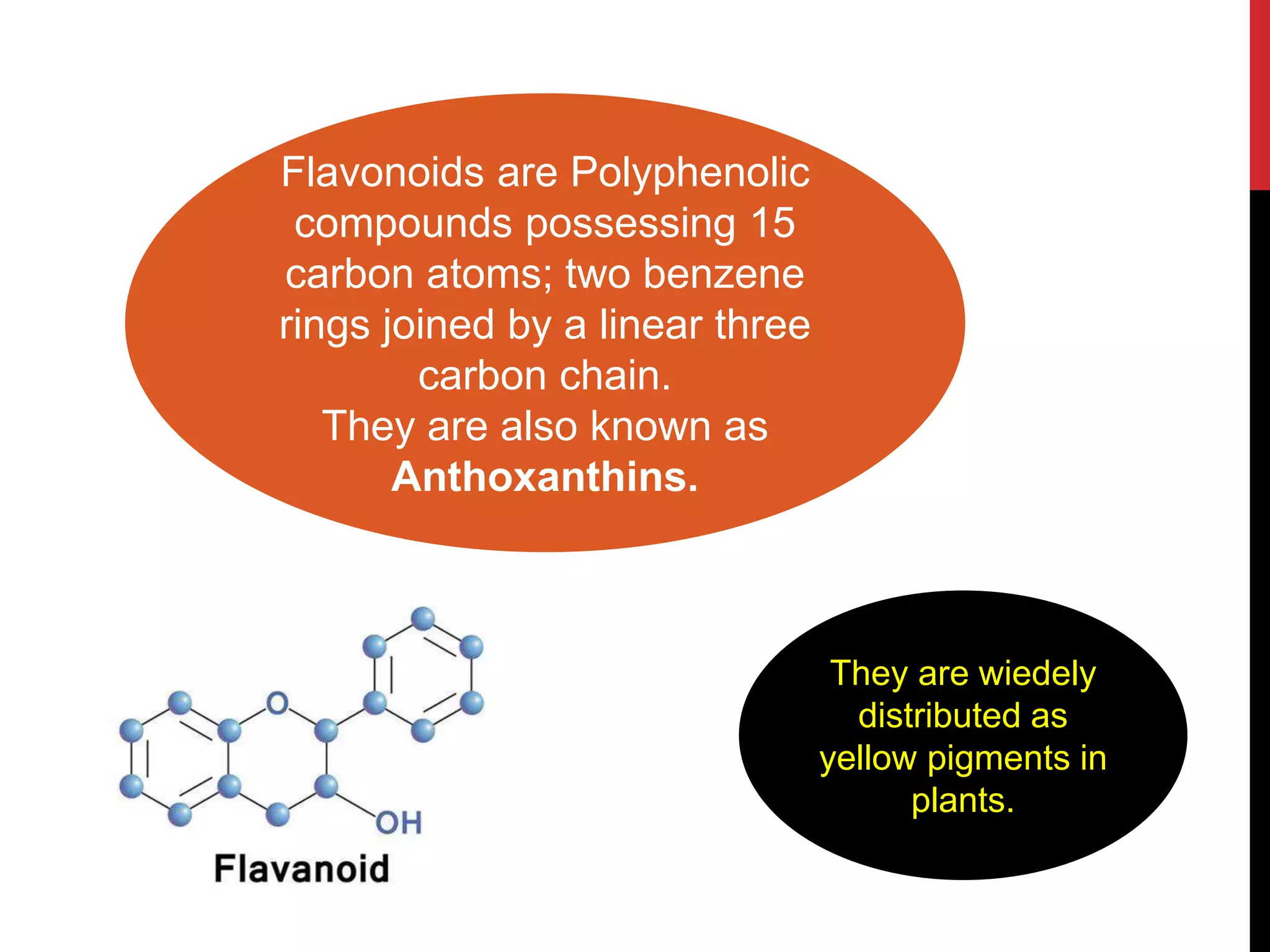
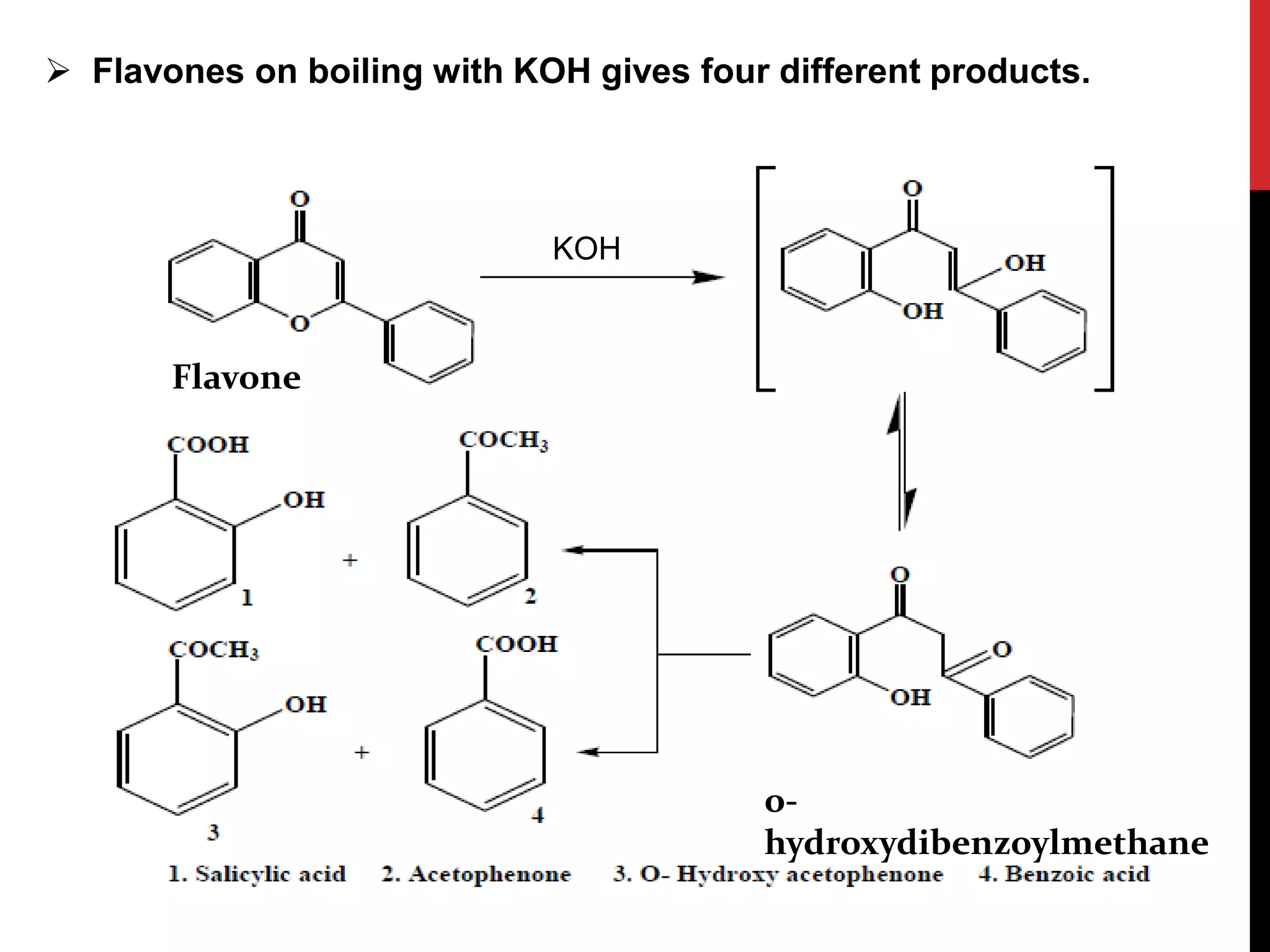
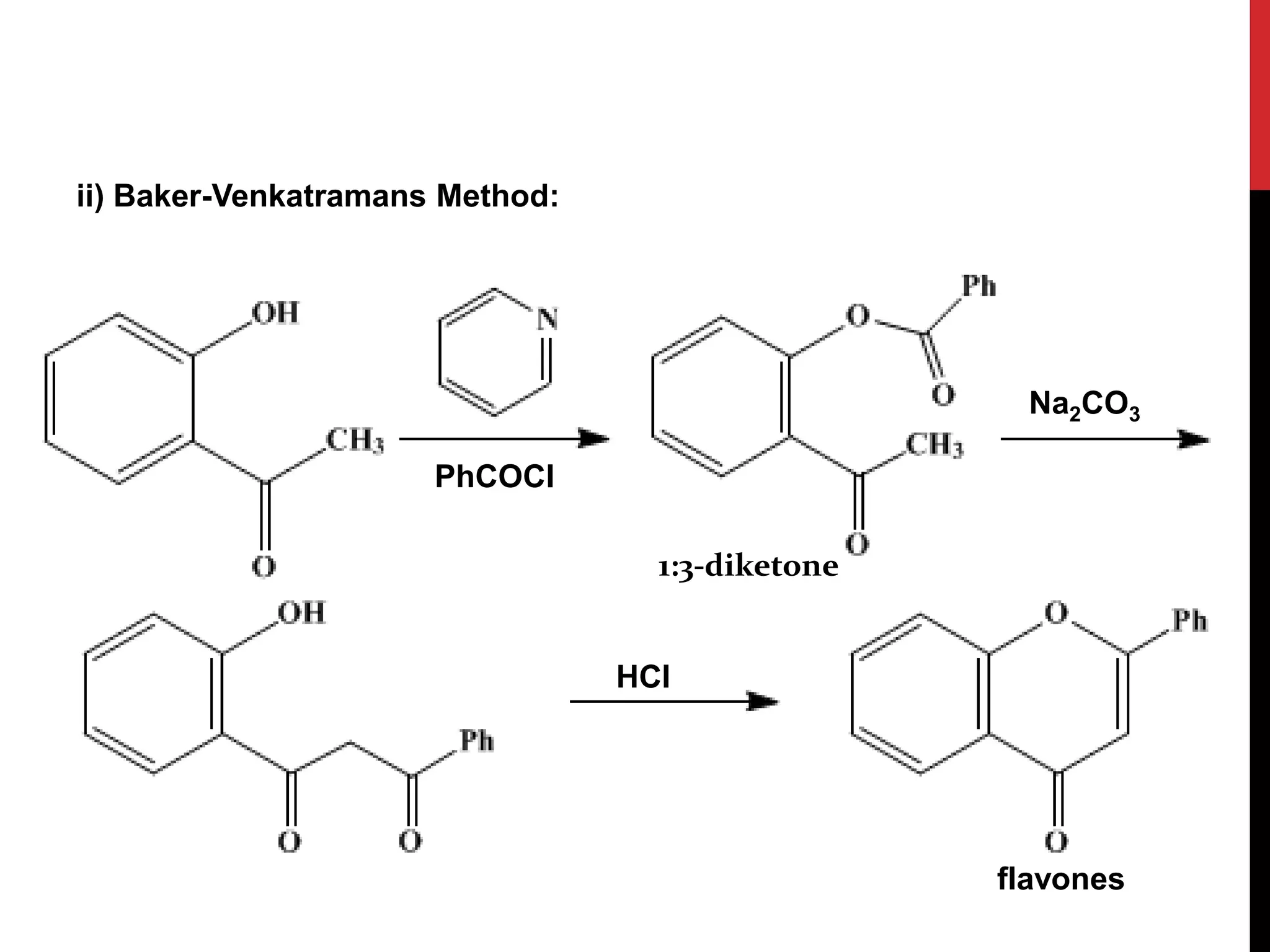
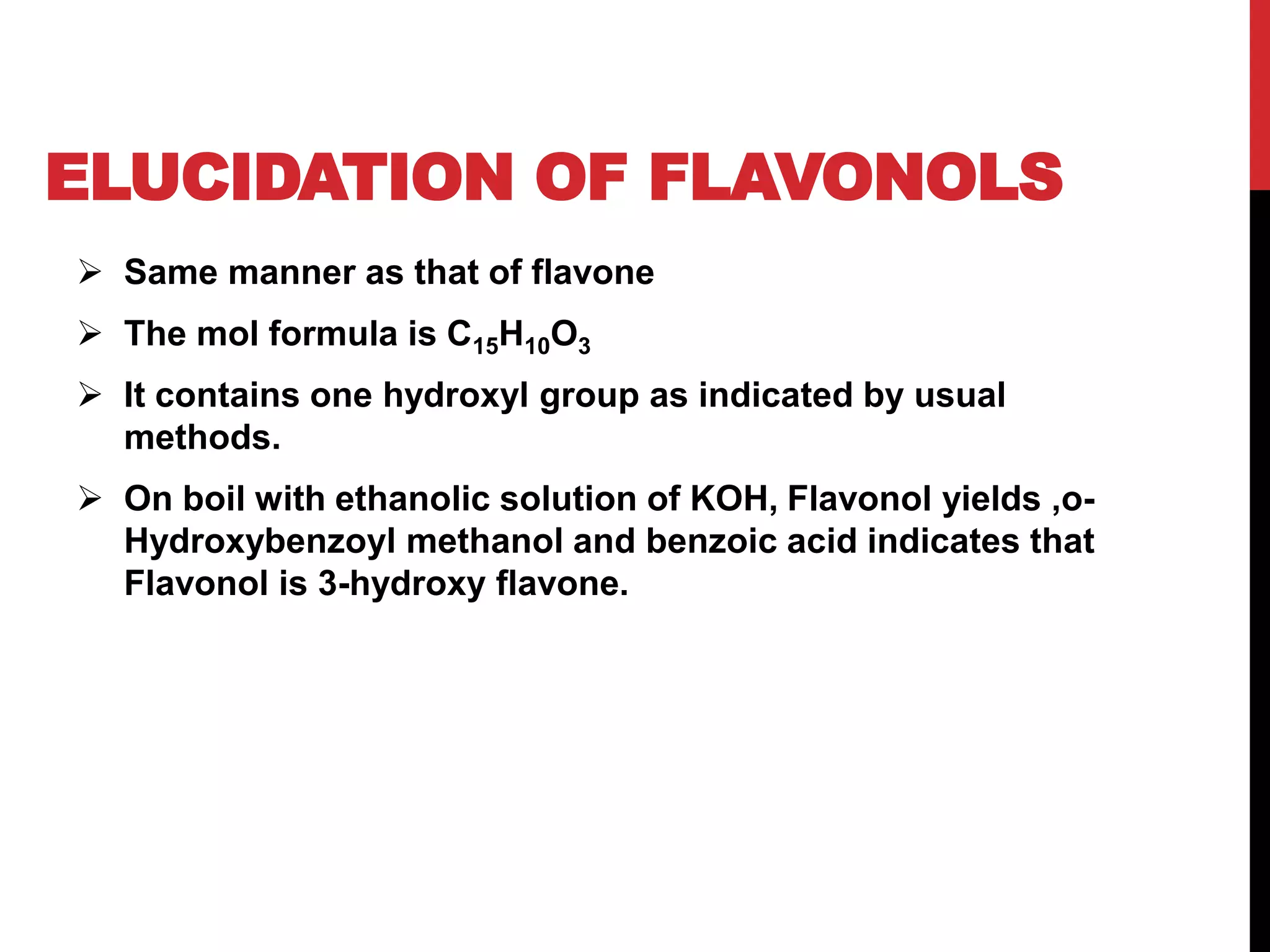
