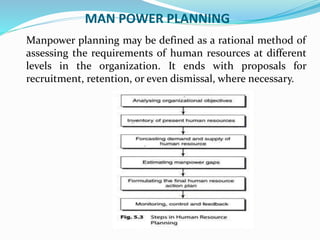
This document discusses key concepts in human resource management including job analysis, job description, job specification, recruitment, selection, induction, placement, training and development, performance appraisal, wages and salary administration, grievance handling, and job evaluation. It defines each concept and describes the typical processes and methods involved. The overall purpose is to outline the main functions and activities within an organization's human resource management.