The Johari Window model is a tool for self-awareness, personal development, and understanding relationships. It was developed in the 1950s by psychologists Joseph Luft and Harry Ingham.
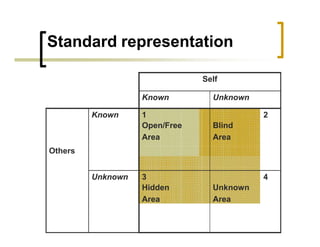
The model represents information about a person from four perspectives based on what is known or unknown by the person and others. The four "windows" or areas are: open area (known to self and others), blind area (known to others but not self), hidden area (known to self but not others), and unknown area (unknown to self and others).
The goal is to increase the open area through feedback and disclosure to reduce blind, hidden, and unknown areas. This improves self-awareness, communication, and effectiveness