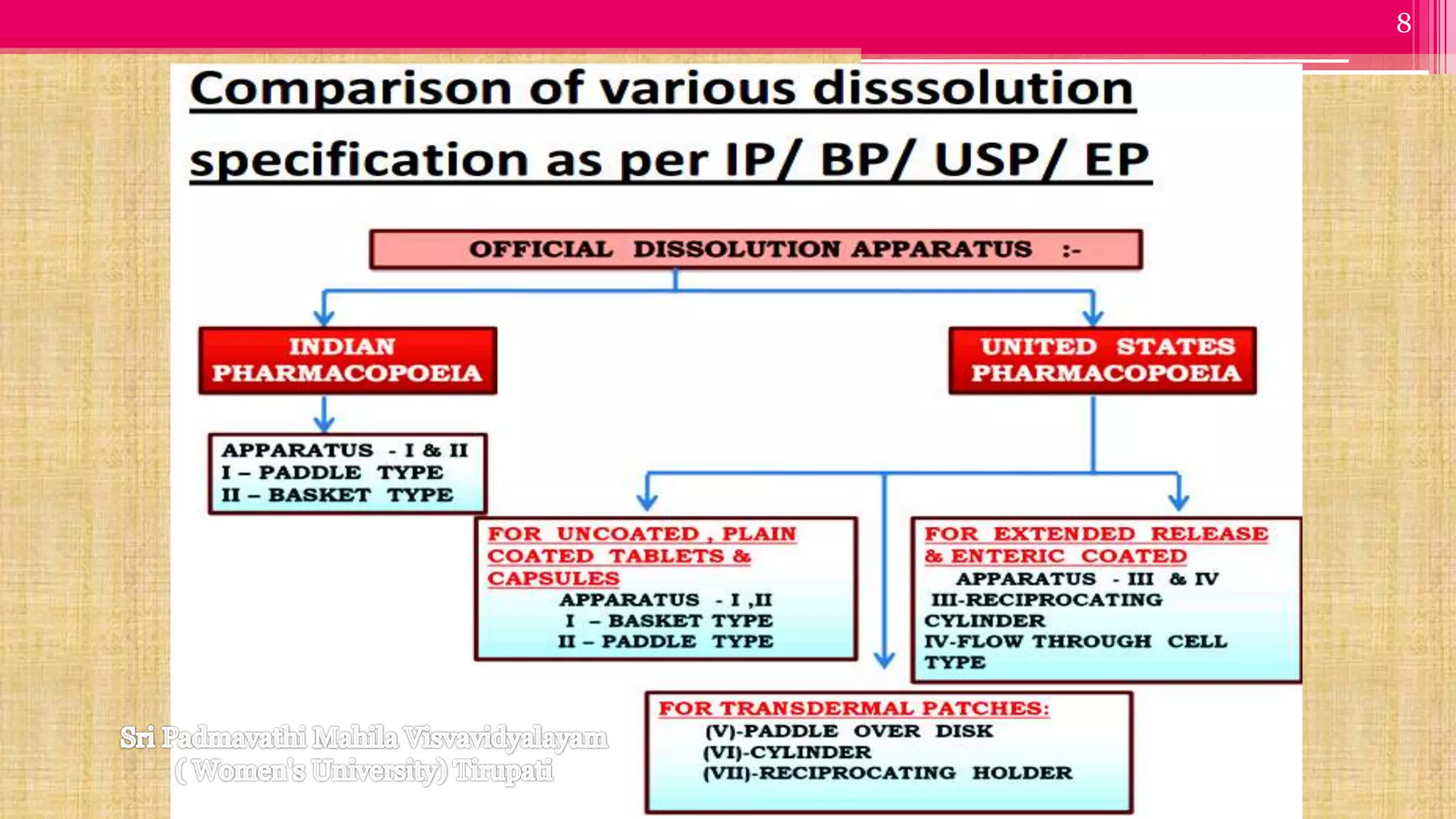
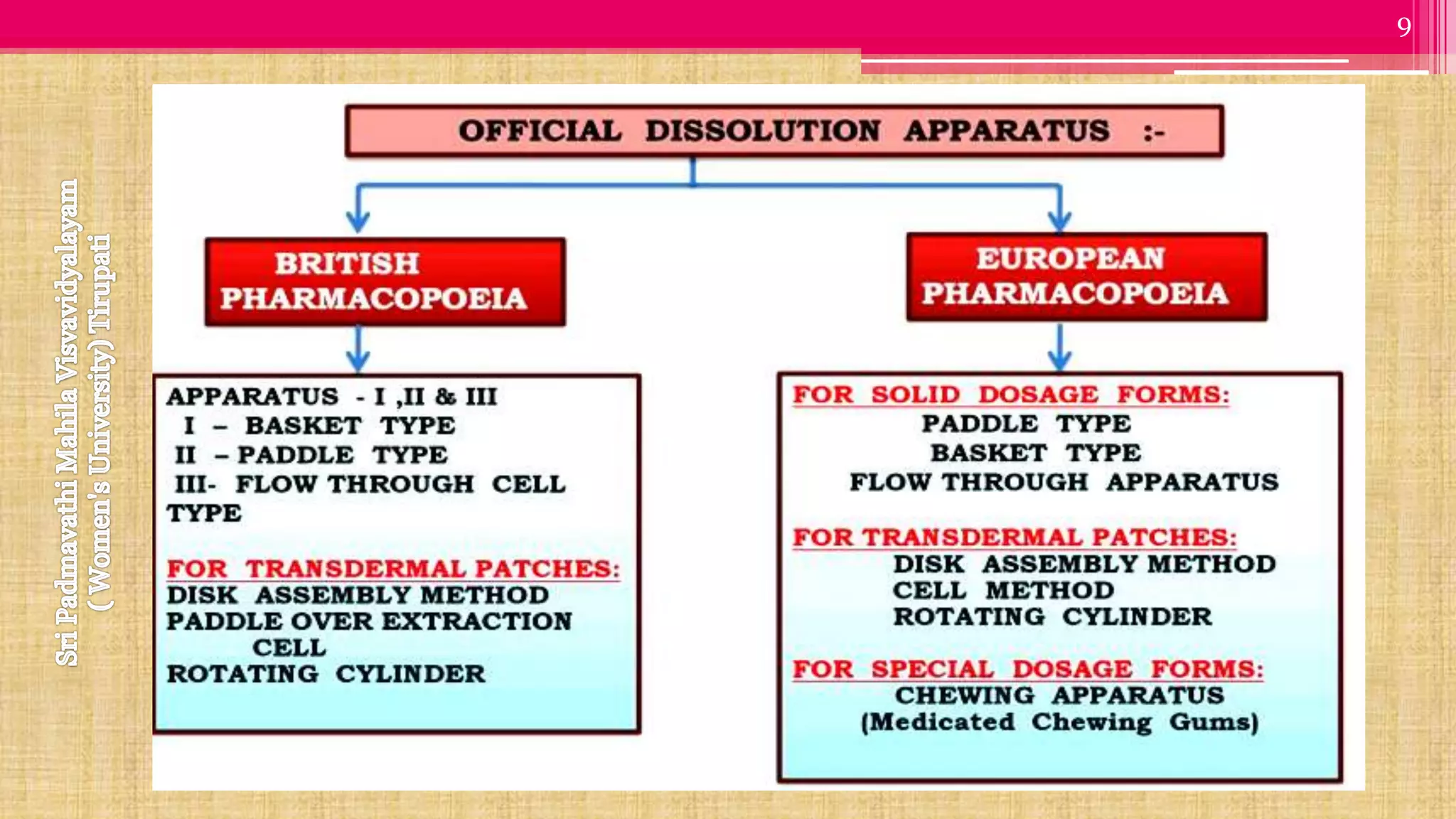
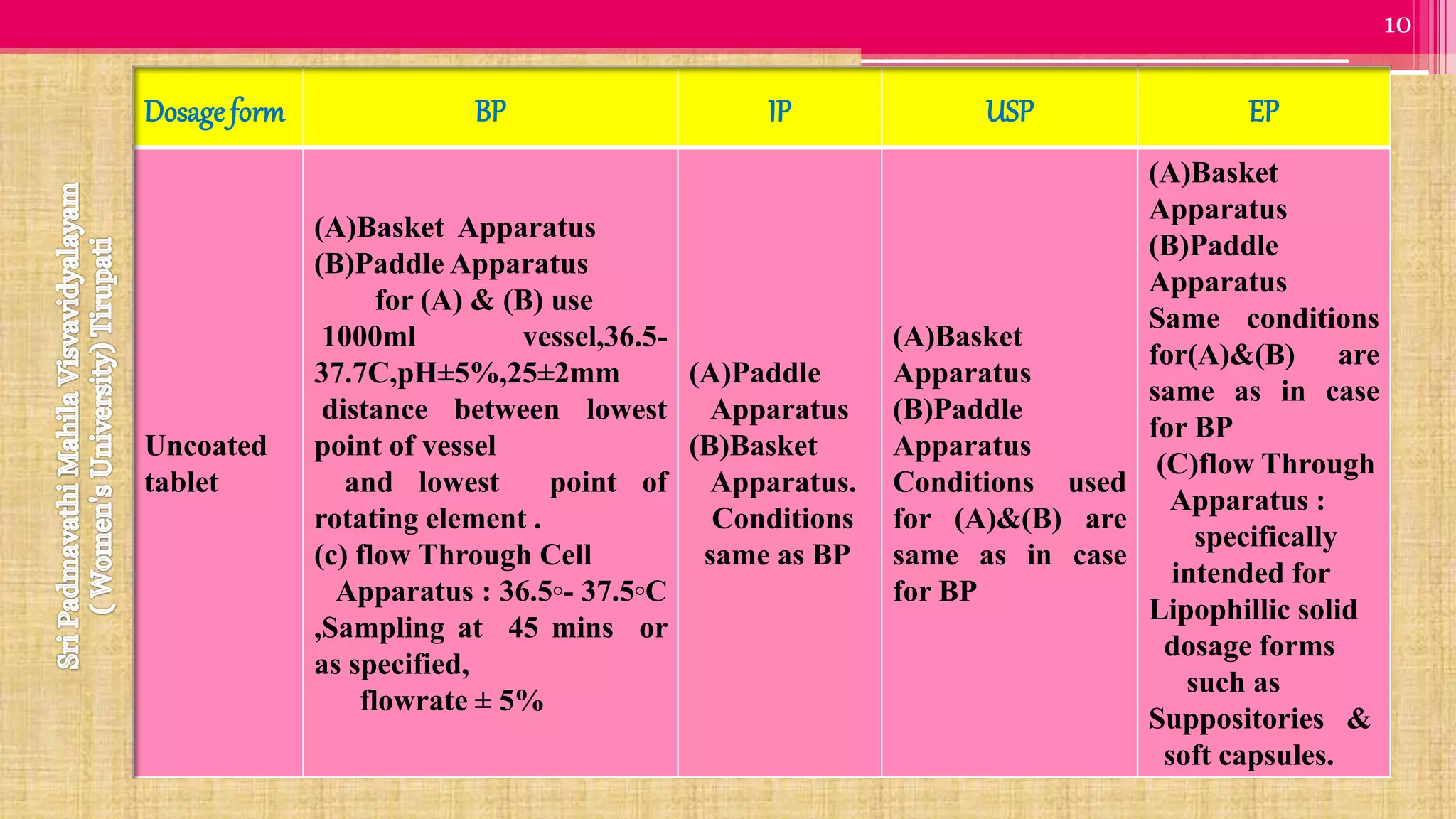
