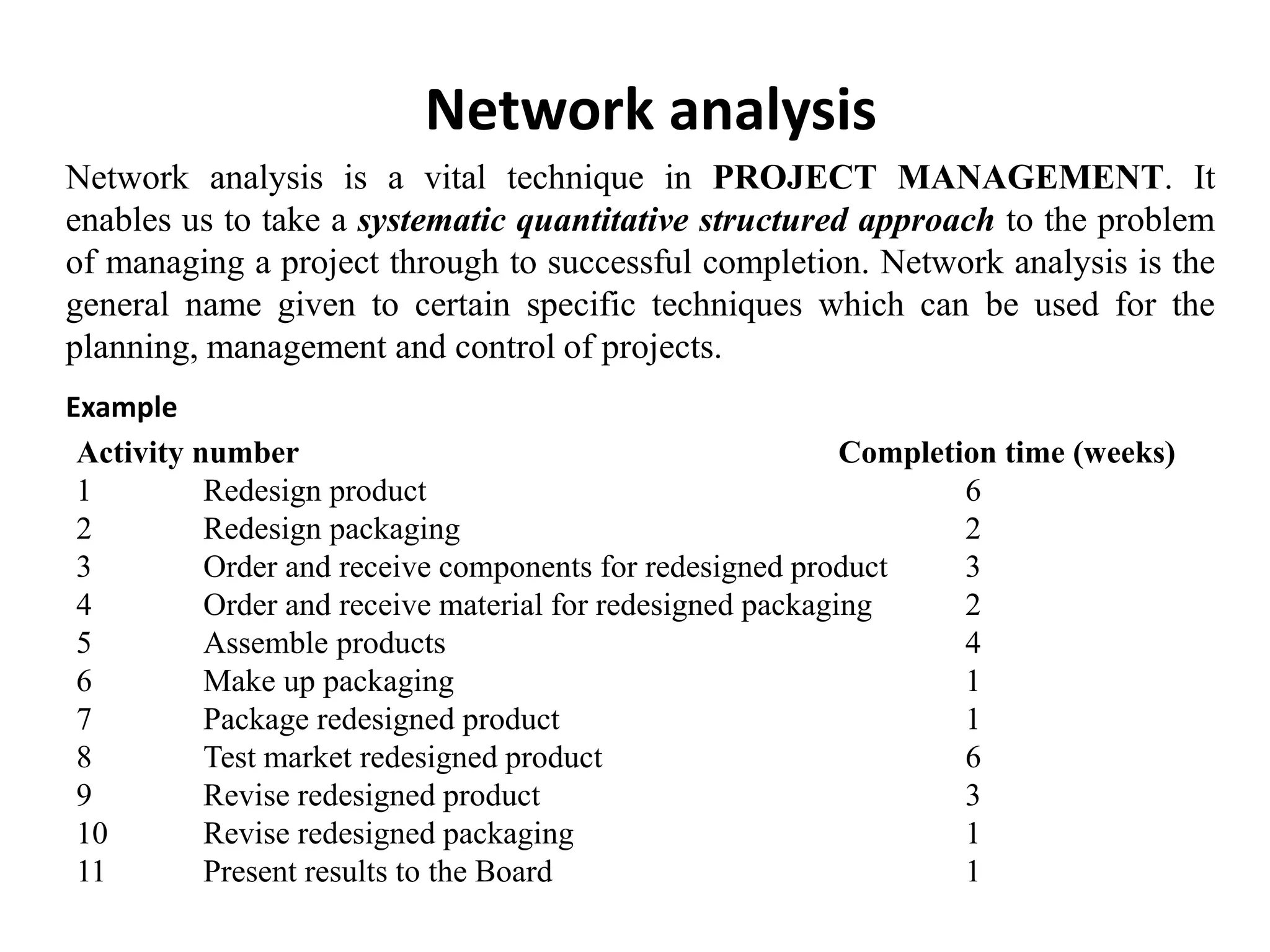
This document provides an overview of strategic management and project management. It defines strategy as a long-term plan to achieve objectives. There are three levels of strategy: corporate, business, and functional. Strategic management is the process of analyzing the environment, formulating strategy, implementing strategy, and evaluating performance. Project management is initiating, planning, executing, controlling, and closing work to achieve goals within constraints. Network analysis and PERT/CPM are techniques to systematically plan and manage projects.