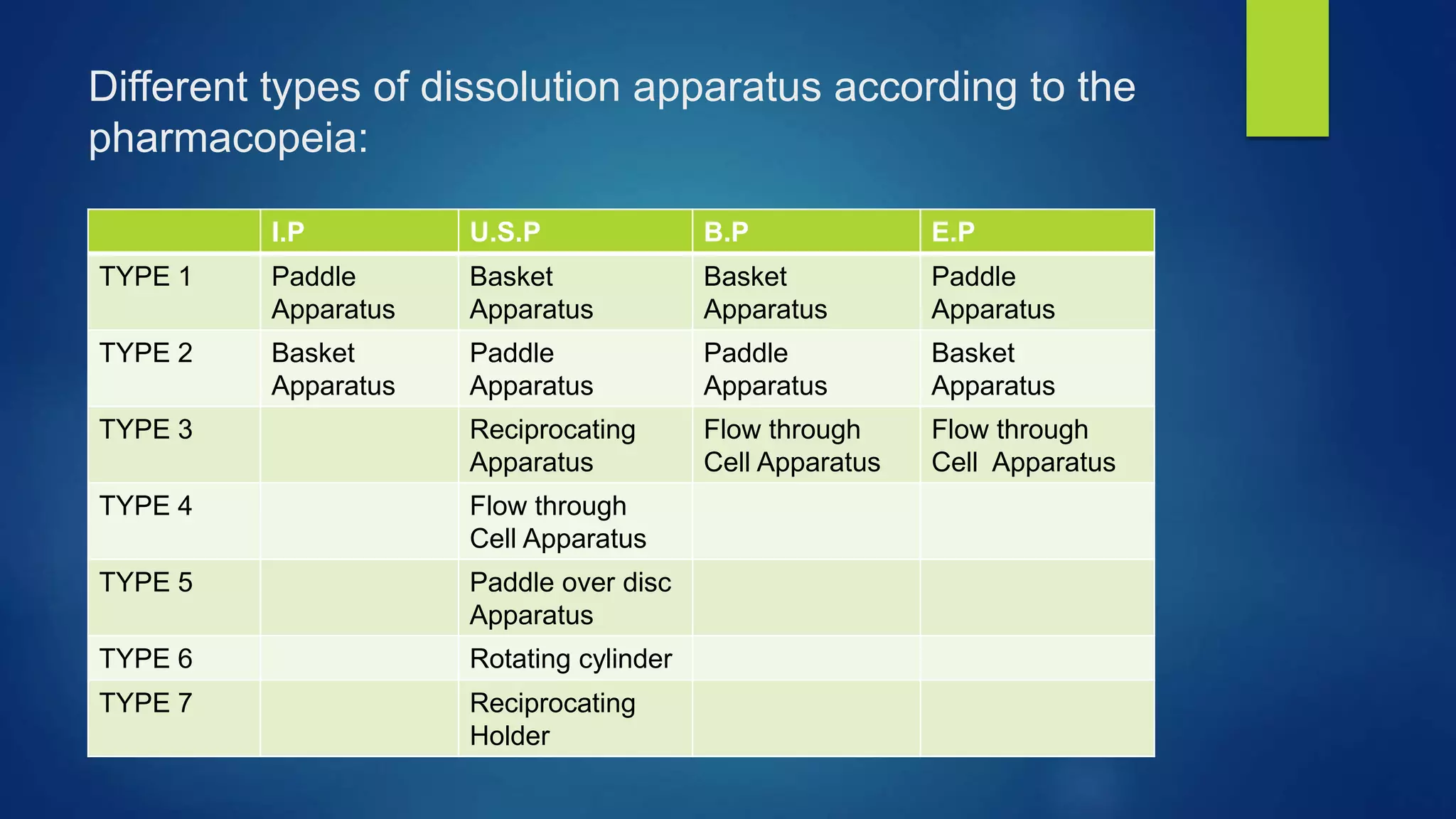
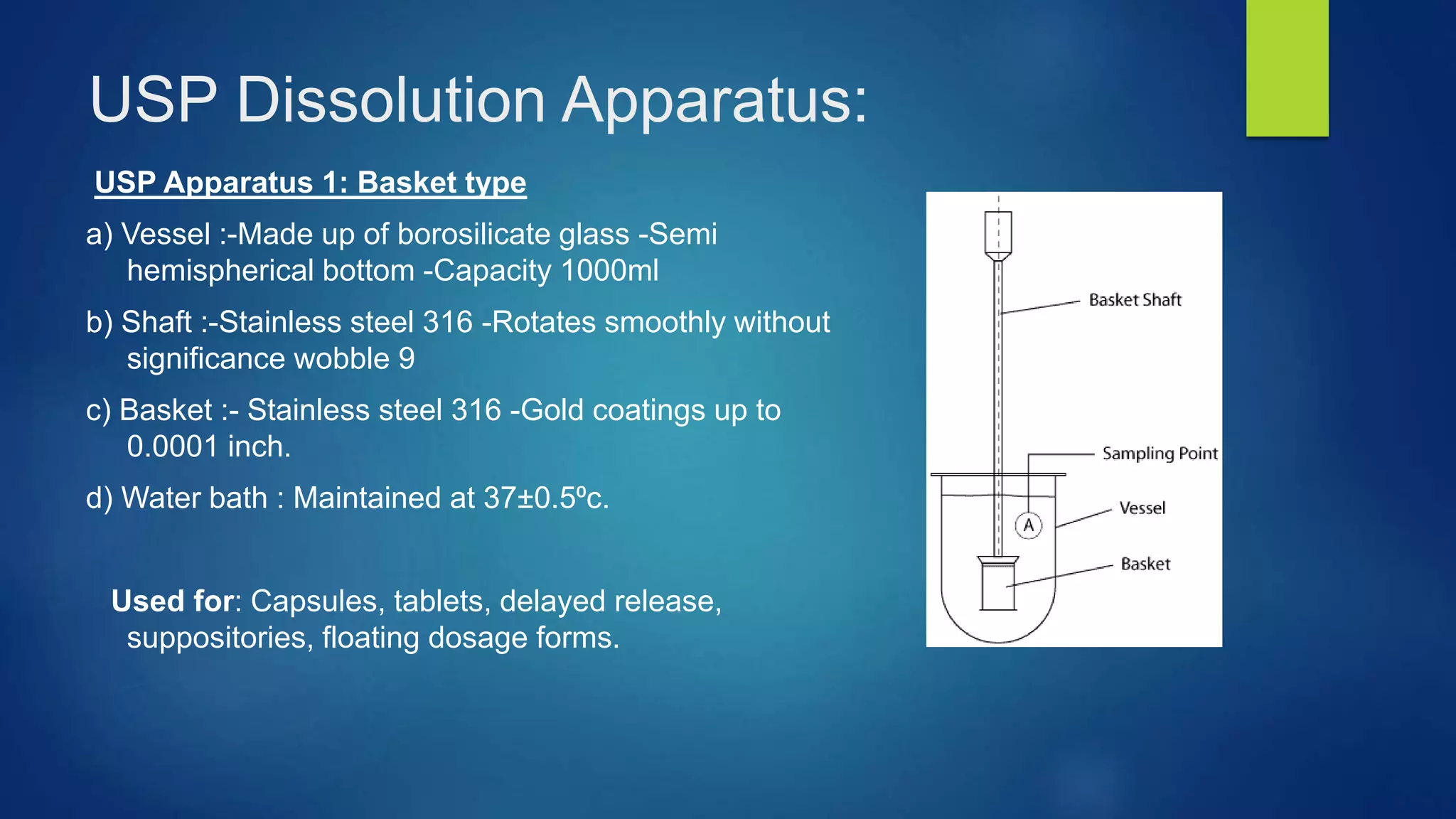
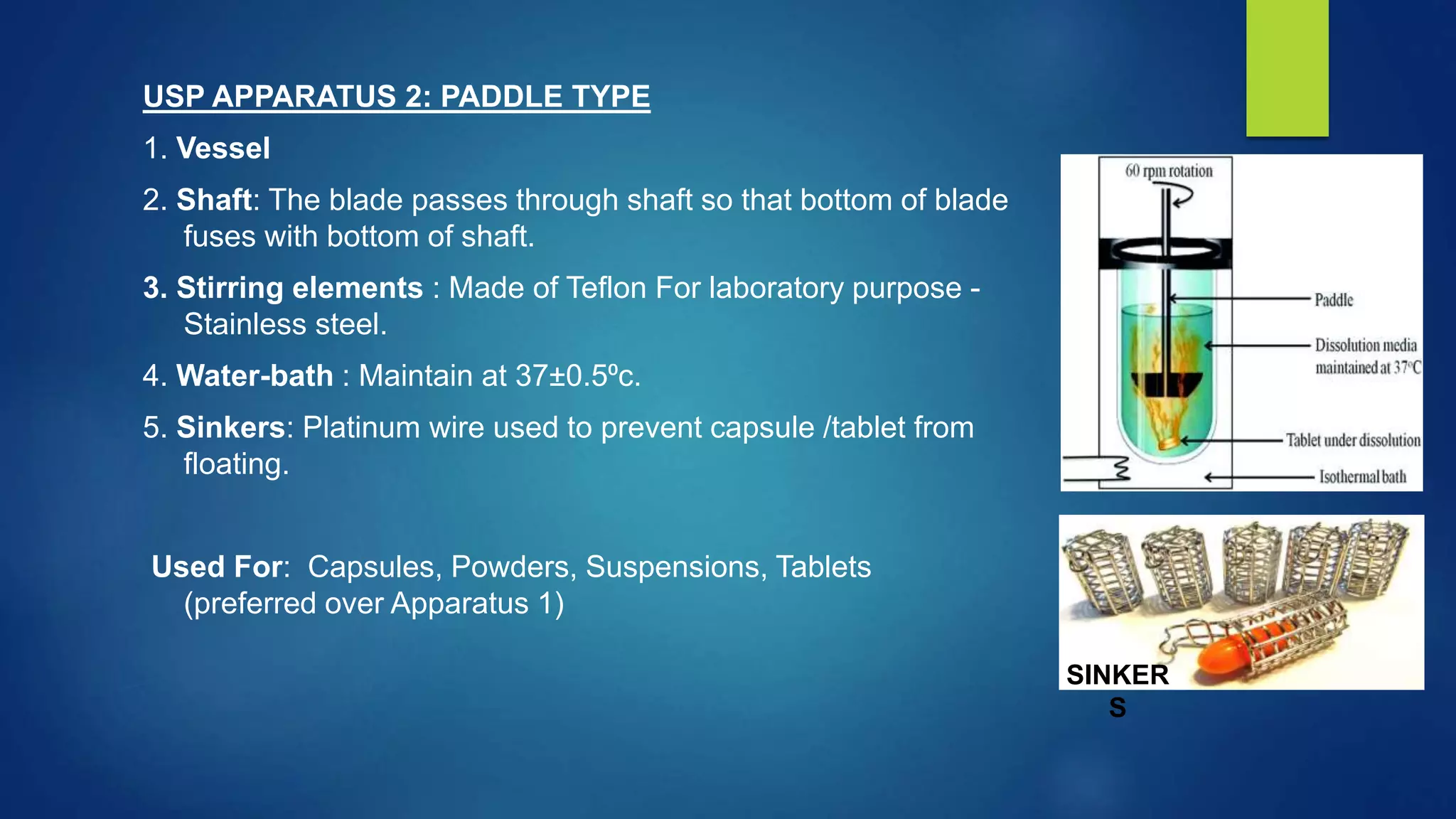
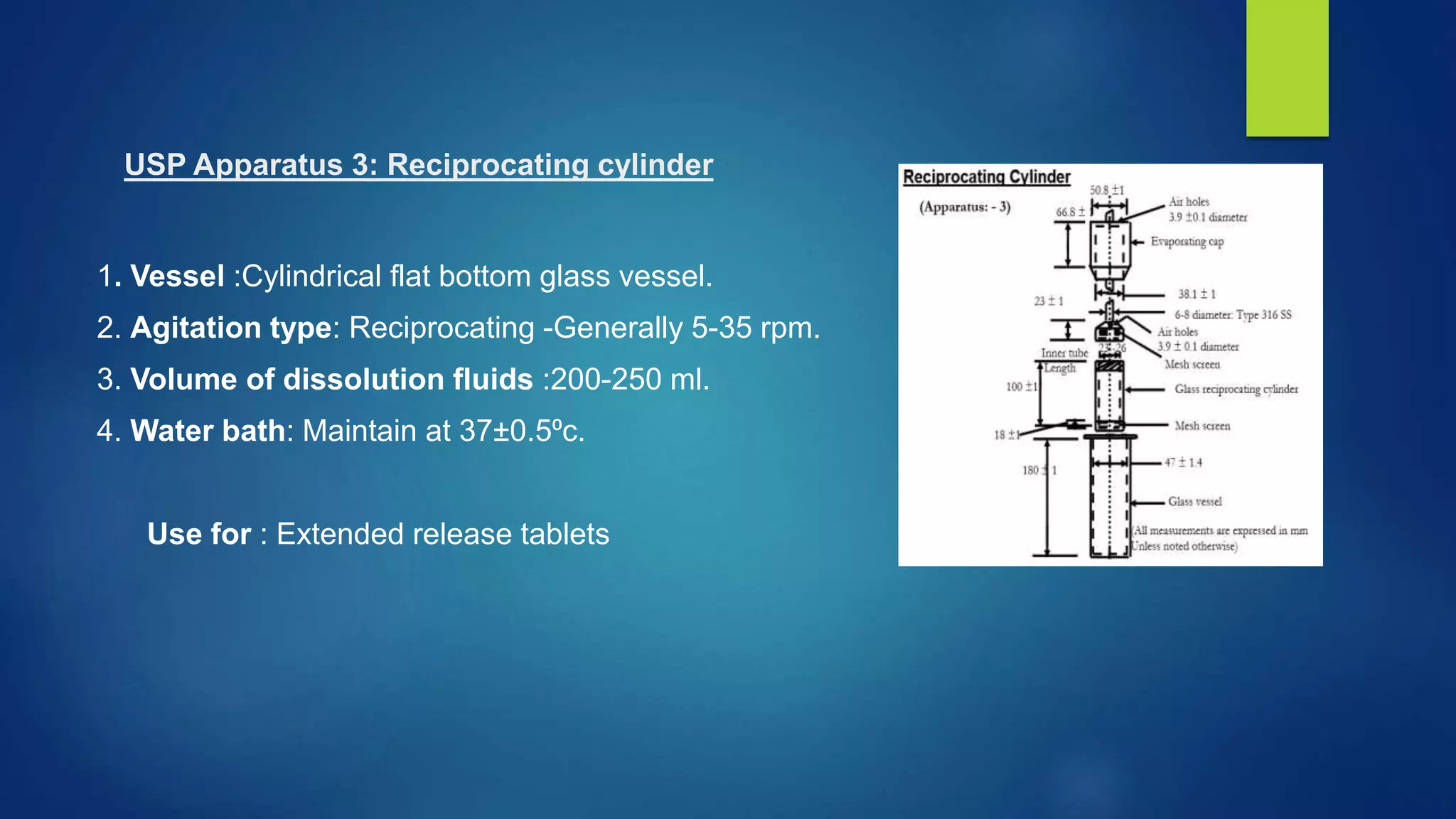
