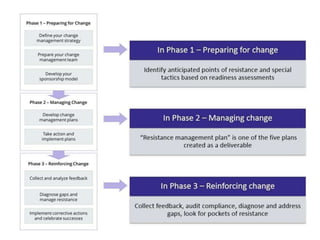
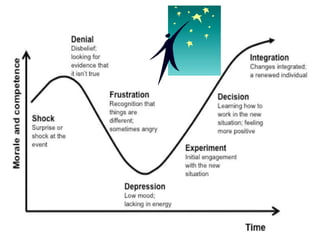
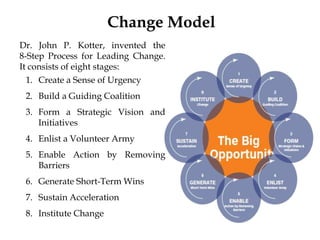
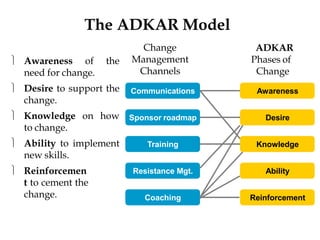
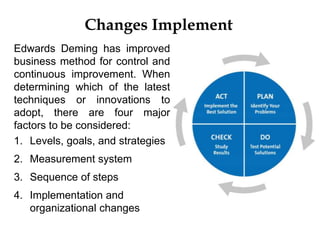
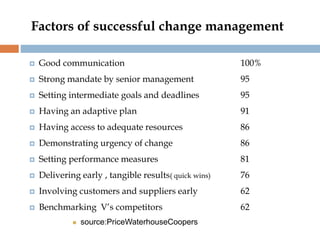
Change management is a systematic approach to preparing and supporting individuals and organizations in making organizational changes. It involves understanding the reasons for change, effective communication, and applying models such as Kotter's 8-step process and the ADKAR model. Successful change management depends on clear communication, strong management support, and the ability to adapt plans and resources.