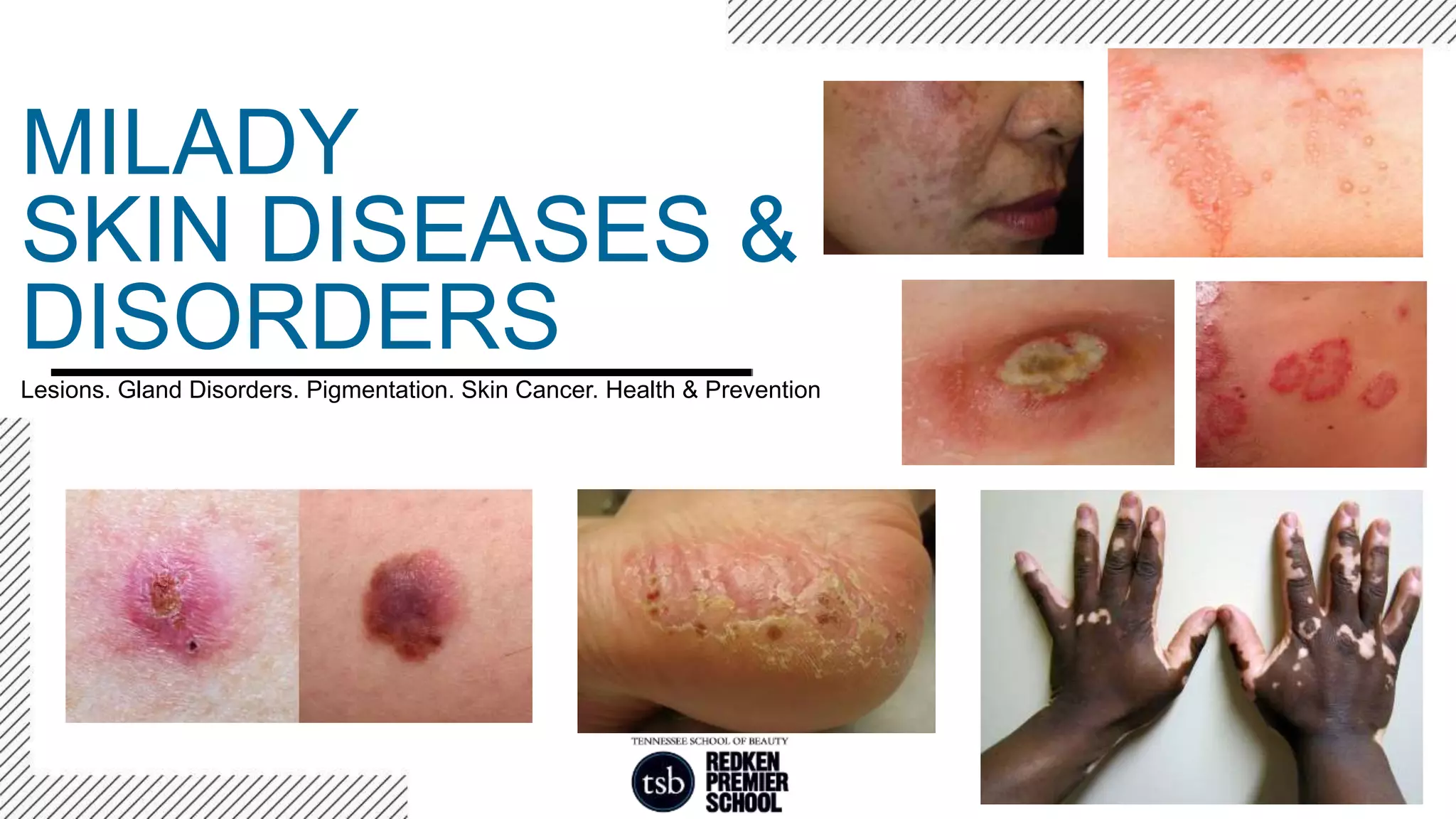
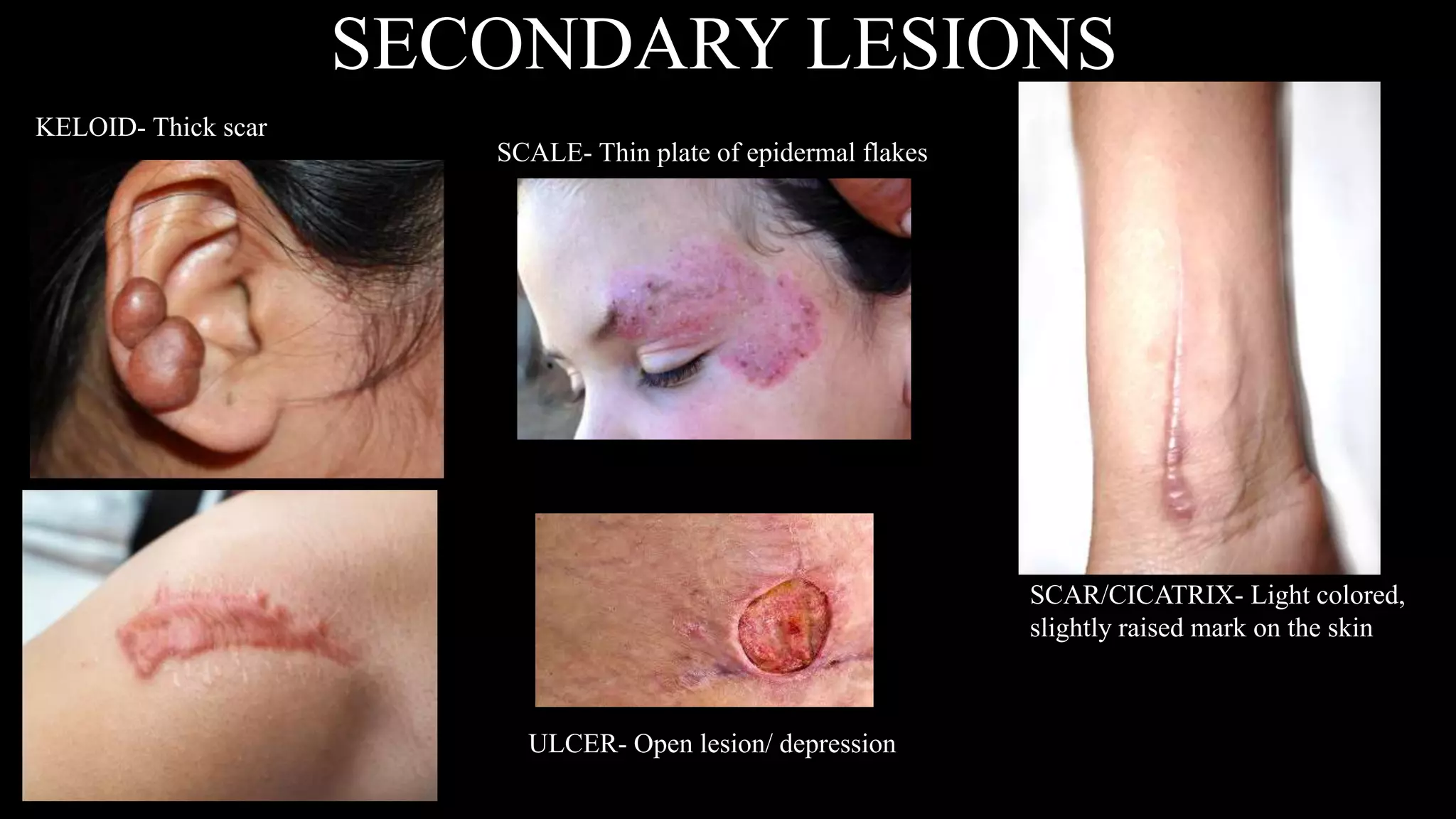
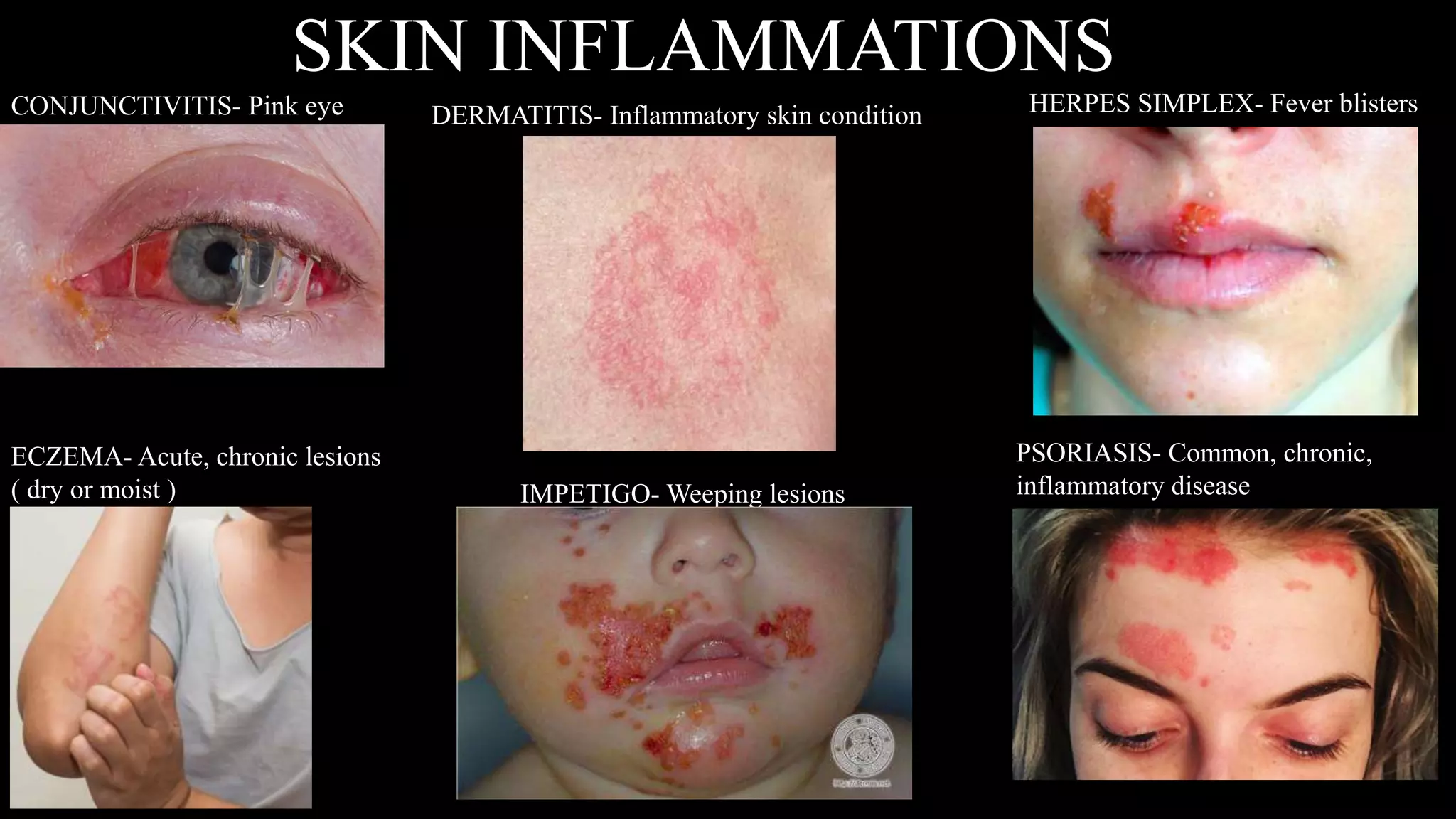
