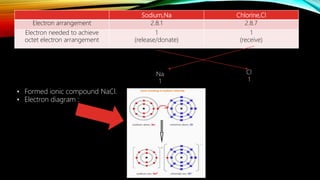
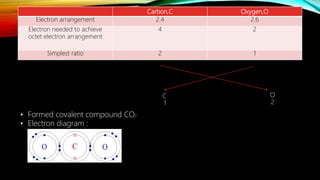
This document discusses how to determine if an atom is a metal or non-metal based on its valence electrons, and describes the formation of ionic and covalent bonds. Ionic bonds form between metal and non-metal atoms through the transfer of electrons from the metal to the non-metal. Covalent bonds form between non-metal atoms through the sharing of electrons. Examples of ionic bond formation in sodium chloride and covalent bond formation in carbon dioxide are provided, along with electron diagrams to illustrate bonding.