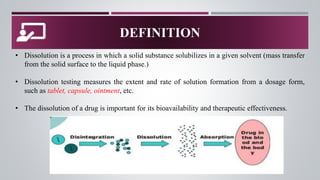
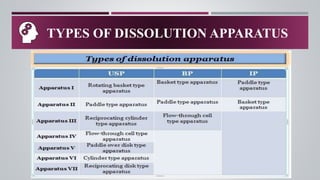
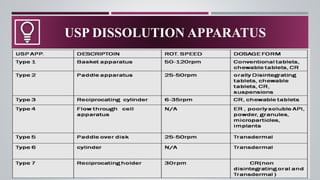
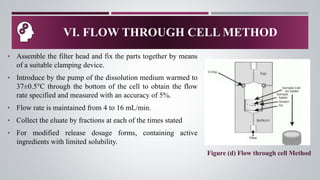
La prueba de disolución in vitro es una herramienta fundamental para evaluar el rendimiento de productos farmacéuticos, determinando la extensión y la rapidez de la formación de soluciones desde formas de dosificación como tabletas y cápsulas. El proceso de disolución incluye la desintegración, la deagregación y la disolución real del fármaco, lo cual es crucial para su biodisponibilidad y efectividad terapéutica. Diversos métodos de disolución se emplean, como el aparato de cesta y el método paddle, adaptados a diferentes formas de dosificación y requerimientos específicos.