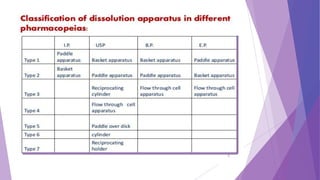
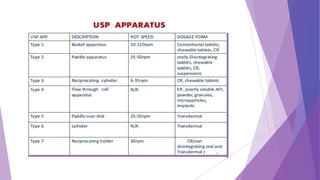
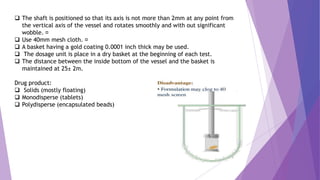
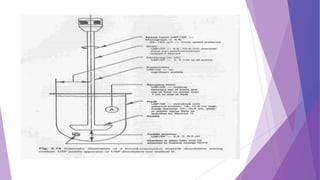
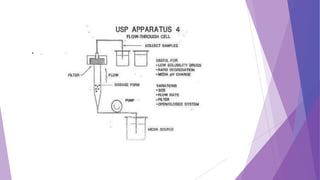
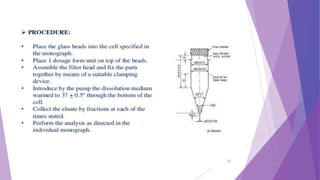
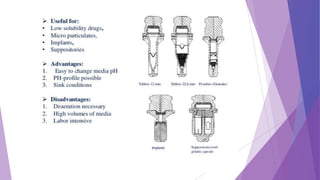
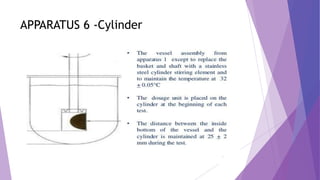
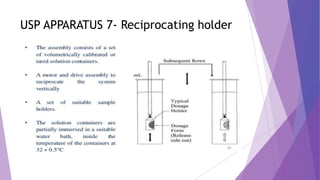
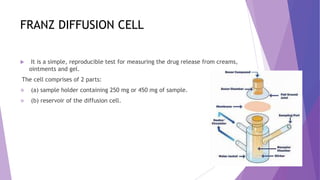
The document discusses various dissolution testing methods and apparatuses. It describes the need for dissolution testing to estimate the rate of drug release from solid oral dosage forms. Common dissolution testing conditions involve simulating gastric and intestinal fluids at 37°C. Four common apparatuses are described for immediate-release and controlled-release drug products: the basket, paddle, reciprocating cylinder, and flow-through cell apparatuses. Limitations of the basket and paddle apparatuses are noted. Additional apparatuses for transdermal and topical dosage forms as well as the Franz diffusion cell are also summarized.