Embed presentation
Downloaded 11 times



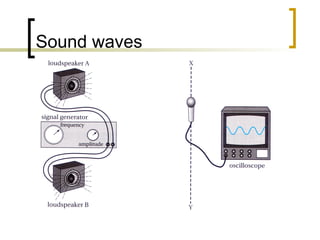


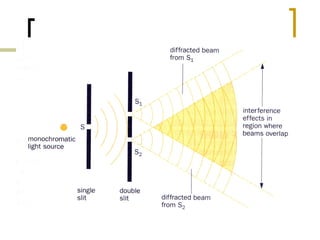



1) Interference patterns can occur for both sound waves and light waves when the conditions of coherence and monochromaticity are met. 2) Young's double slit experiment demonstrated interference of light waves by producing alternating bright and dark bands on a screen, with the spacing of the bands determined by the wavelength, slit separation, and screen distance. 3) All waves, including sound and light, can exhibit constructive and destructive interference depending on the relative phases of the waves, which is determined by path length differences.








