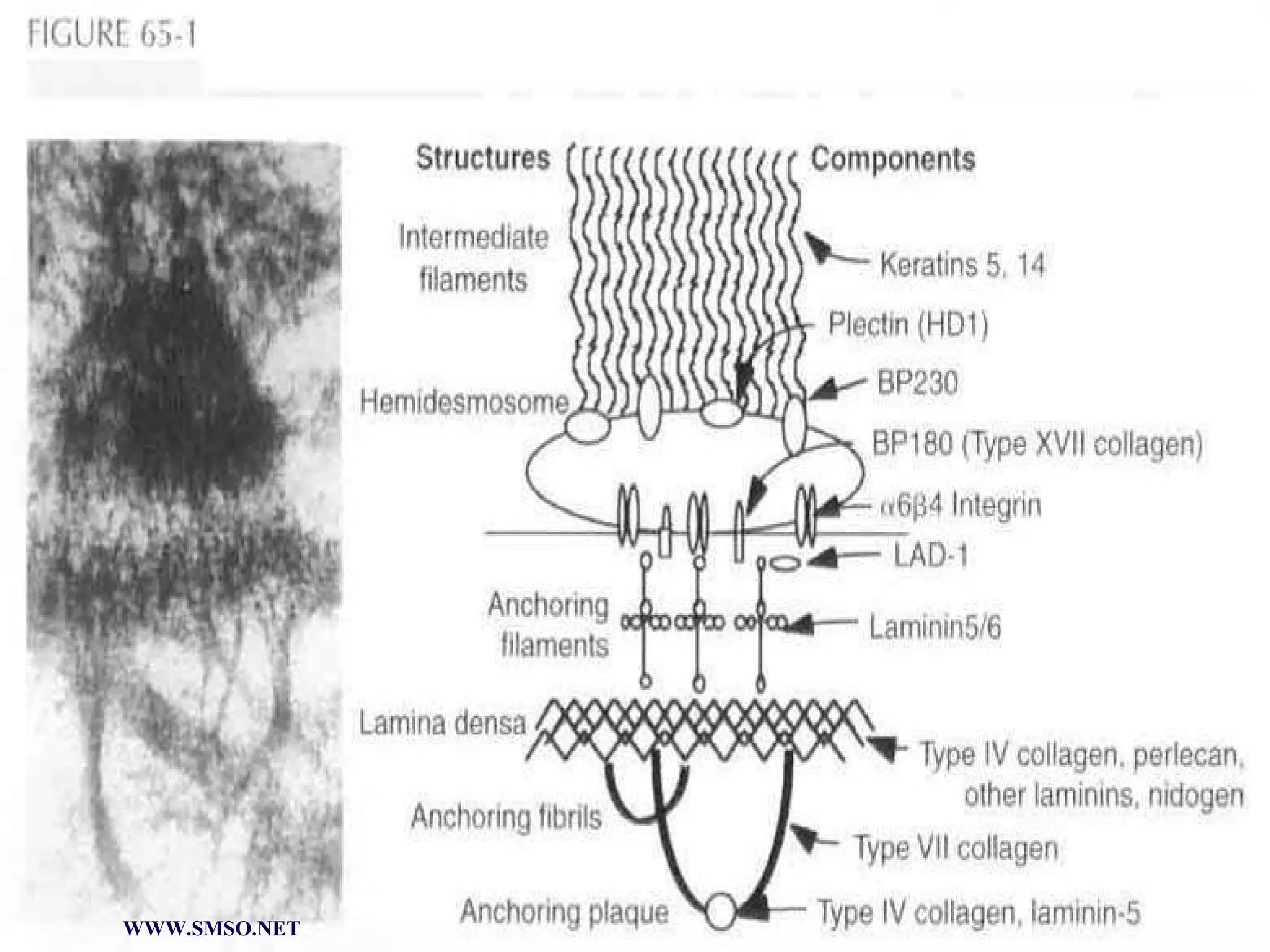
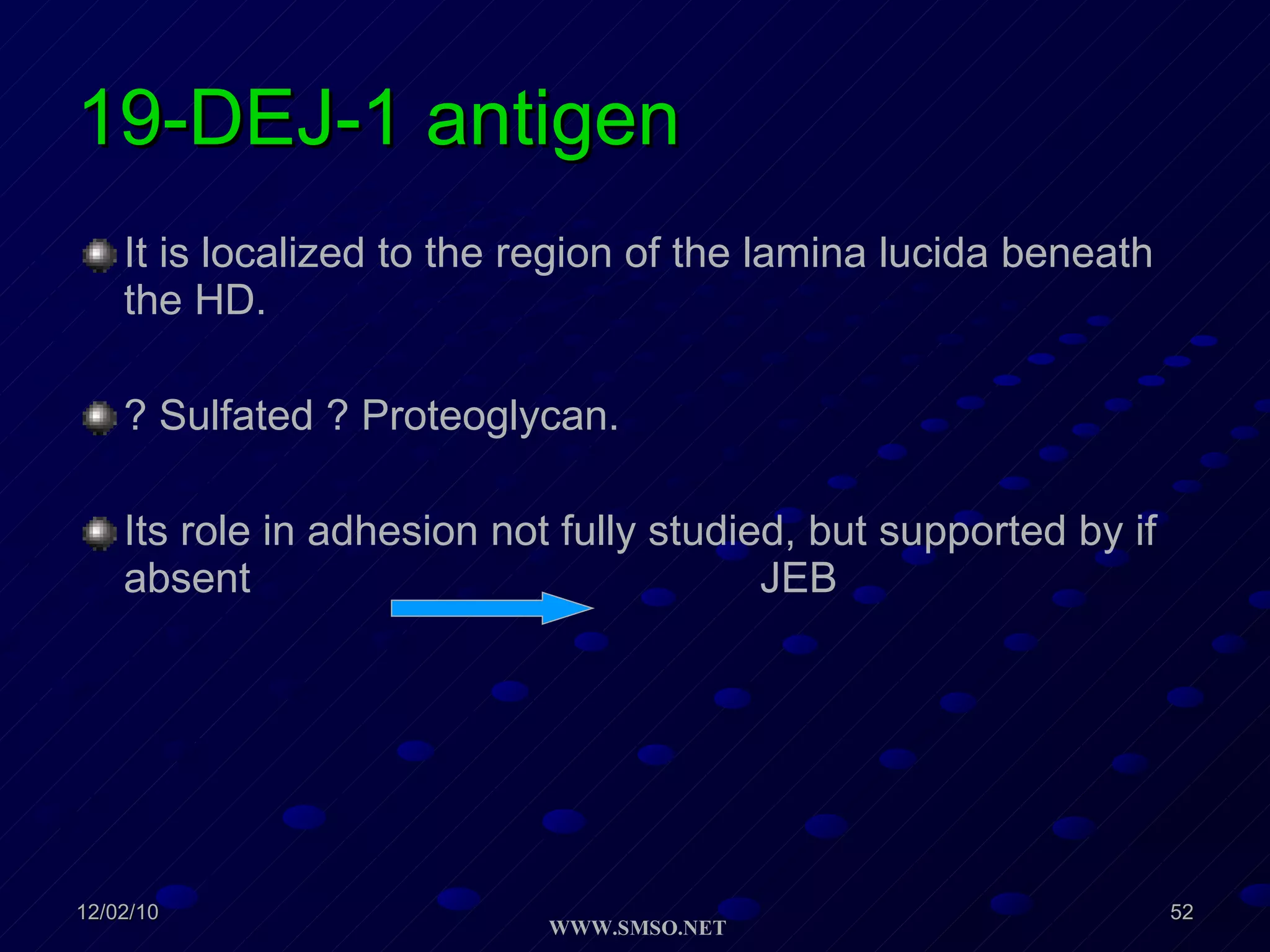
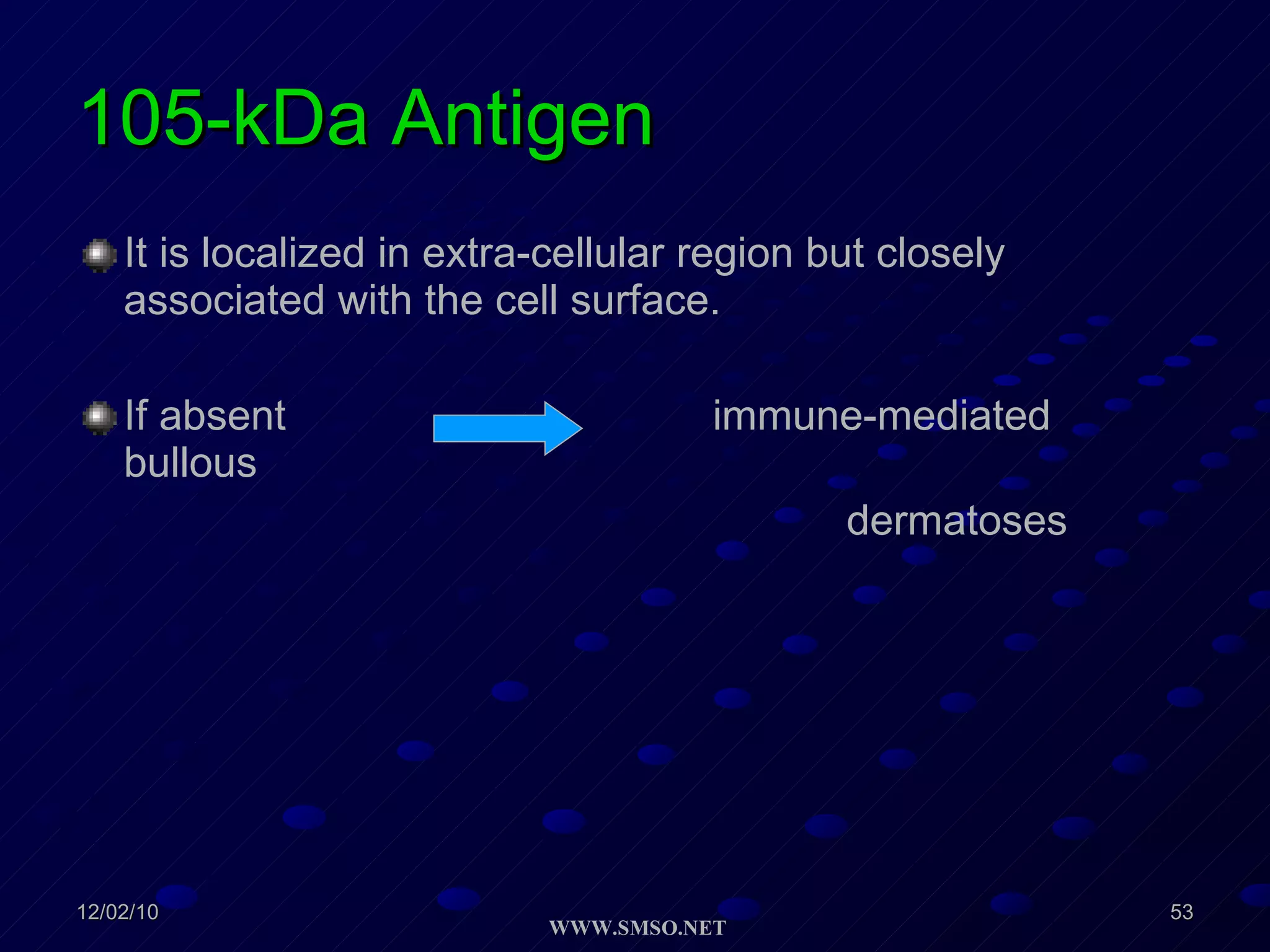
