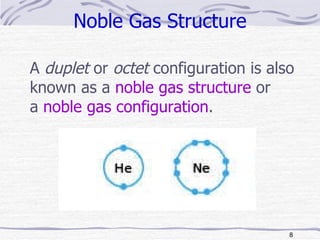
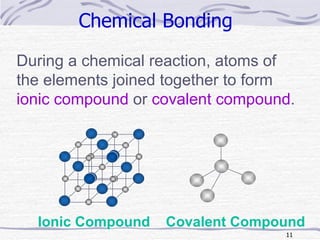
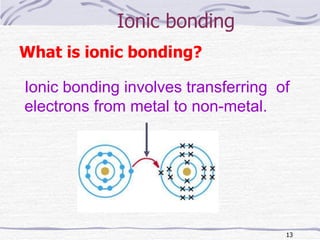
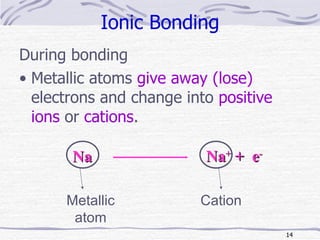
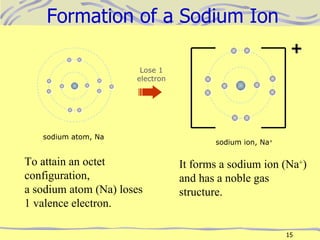
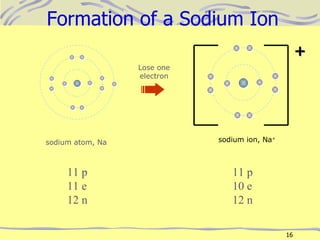
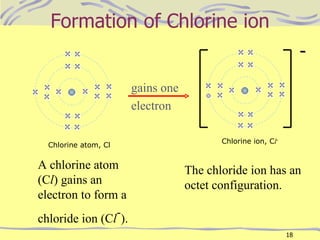
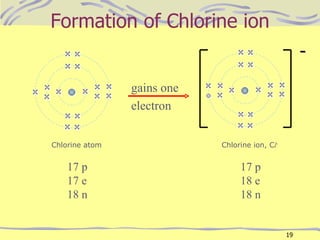
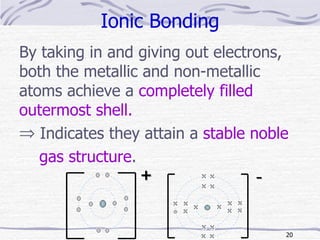
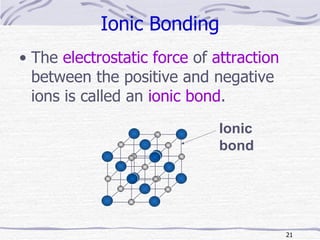
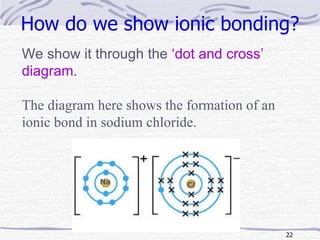
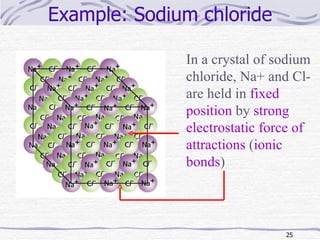
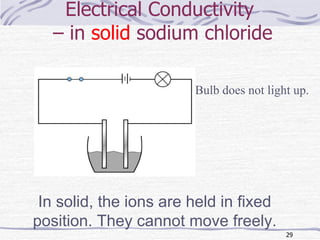
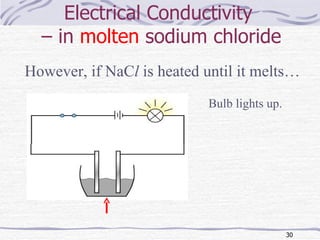
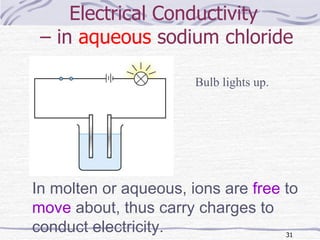
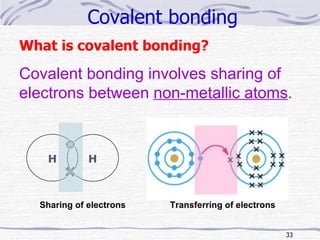
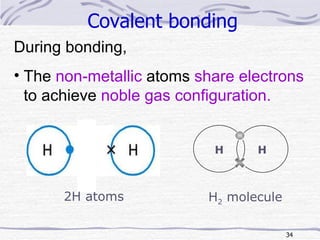
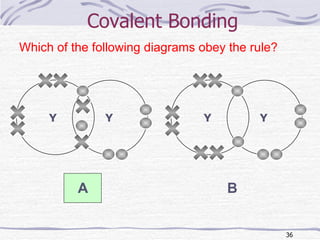
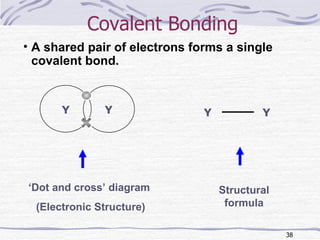
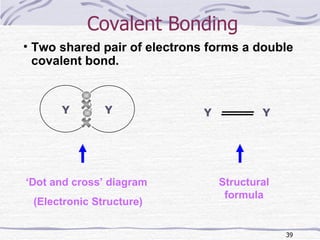
The document discusses chemical bonding, specifically ionic and covalent bonding. Ionic bonding involves the transfer of electrons between metals and non-metals to form ions that achieve stable noble gas electron configurations. Covalent bonding involves the sharing of electrons between non-metals. Both ionic and covalent bonds form when atoms attain noble gas electron configurations. Ionic compounds have characteristics like high melting points and conductivity when molten or dissolved, while covalent compounds have low melting points and are non-conductive.