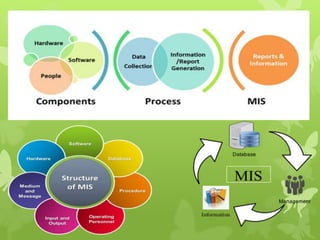
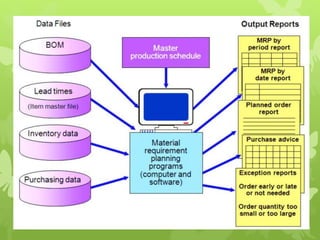
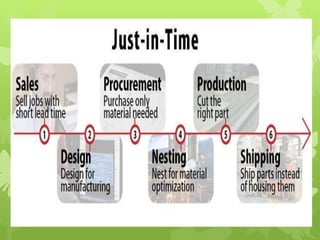
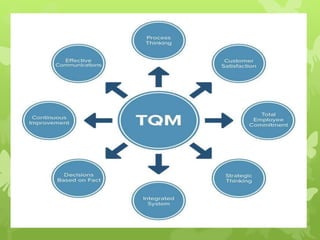
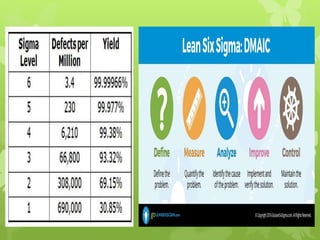
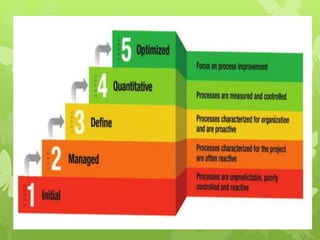
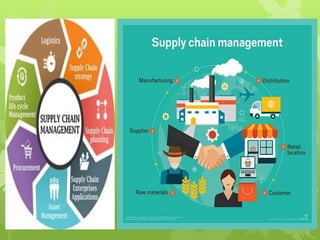
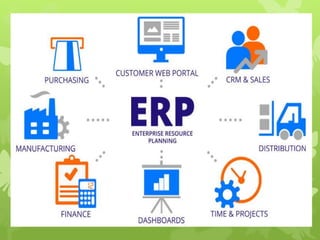
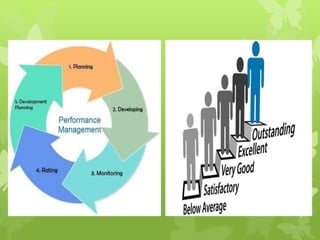
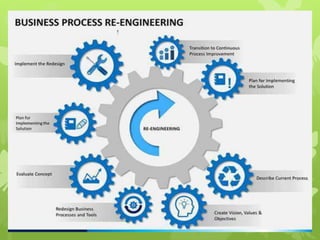
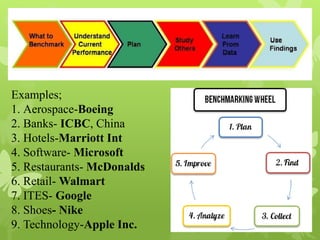
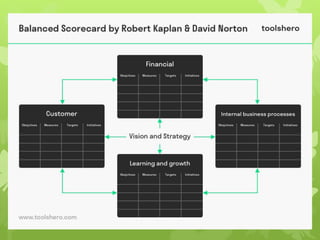
This document discusses several operations management concepts including MIS, MRP, JIT, TQM, Six Sigma, CMM, supply chain management, ERP, performance management, BPO, BPR, benchmarking, and the balanced scorecard. It provides definitions and key aspects of each concept in 1-2 paragraphs with some including objectives and principles.