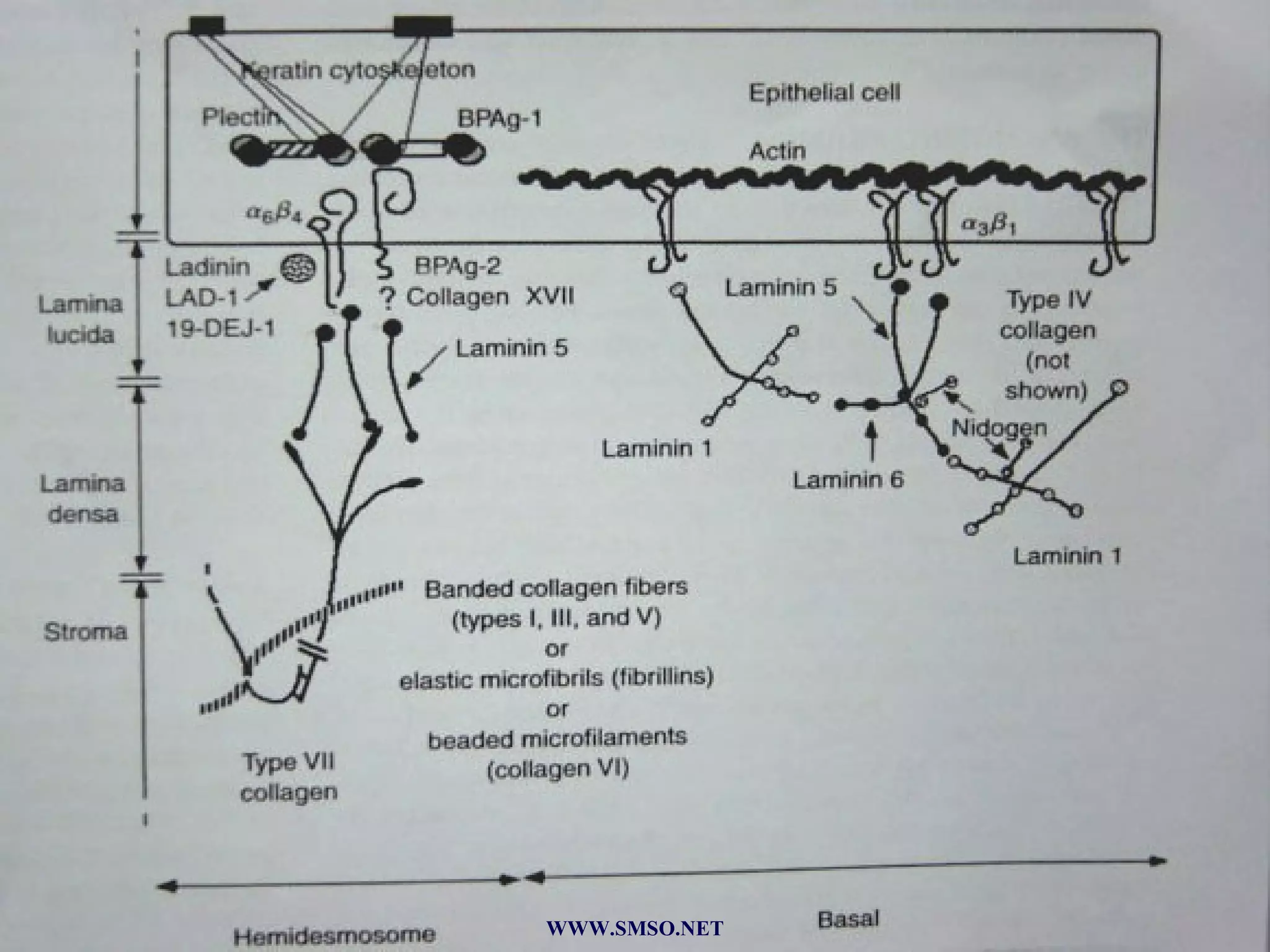
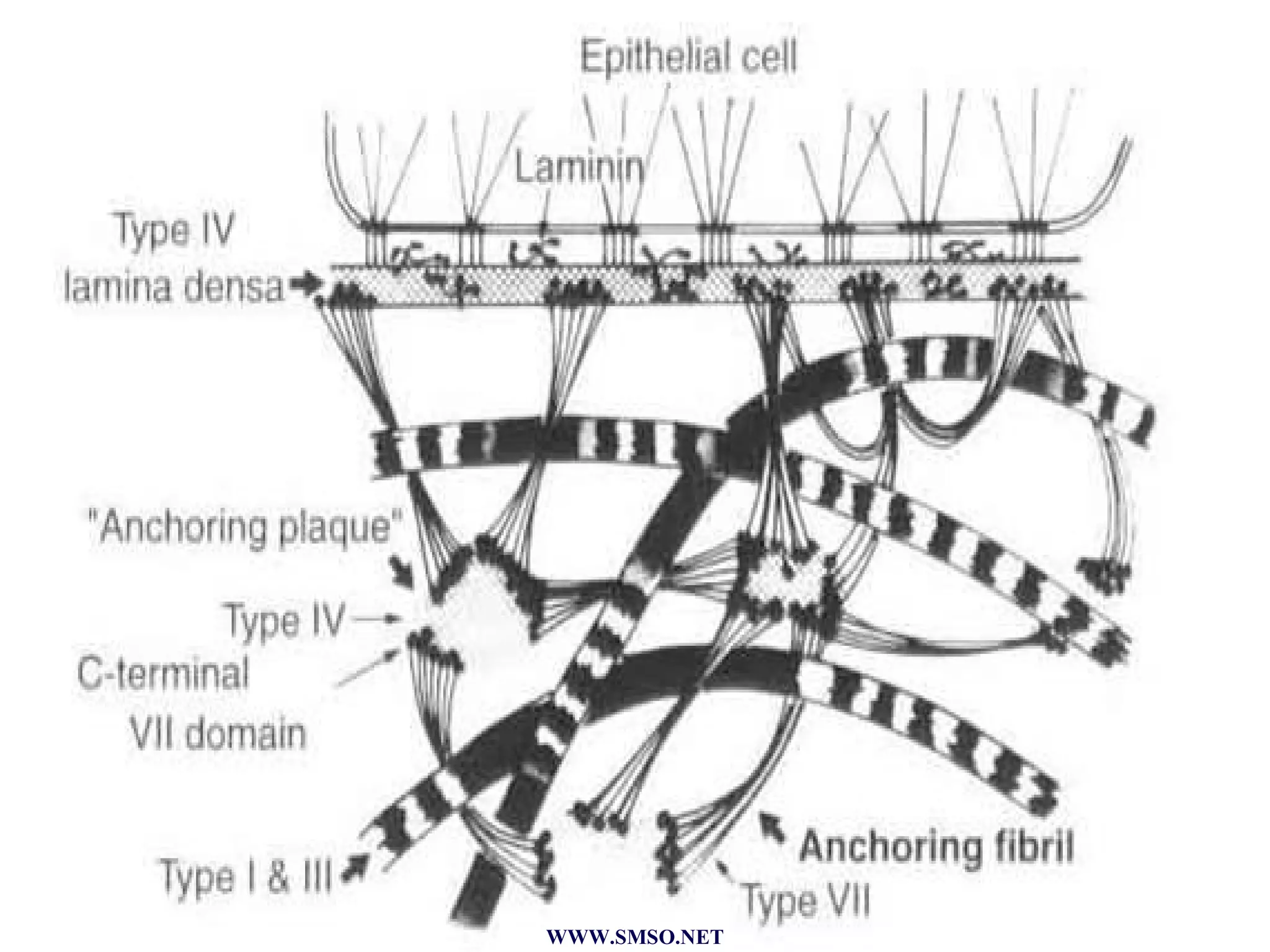
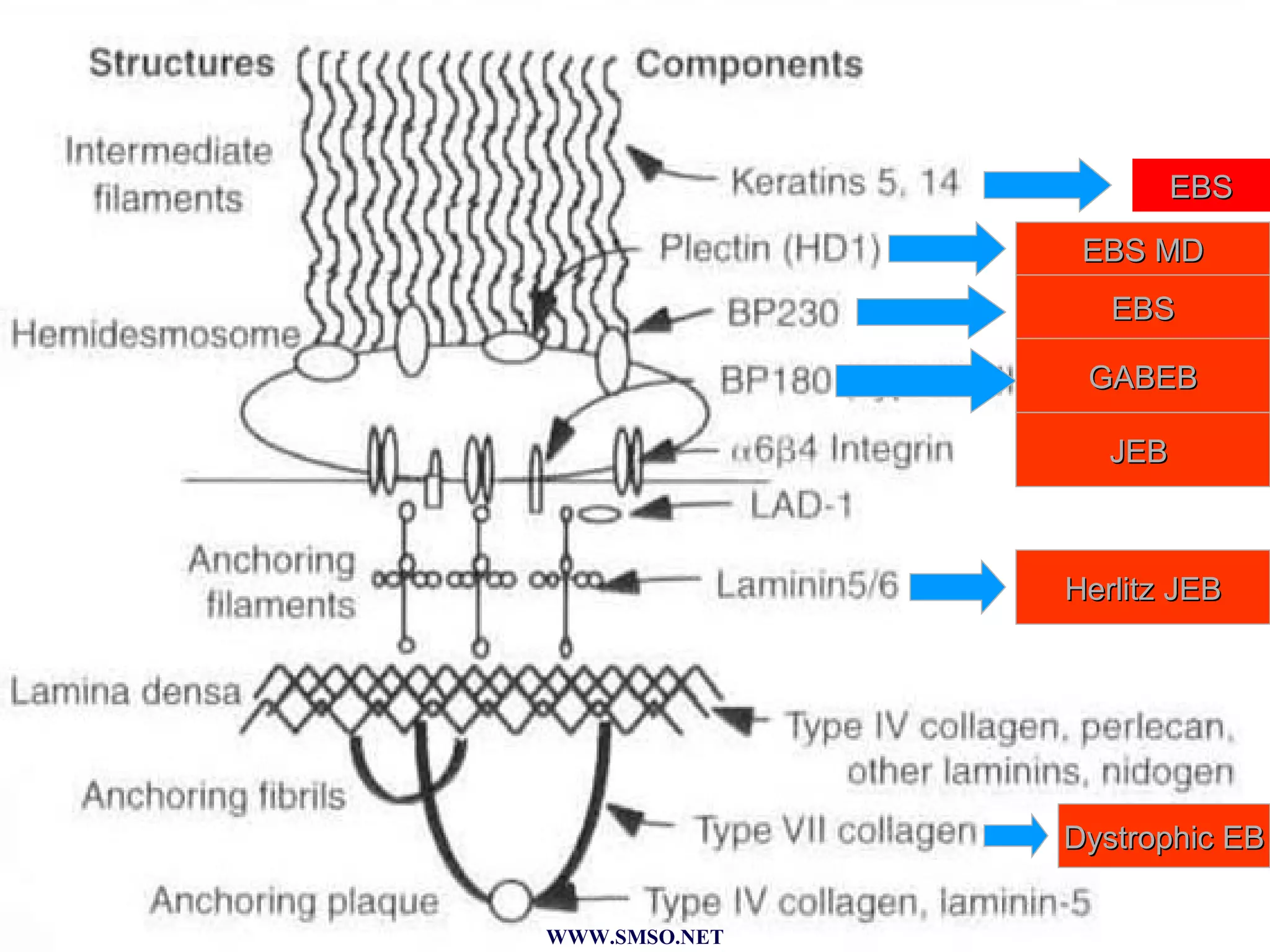
