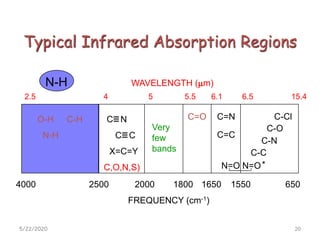
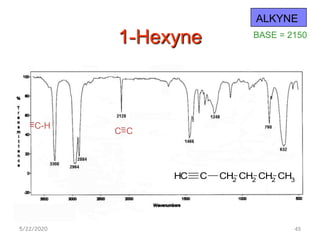
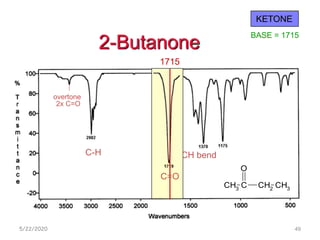
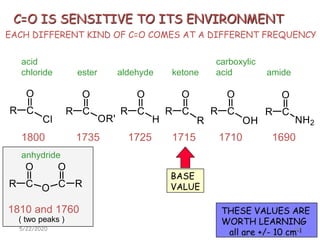
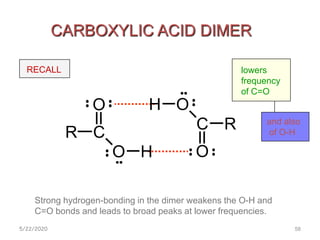
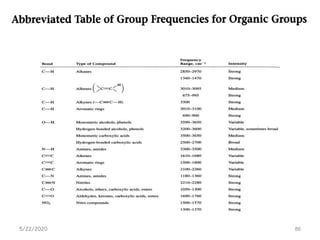
Infrared spectroscopy can be used to identify functional groups on molecules through their characteristic absorption peaks. A Fourier transform converts the interferogram pattern into a spectrum showing absorption as a function of frequency. Key regions of the infrared spectrum include the O-H, N-H, C-H, C=O, C=C, and C≡C stretches between 4000-400 cm-1. Absorption peaks are indicative of bond strength and hydrogen bonding environment. Infrared spectroscopy allows quantitative analysis through Beer's Law.