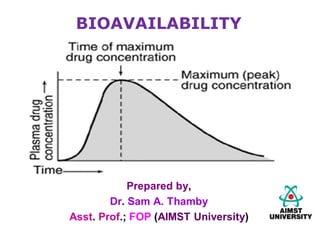
Bioavailability refers to the rate and extent to which an active drug ingredient is absorbed and becomes available at the site of drug action. Key parameters of bioavailability include Cmax, Tmax, and AUC, which describe the peak concentration, time to reach peak concentration, and total drug exposure over time, respectively. Bioavailability is influenced by formulation factors like drug solubility and physiological factors like gastric emptying and first-pass metabolism in the liver. Comparative bioavailability studies evaluate the bioequivalence of generic and innovator drug products.







![Bioavailability (BA ) (BA) (F)
2 types: Absolute and Relative
Absolute BA
Assessed by comparing (AUC)0
∞ and / or cumulative mass of drug
excreted in the urine (Xu), following administration of a drug in an
extravascular dosage form and an equal dose of the same drug in I.V.
form;
Absolute BA = fraction of drug absorbed (F)
Value can range till 1.0
From plasma conc.-time curve data
F = (AUC)extravascular/Dose extravascular // (AUC) IV/Dose IV
F = [(AUC)extravascular x Dose IV]
______________________
[(AUC) IV x Dose extravascular]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioavailabilityinanutshell-230518042822-fbc52132/85/BIOAVAILABILITY-IN-A-NUTSHELL-pdf-9-320.jpg)
![ If we compare BA of oral vs the I.V.
F = [(AUC)oral xDose IV]
_______________
[(AUC) IV x Dose oral]
From urinary data:
Xu:
• Is the cumulative amt. of drug excreted in the urine;
• Analogous to AUC
Tu(max):
• Is the time required for max. excretion rate;
• Analogous to tmax
(dXu/dt)max:
• Is the max. urinary excretion rate;
• Obtained from the peak of plot between urinary excretion rate and
midpoint time of urine collection period. (analogous to Cmax)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioavailabilityinanutshell-230518042822-fbc52132/85/BIOAVAILABILITY-IN-A-NUTSHELL-pdf-10-320.jpg)

![ Method:
• Collection of urine at regular intervals for a time span of 7 t1/2;
• Analyze unchanged drug in the samples;
• Determine amt. of drug excreted in each interval, and cumulative
amt. excreted;
• At each sample collection, total emptying of the bladder is
mandatory (to prevent addition of residual amt. of drug into the next
sample collection which will lead to errors)
F = [(Xu)oral
7t1/2 xDose IV]
_______________
[(Xu) IV
7t1/2 x Dose oral]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioavailabilityinanutshell-230518042822-fbc52132/85/BIOAVAILABILITY-IN-A-NUTSHELL-pdf-12-320.jpg)
![Relative BA (Frel)
Is assessed by comparing the BA parameters (either from plasma con.-
time curve or urinary data) of the same drug moiety…..
• in two or more different dosage forms (tablet, soln., syrup, capsule, etc..);
• Via two or more different extravascular routes of admn. (oral, IM, IP)
F = [(Xu)tablet
7t1/2 x Dose solution]
_______________
[(Xu) solution
7t1/2 x Dose tablet]
Frel = [(AUC)oral x Dose IM]
_______________
[(AUC) IM x Dose oral]
The reference standard when determining comparative or Frel must
be chosen by considering which dosage form is being compared
with the other dosage form.
Can range from <1, 1, or >1
Plasma
conc.-time
curve
Urinary excretion
data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioavailabilityinanutshell-230518042822-fbc52132/85/BIOAVAILABILITY-IN-A-NUTSHELL-pdf-13-320.jpg)





![ Bioequivalence studies: A type of comparative or relative BA study,
where the peak plasma concentration and peak time are determined
for two (or more) chemically or pharmaceutically-equivalent
products, where one of them is an ‘Innovator’.
Innovator: Is the reference or standard drug.
F = [(AUC)generic xDose standard]
_______________
[(AUC) standard x Dose generic]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioavailabilityinanutshell-230518042822-fbc52132/85/BIOAVAILABILITY-IN-A-NUTSHELL-pdf-19-320.jpg)