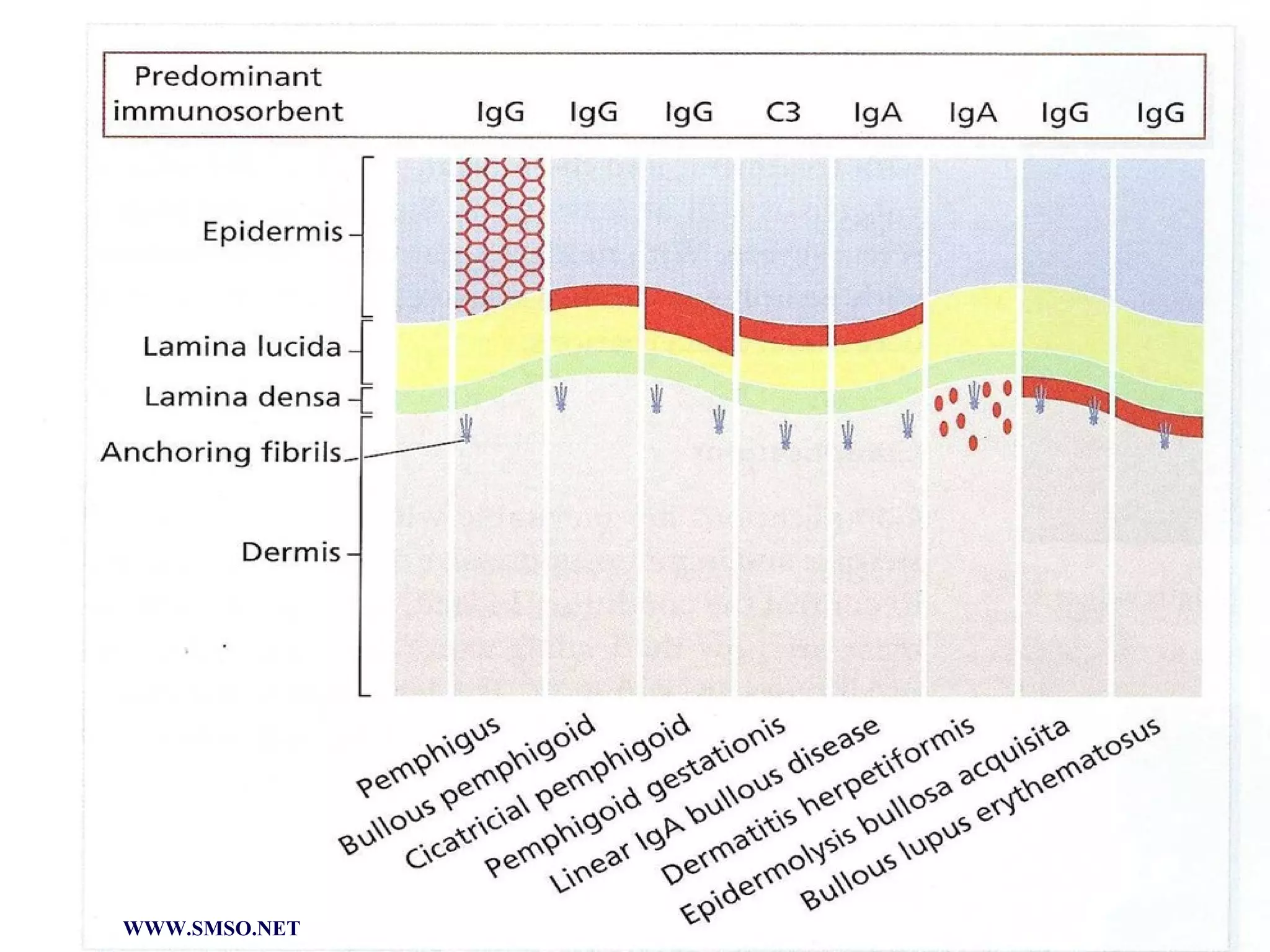
This document summarizes the structure and components of the dermal-epidermal junction (DEJ). The DEJ is a specialized basement membrane that separates the dermis and epidermis. It has three zones: 1) the basal lamina with hemidesmosomes that attach basal keratinocytes, 2) the lamina densa containing collagen and laminin fibers, and 3) anchoring fibrils that attach to the dermis. Key components include type IV collagen, laminin isoforms, nidogen, and proteoglycans. The DEJ provides stable attachment and communication between the skin layers.