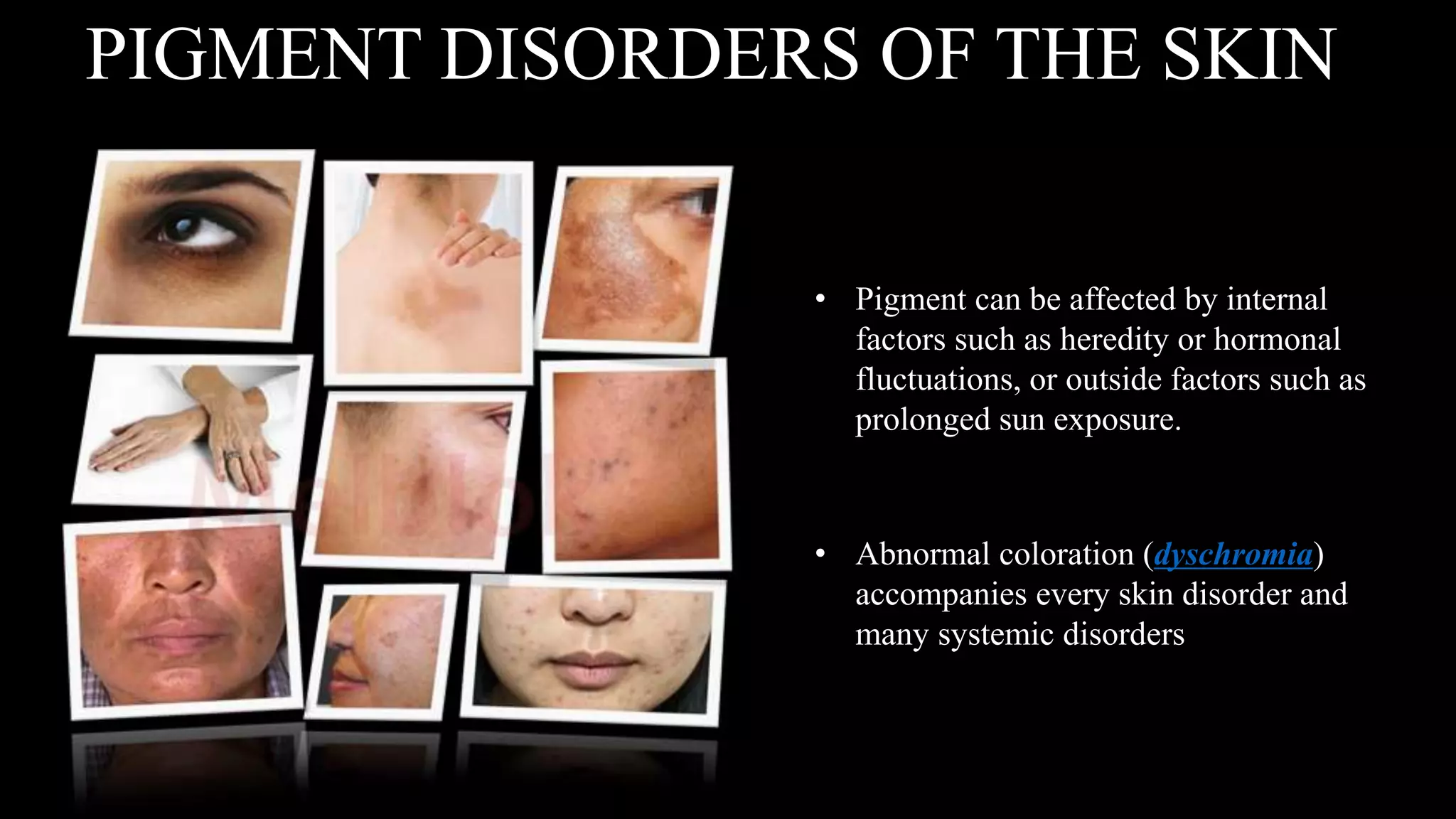
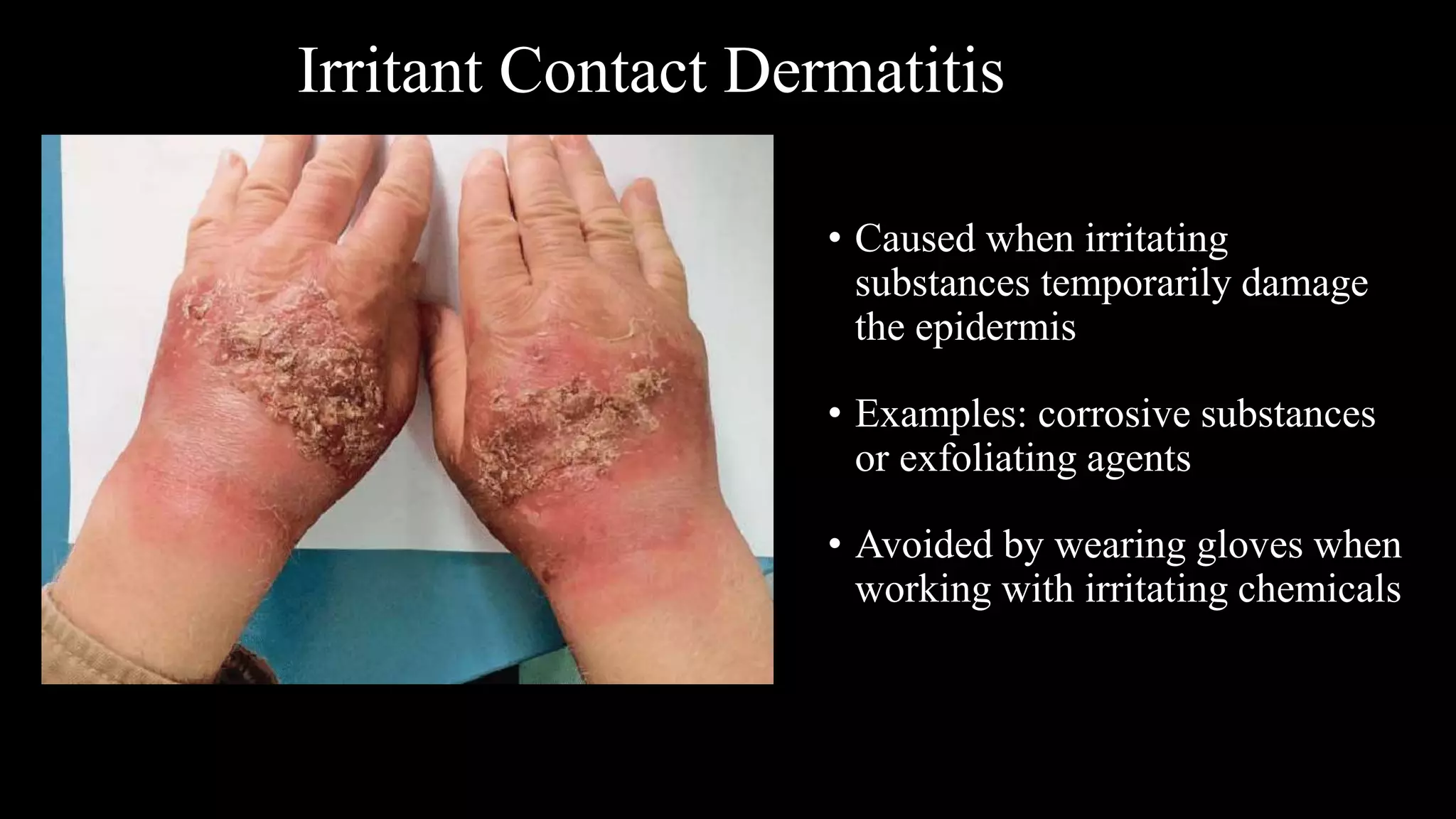
This document provides an overview of common skin lesions, disorders of the sebaceous and sudoriferous glands, pigmentation disorders, skin inflammations, and skin cancer. It discusses the primary causes of acne and treatments, factors that contribute to skin aging both intrinsically and from extrinsic sources like sun exposure, what contact dermatitis is and how to prevent it, and self-protection measures for professionals.