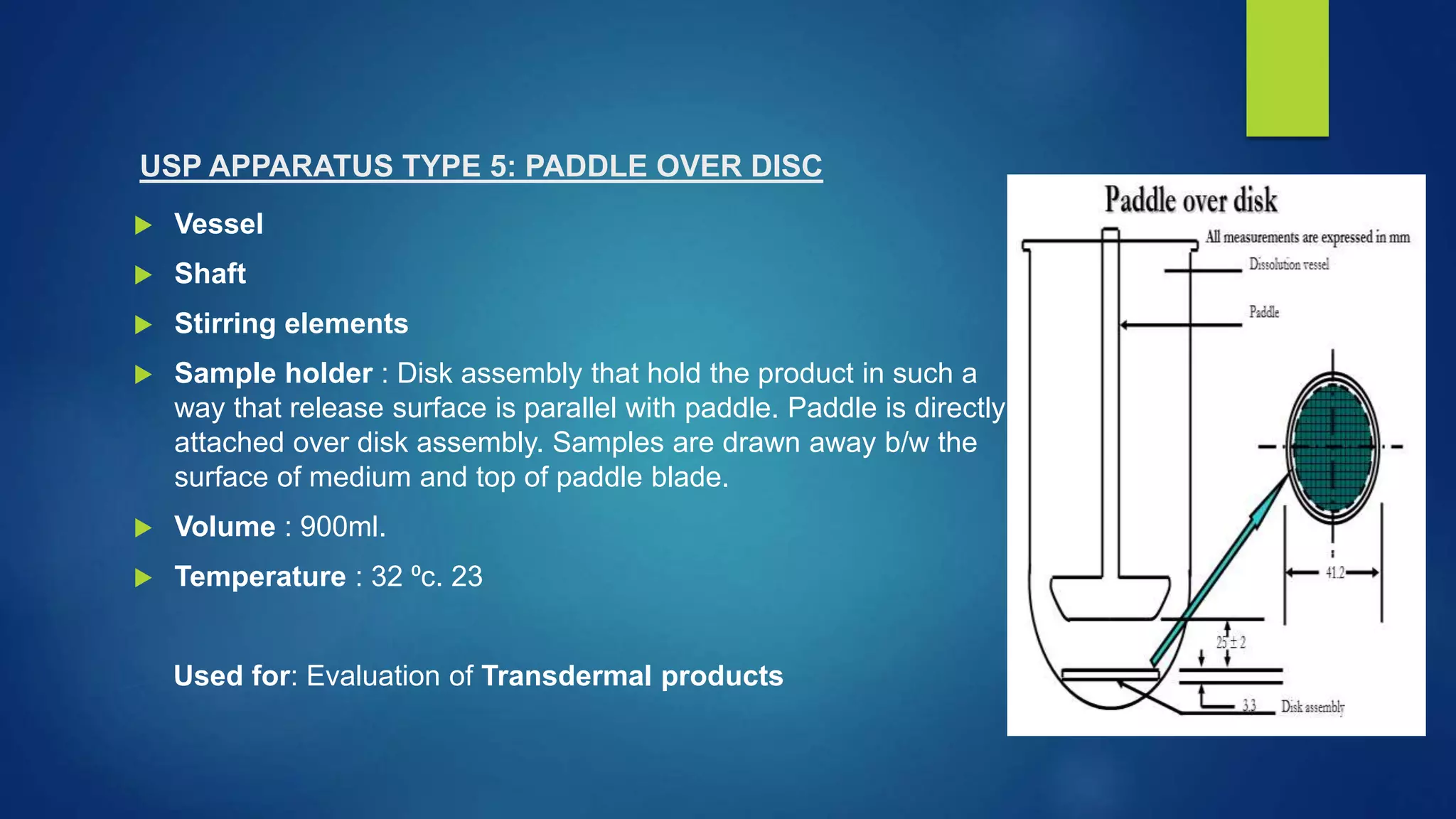
This document discusses various dissolution apparatus used to test the dissolution of pharmaceutical dosage forms. It describes the 7 main types of apparatus specified in pharmacopeias like USP including basket, paddle, flow-through cell and reciprocating cylinder apparatuses. Each type of apparatus has a specific design and is used to test different dosage forms like tablets, capsules, transdermal patches based on simulating their dissolution environment in the body. Dissolution testing provides critical information for quality control and drug development.