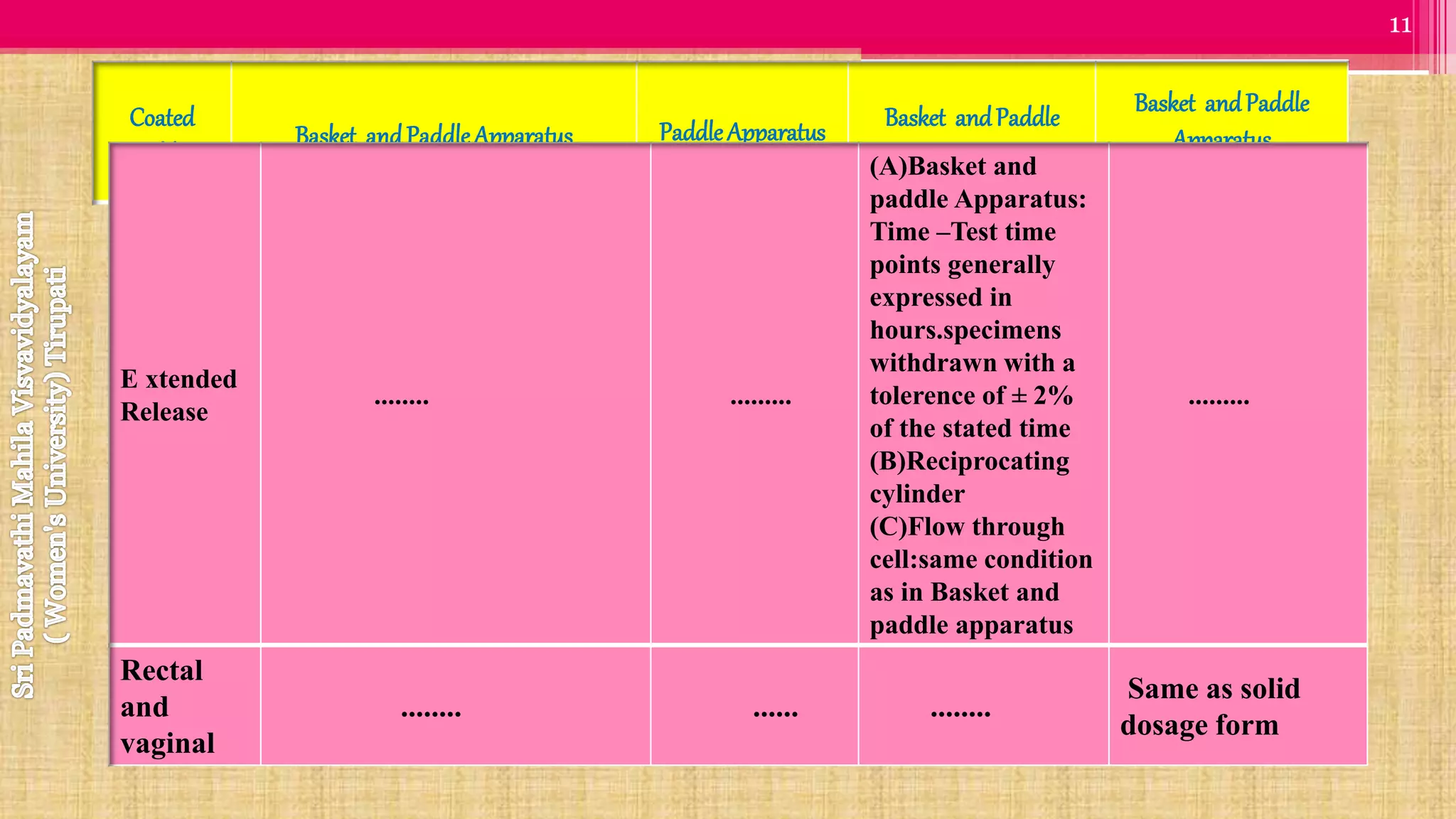
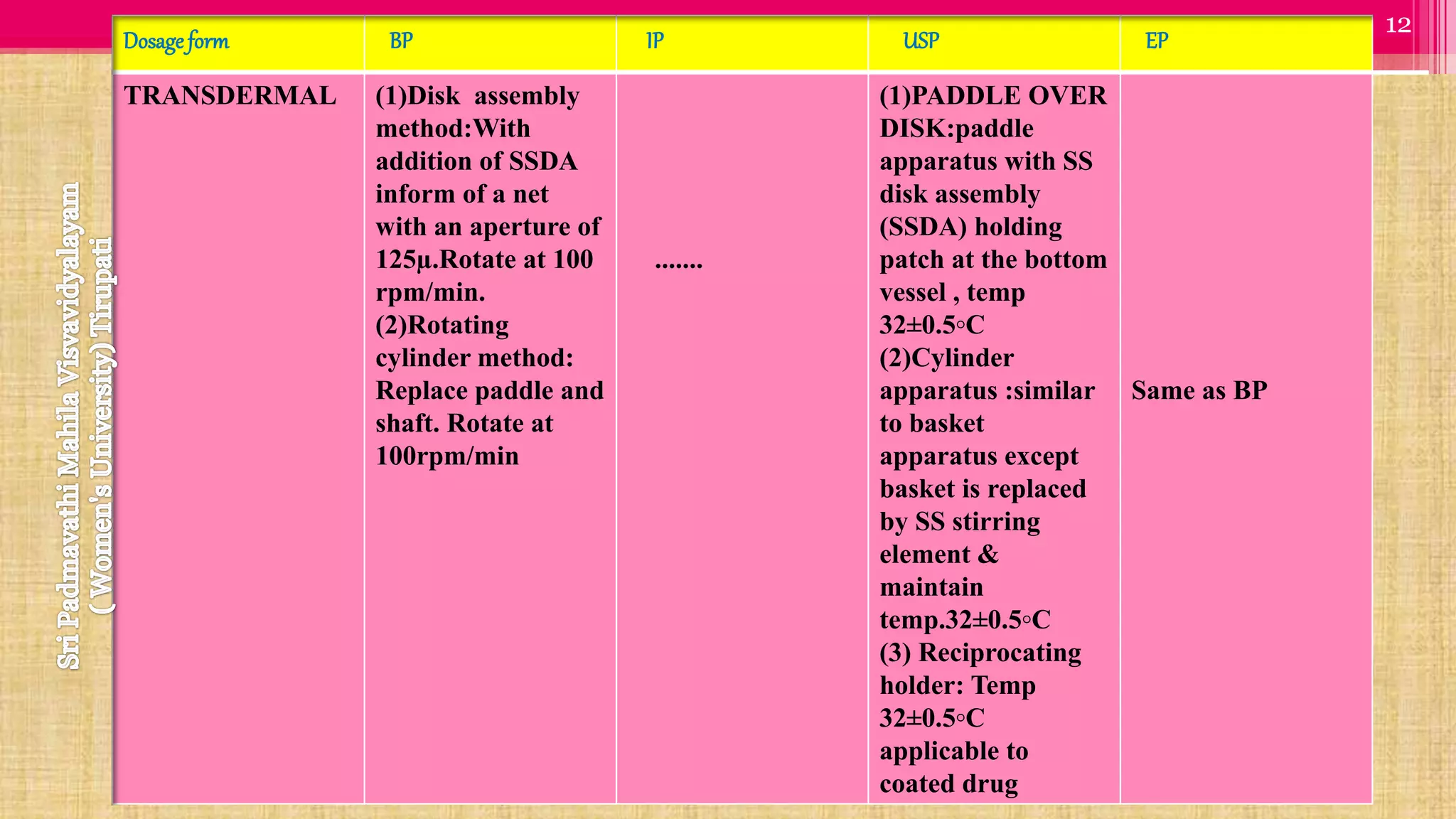
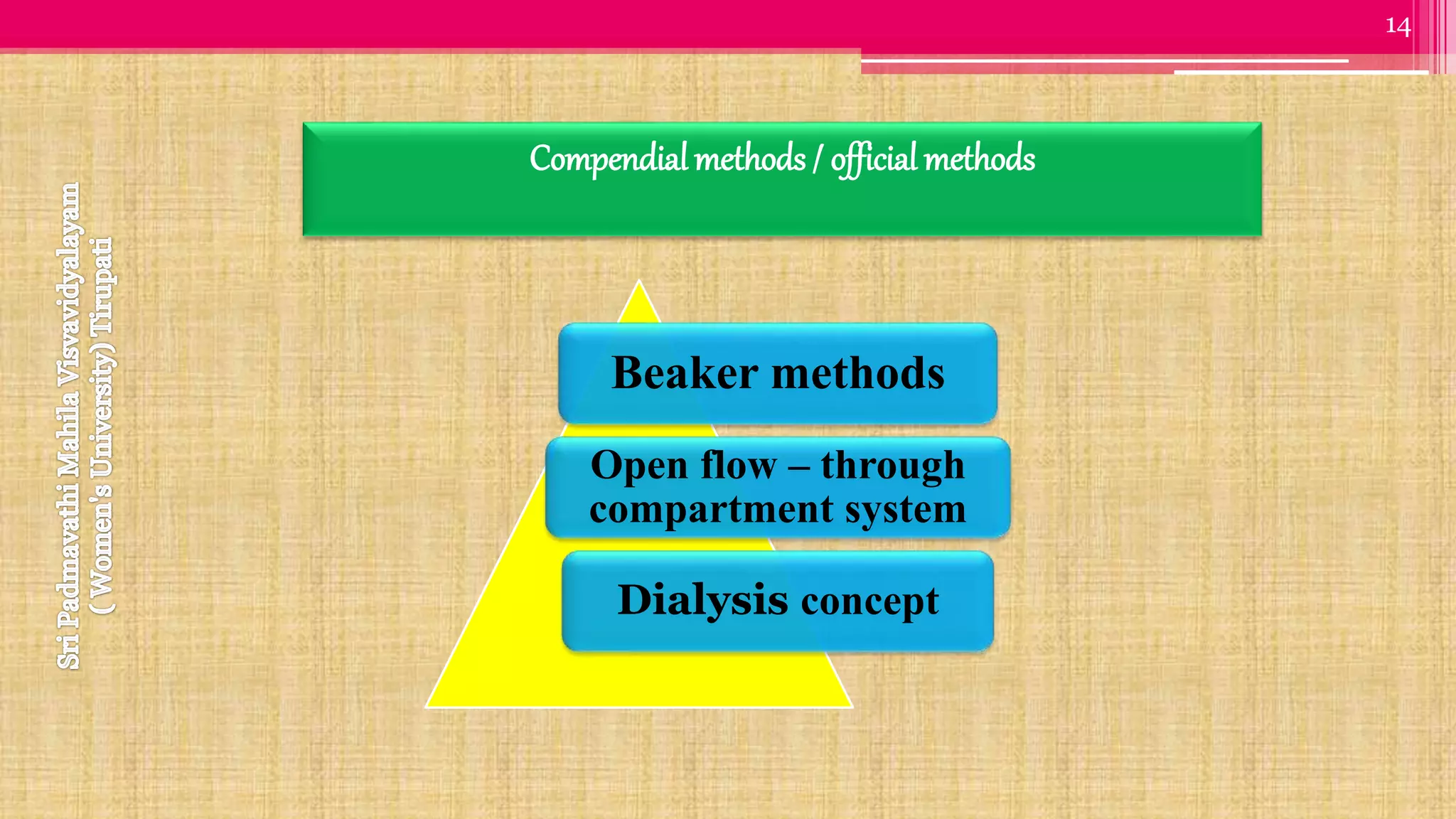
