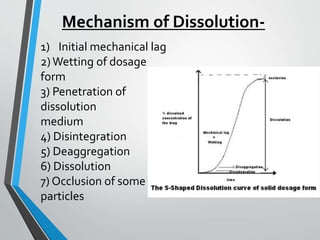
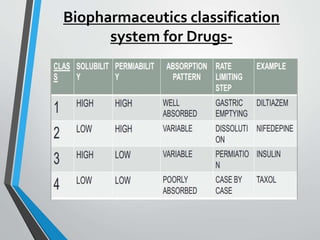
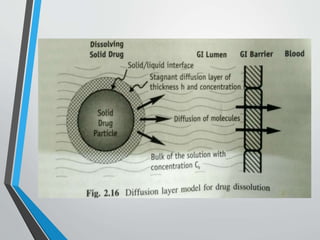
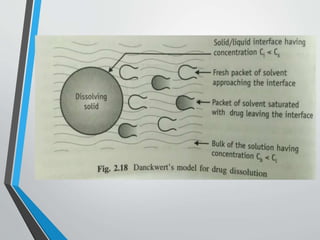
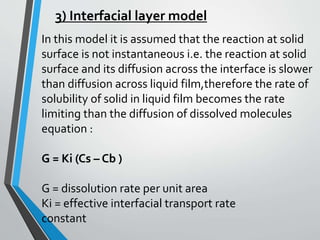
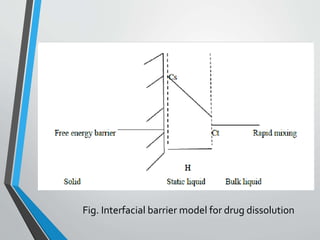
The document discusses drug dissolution, detailing the mechanisms and factors influencing gastrointestinal absorption of drugs administered orally. Multiple theories of dissolution, such as the diffusion layer model and Danckwert's model, are explained, along with factors affecting dissolution rates like physicochemical properties, formulation aspects, and processing conditions. Key parameters influencing drug solubility and dissolution are identified, emphasizing the complexity of drug absorption and distribution into systemic circulation.