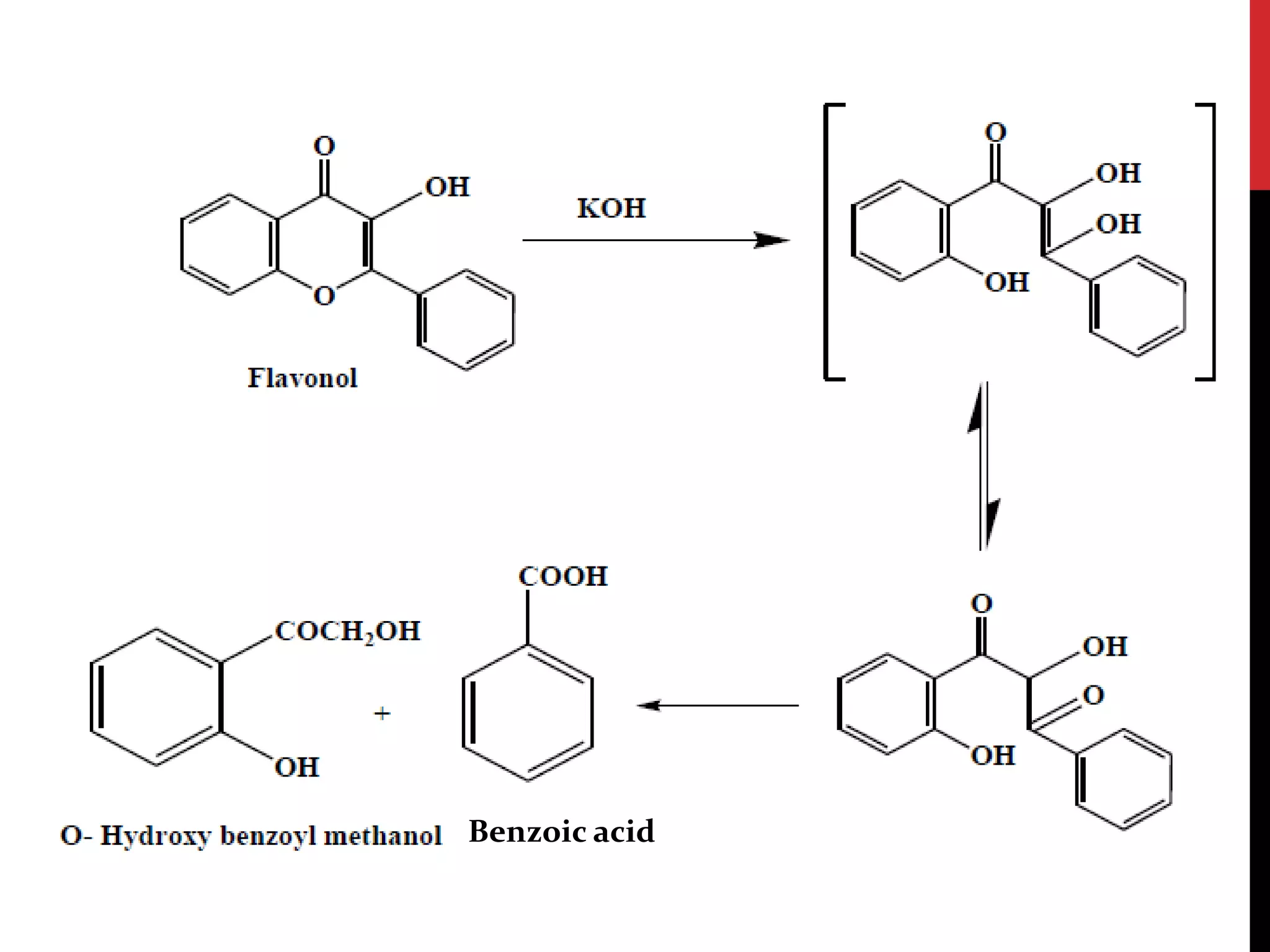
This document discusses the structural elucidation of flavonoids, flavones, and flavonols. Flavonoids contain 15 carbon atoms and consist of two benzene rings joined by a three carbon chain. Flavones do not contain hydroxyl groups, and when fused with alkali degrade into a phenol and aromatic acids. Flavonols contain one hydroxyl group, and when boiled with potassium hydroxide yield o-hydroxybenzoyl methanol and benzoic acid, indicating the structure is 3-hydroxy flavone. The proposed structures are then proven through synthesis methods like Robinson's method.