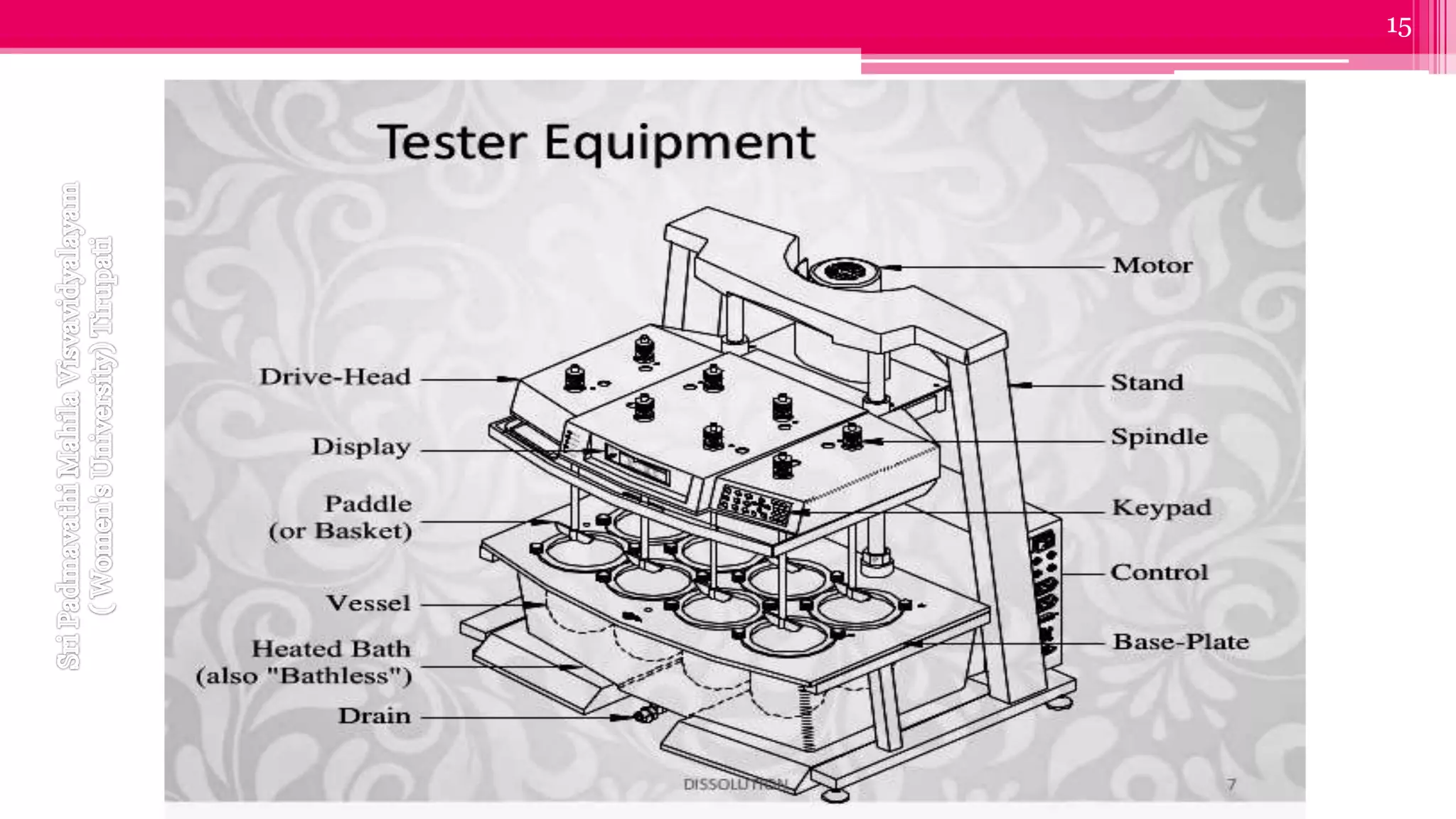
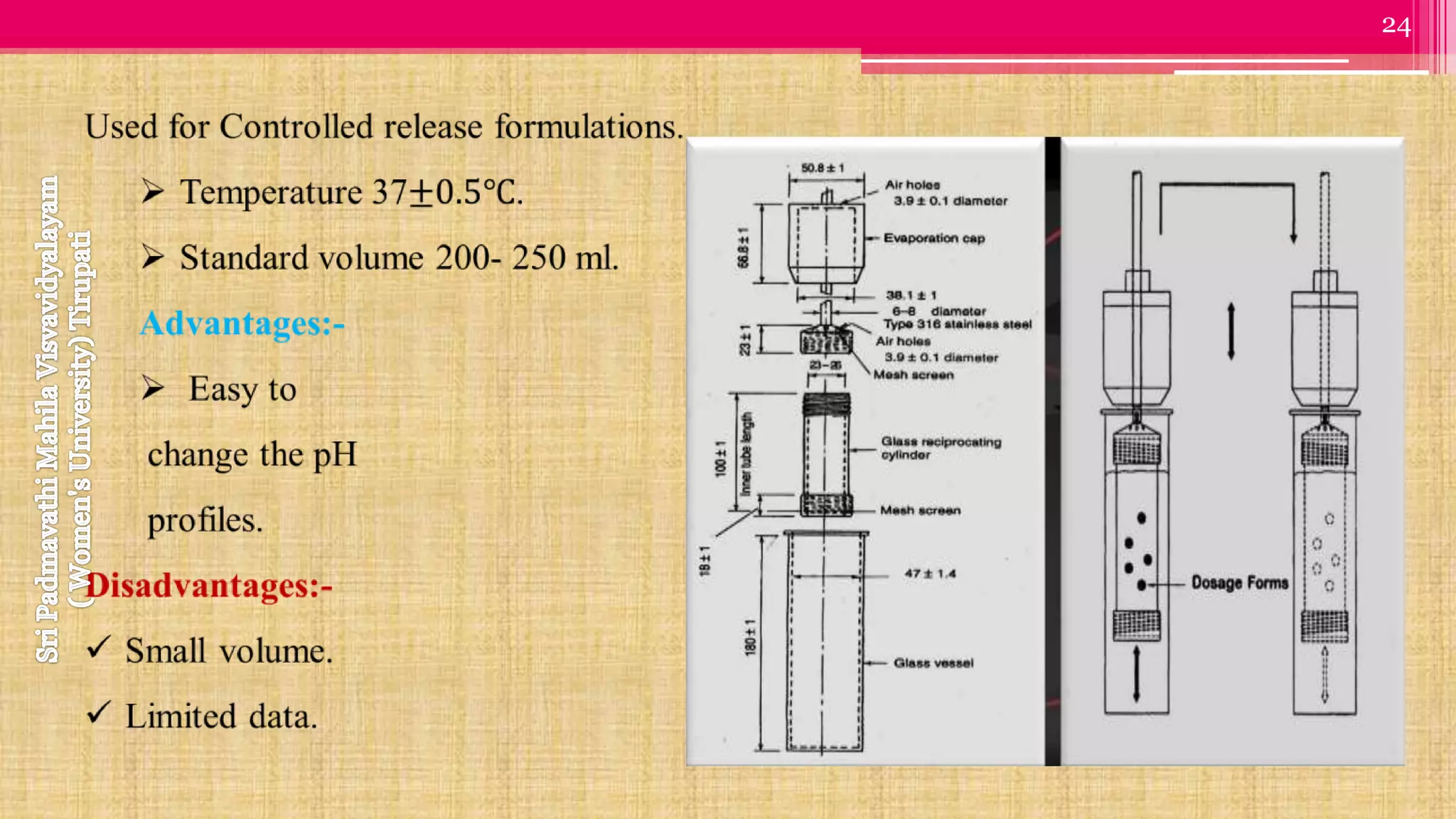
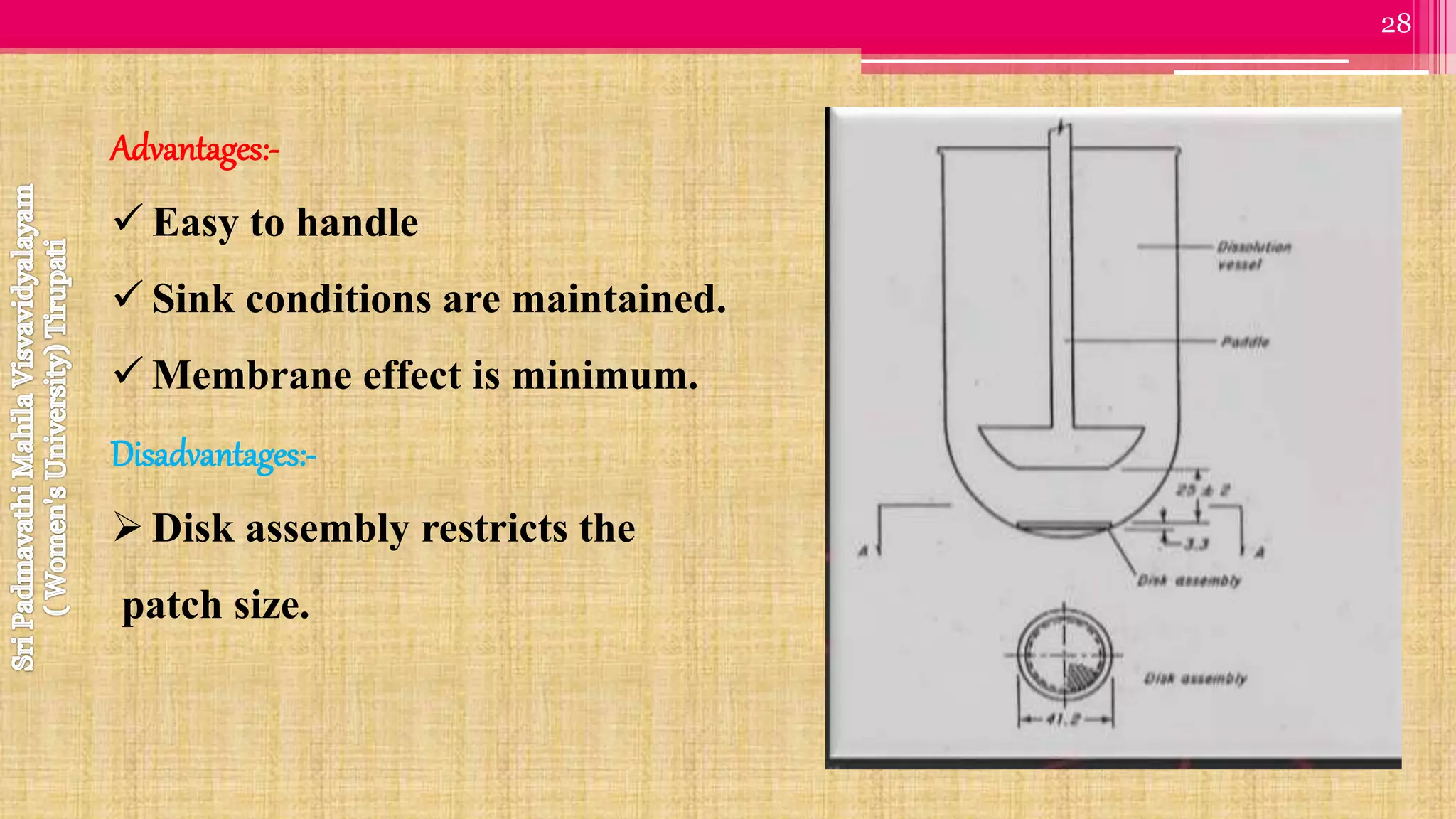
