1. The document discusses different types of chemical bonding including ionic bonding, covalent bonding, and metallic bonding.
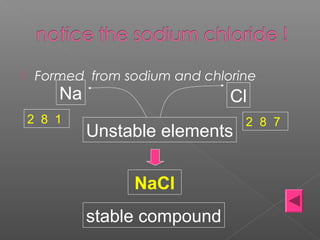
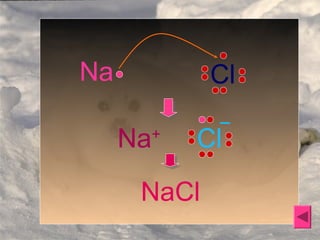
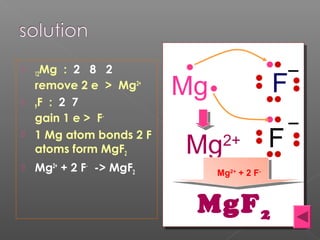
2. Ionic bonding occurs when atoms transfer electrons to form oppositely charged ions that are then attracted via electrostatic forces, such as in sodium chloride (NaCl).
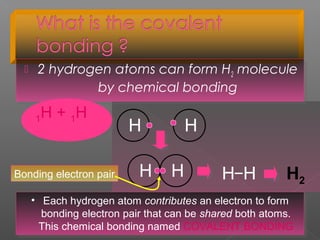
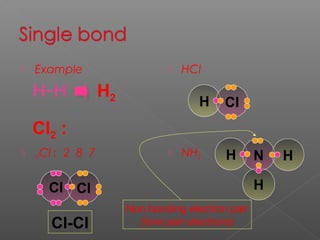
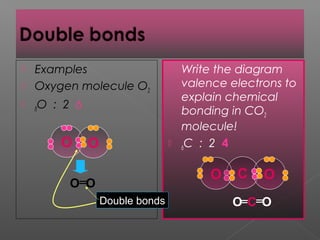
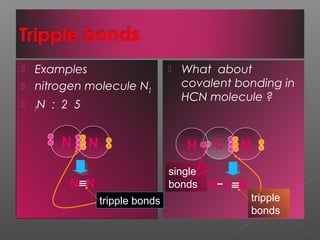
3. Covalent bonding involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms to form molecular compounds, like in water (H2O) and methane (CH4).