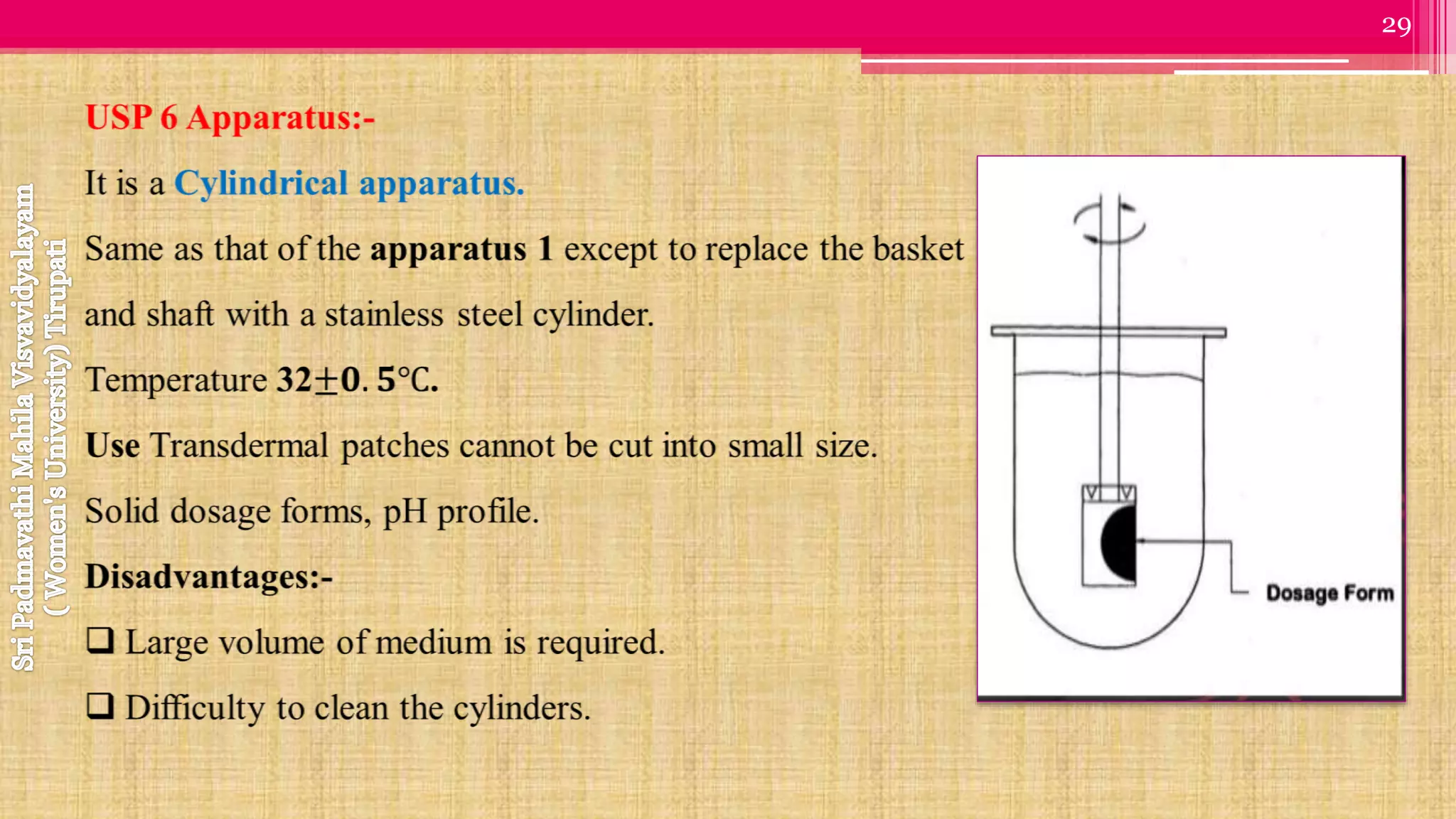
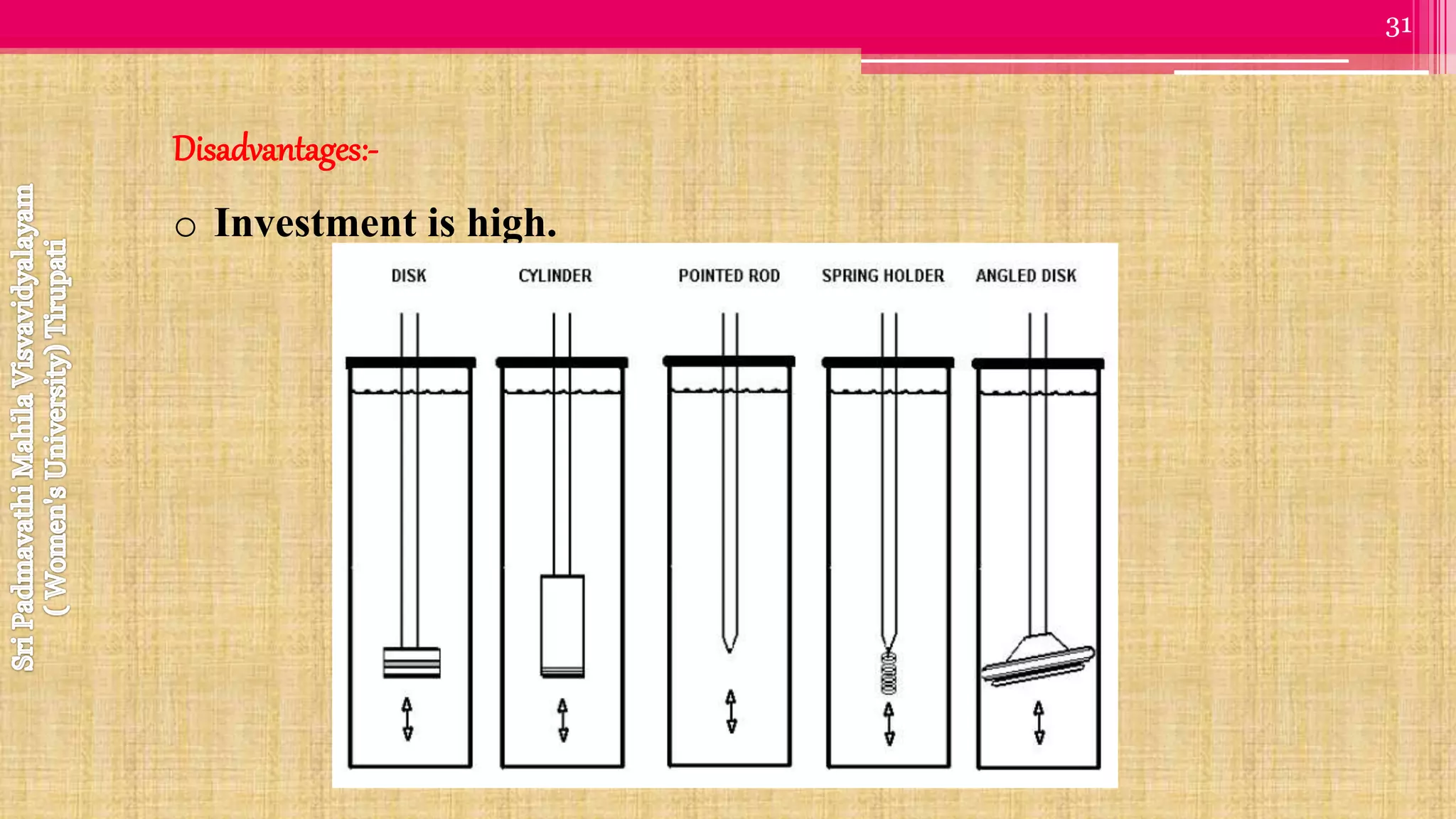
The document discusses compendial methods of dissolution testing according to pharmacopoeia standards. It describes the need for dissolution testing to evaluate drug release from solid dosage forms and ensure bioavailability. The key compendial apparatuses discussed are the basket, paddle, flow-through cell, and dissolution testing methods for modified release forms. The document provides details on the components, operating conditions and applications of the various apparatuses specified in pharmacopoeias for testing common oral and other dosage forms.